|
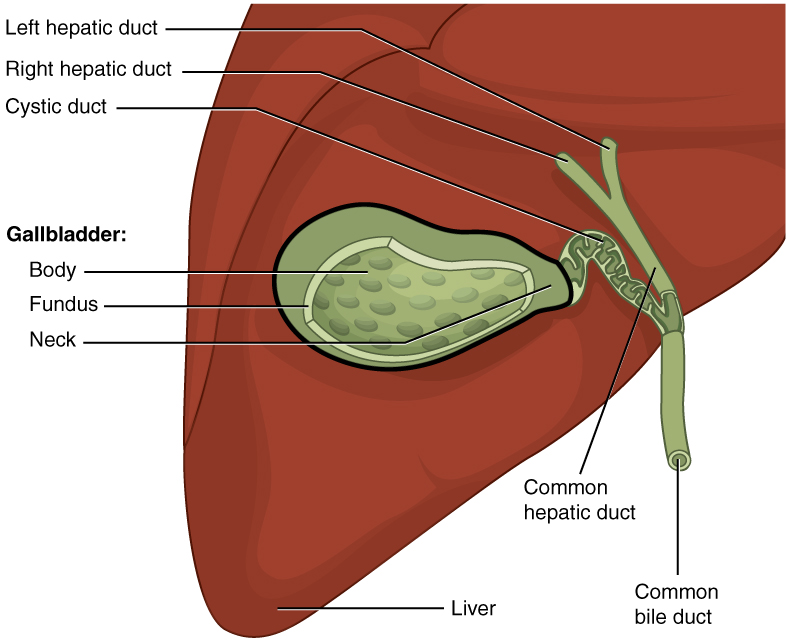
Cystic Duct
The cystic duct is the short duct that joins the gallbladder to the common hepatic duct. It usually lies next to the cystic artery. It is of variable length. It contains 'spiral valves of Heister', which do not provide much resistance to the flow of bile. Function Bile can flow in both directions between the gallbladder and the common bile duct and the hepatic duct. In this way, bile is stored in the gallbladder in between meal times. The hormone cholecystokinin, when stimulated by a fatty meal, promotes bile secretion by increased production of hepatic bile, contraction of the gall bladder, and relaxation of the Sphincter of Oddi. Clinical significance Gallstones can enter and obstruct the cystic duct, preventing the flow of bile. The increased pressure in the gallbladder leads to swelling and pain. This pain, known as biliary colic, is sometimes referred to as a gallbladder "attack" because of its sudden onset. During a cholecystectomy, the cystic duct is clipped two or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Lobe Of Liver
In human anatomy, the liver is divided grossly into four parts or lobes: the right lobe, the left lobe, the caudate lobe, and the quadrate lobe. Seen from the front – the diaphragmatic surface - the liver is divided into two lobes: the right lobe and the left lobe. Viewed from the underside – the visceral surface, the other two smaller lobes the caudate lobe, and the quadrate lobe are also visible. The two smaller lobes, the caudate lobe and the quadrate lobe, are known as superficial or accessory lobes, and both are located on the underside of the right lobe. The falciform ligament, visible on the front of the liver, makes a superficial division of the right and left lobes of the liver. From the underside, the two additional lobes are located on the right lobe. A line can be imagined running from the left of the vena cava and all the way forward to divide the liver and gallbladder into two halves. This line is called Cantlie's line and is used to mark the division between t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives and stores bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct, and releases it via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats. The gallbladder can be affected by gallstones, formed by material that cannot be dissolved – usually cholesterol or bilirubin, a product of haemoglobin breakdown. These may cause significant pain, particularly in the upper-right corner of the abdomen, and are often treated with removal of the gallbladder (called a cholecystectomy). Cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder, has a wide range of causes, including result from the impaction of gallstones, inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
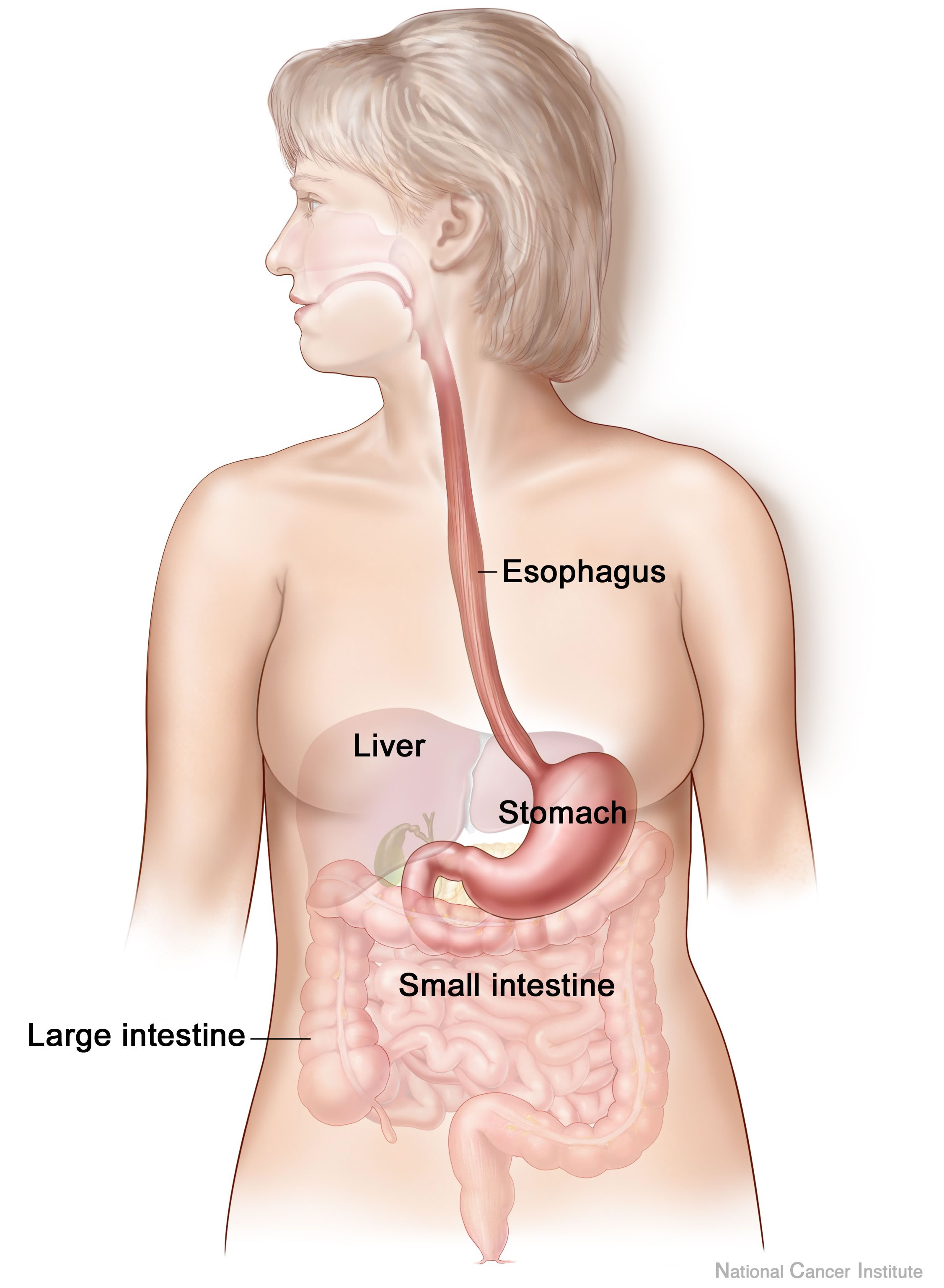
Digestive System
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components, until they can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The process of digestion has three stages: the cephalic phase, the gastric phase, and the intestinal phase. The first stage, the cephalic phase of digestion, begins with secretions from gastric glands in response to the sight and smell of food. This stage includes the mechanical breakdown of food by chewing, and the chemical breakdown by digestive enzymes, that takes place in the mouth. Saliva contains the digestive enzymes amylase, and lingual lipase, secreted by the salivary and serous glands on the tongue. Chewing, in which the food is mixed with saliva, begins the mechanical process of digestion. This produces a bolus which is swallowed down the esophagus to enter the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accessory Bile Duct
An accessory bile duct is a conduit that transports bile and is considered to be supernumerary or auxiliary to the biliary tree. It may be described by its location relative to the gallbladder as supravesicular (superior to the gallbladder body) or subvesicular (inferior to the gallbladder body). Duct of Luschka In the surgical literature, the term duct of Luschka is used to refer to an accessory bile duct. They are small ducts that distinctly enter the gallbladder bed, or small tributaries of minor intrahepatic radicals of the right hepatic ductal system. Originating from the hepatic parenchyma the accessory bile duct may enter a large bile duct or the gallbladder at any location. Rarely it is found to be connected directly to the GIT. They may not always drain bile and sometimes can have blind distal ends. One study showed them originating from the liver parenchyma of the right anterior inferior dorsal subsegment or from the connective tissue of the gallbladder bed. The study sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholecystectomy
Cholecystectomy is the surgical removal of the gallbladder. Cholecystectomy is a common treatment of symptomatic gallstones and other gallbladder conditions. In 2011, cholecystectomy was the eighth most common operating room procedure performed in hospitals in the United States. Cholecystectomy can be performed either laparoscopically, or via an open surgical technique. The surgery is usually successful in relieving symptoms, but up to 10 percent of people may continue to experience similar symptoms after cholecystectomy, a condition called postcholecystectomy syndrome. Complications of cholecystectomy include bile duct injury, wound infection, bleeding, retained gallstones, abscess formation and stenosis (narrowing) of the bile duct. Medical use Pain and complications caused by gallstones are the most common reasons for removal of the gallbladder. The gallbladder can also be removed in order to treat biliary dyskinesia or gallbladder cancer. Gallstones are very common but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biliary Colic
Biliary colic, also known as symptomatic cholelithiasis, a gallbladder attack or gallstone attack, is when a colic (sudden pain) occurs due to a gallstone temporarily blocking the cystic duct. Typically, the pain is in the right upper part of the abdomen, and can be severe. Pain usually lasts from 15 minutes to a few hours. Often, it occurs after eating a heavy meal, or during the night. Repeated attacks are common. Gallstone formation occurs from the precipitation of crystals that aggregate to form stones. The most common form is cholesterol gallstones. Other forms include calcium, bilirubin, pigment, and mixed gallstones. Other conditions that produce similar symptoms include appendicitis, stomach ulcers, pancreatitis, and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Treatment for gallbladder attacks is typically surgery to remove the gallbladder. This can be either done through small incisions or through a single larger incision. Open surgery through a larger incision is associated w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallstone
A gallstone is a calculus (medicine), stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of migrated gallstones within bile ducts. Most people with gallstones (about 80%) are asymptomatic. However, when a gallstone obstructs the bile duct and causes acute cholestasis, a reflexive smooth muscle spasm often occurs, resulting in an intense cramp-like visceral pain in the quadrant (abdomen), right upper part of the abdomen known as a biliary colic (or "gallbladder attack"). This happens in 1–4% of those with gallstones each year. Complications from gallstones may include inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis), inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), Jaundice#Post-hepatic, obstructive jaundice, and infection in bile ducts (ascending cholangitis, cholangitis). Symptoms of these complications may include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphincter Of Oddi
The sphincter of Oddi (also hepatopancreatic sphincter or Glisson's sphincter), abbreviated as SO, is a muscular valve that in some animals, including humans, controls the flow of digestive juices (bile and pancreatic juice) out of the pancreas through the ampulla of Vater into the second part of the duodenum. It is named after Ruggero Oddi. Structure The sphincter of Oddi is a circular muscle band (Sphincter) that surrounds the major duodenal papilla. Function The sphincter regulates the secretion of pancreatic juice and bile into the duodenum. It also prevents reflux of duodenal contents into the ampulla of Vater. The sphincter of Oddi is relaxed by the hormone cholecystokinin via vasoactive intestinal peptide. Clinical significance Opiates may cause spasms of the sphincter of Oddi, leading to increased serum amylase levels. History The sphincter was described for the first time by Ruggero Oddi when he was a young student in 1887. This description followed extensive r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholecystokinin
Cholecystokinin (CCK or CCK-PZ; from Greek ''chole'', "bile"; ''cysto'', "sac"; ''kinin'', "move"; hence, ''move the bile-sac (gallbladder)'') is a peptide hormone of the gastrointestinal system responsible for stimulating the digestion of fat and protein. Cholecystokinin, formerly called pancreozymin, is synthesized and secreted by enteroendocrine cells in the duodenum, the first segment of the small intestine. Its presence causes the release of digestive enzymes and bile from the pancreas and gallbladder, respectively, and also acts as a hunger suppressant. History Evidence that the small intestine controls the release of bile was uncovered as early as 1856, when French physiologist Claude Bernard showed that when dilute acetic acid was applied to the orifice of the bile duct, the duct released bile into the duodenum. In 1903 the French physiologist showed that this reflex was not mediated by the nervous system. In 1904 the French physiologist Charles Fleig showed that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatic Duct
The common hepatic duct is the first part of the biliary tract. It joins the cystic duct coming from the gallbladder to form the common bile duct. Structure The common hepatic duct is the first part of the biliary tract. It is formed by the convergence of the right hepatic duct (which drains bile from the right functional lobe of the liver) and the left hepatic duct (which drains bile from the left functional lobe of the liver). It then joins the cystic duct coming from the gallbladder to form the common bile duct. The duct is usually 6–8 cm long. The common hepatic duct is about 6 mm in diameter in adults, with some variation.Gray's Anatomy, 39th ed, p. 1228 The inner surface is covered in a simple columnar epithelium. Variation Around 1.7% of people have additional accessory hepatic ducts that join onto the common hepatic duct. Rarely, the common hepatic duct joins onto the gallbladder directly, leading to illness. Function The hepatic duct is part of the bil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiral Valves Of Heister
Spiral valves of Heister are undulating folds or valves in the proximal mucosa of the cystic duct. The cystic duct attaches the gallbladder to the common bile duct. The spiral valves of Heister are supported by underlying smooth muscle fibers. There is some uncertainty regarding the role of the folds. Historically, physicians believed that their function was to aid in the passage of bile to and from the gallbladder, as well as regulate the degree of gallbladder distension. The presence of the spiral folds, in combination with the tortuosity of the cystic duct, makes endoscopic cannulation and catheterization of the cystic duct extremely difficult. Also, the valves of Heister are susceptible to lacerations and were a serious obstacle to the surgical canalization. Thanks to newer technologies, nowadays this procedure is possible. They were named after German anatomist Lorenz Heister (1683–1758). Imaging On ultrasound, valve of Heister is echogenic. References Further reading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Hepatic Duct
The common hepatic duct is the first part of the biliary tract. It joins the cystic duct coming from the gallbladder to form the common bile duct. Structure The common hepatic duct is the first part of the biliary tract. It is formed by the convergence of the right hepatic duct (which drains bile from the right functional lobe of the liver) and the left hepatic duct (which drains bile from the left functional lobe of the liver). It then joins the cystic duct coming from the gallbladder to form the common bile duct. The duct is usually 6–8 cm long. The common hepatic duct is about 6 mm in diameter in adults, with some variation.Gray's Anatomy, 39th ed, p. 1228 The inner surface is covered in a simple columnar epithelium. Variation Around 1.7% of people have additional accessory hepatic ducts that join onto the common hepatic duct. Rarely, the common hepatic duct joins onto the gallbladder directly, leading to illness. Function The hepatic duct is part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |