|
Cynomya Cadaverina
''Cynomya cadaverina'', also known as the shiny blue bottle fly, is a member of the family Calliphoridae, which includes blow flies as well as bottle flies. In recent years, this family has become a forensically important facet in many medicocriminal investigations in the growing field of forensic entomology. ''C. cadaverina'' is specifically important in determining a post-mortem interval, as well as other important factors. Taxonomy ''Cynomya cadaverina'' was first described in 1830 by the French entomologist Jean-Baptiste Robineau-Desvoidy. Its epithet ''cadaverina'' is derived from the Latin word, meaning ‘(that feed on) dead bodies.’Beard, J.R., & C., Cassell's Latin Dictionary, 1977, Cassell's, Pg. 501 This species is a member of the order Diptera and the diverse family Calliphoridae. Description ''C. cadaverina'' is a fairly large species, ranging anywhere from 9-14 millimeters long. and has many characteristics that are common to its family, Calliphoridae.Hall, G., D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robineau-Desvoidy
André Jean Baptiste Robineau-Desvoidy (1 January 1799 in Saint-Sauveur-en-Puisaye – 25 June 1857 in Paris) was a French physician and entomologist specialising in the study of Diptera (flies) and to some extent of the Coleoptera (beetles). Achievements Because he worked on difficult to identify flies (specifically the Schizophora), the existing descriptions of which were poor, and because he had few contacts, many of the new species he described were already named. Also he was over reliant on colour and pattern as characters, and this led to his improperly defining species. He also worked on too many species. Much later criticism ensued but it must be remembered that he was an early worker and, in the aftermath of the Napoleonic Wars, French scientists were unduly criticised for nationalistic reasons. Very many of his generic and species names survive. In all these respects, as well as his genuine love of entomology and boundless enthusiasm, Robineau-Desvoidy is reminiscen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imago
In biology, the imago (Latin for "image") is the last stage an insect attains during its metamorphosis, its process of growth and development; it is also called the imaginal stage, the stage in which the insect attains maturity. It follows the final ecdysis of the immature instars.Carpenter, Geo. H., The Life-Story of Insects. Cambridge University Press 1913. May be downloaded from: https://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/16410 or https://archive.org/details/thelifestoryofin16410gut In a member of the Ametabola or Hemimetabola, in which metamorphosis is "incomplete", the final ecdysis follows the last immature or '' nymphal'' stage. In members of the Holometabola, in which there is a pupal stage, the final ecdysis follows emergence from the pupa, after which the metamorphosis is complete, although there is a prolonged period of maturation in some species. The imago is the only stage during which the insect is sexually mature and, if it is a winged species, has functional wings. The i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogens
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ. The term ''pathogen'' came into use in the 1880s. Typically, the term ''pathogen'' is used to describe an ''infectious'' microorganism or agent, such as a virus, bacterium, protozoan, prion, viroid, or fungus. Small animals, such as helminths and insects, can also cause or transmit disease. However, these animals are usually referred to as parasites rather than pathogens. The scientific study of microscopic organisms, including microscopic pathogenic organisms, is called microbiology, while parasitology refers to the scientific study of parasites and the organisms that host them. There are several pathways through which pathogens can invade a host. The principal pathways have different episodic time frames, but soil has the longest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration (United States)
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, prescription and over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, animal foods & feed and veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C), but the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act, as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is not directly related to food or drugs, but involves such things as regulating lasers, cellular phones, and condoms, as well as control of disease in contexts varying fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
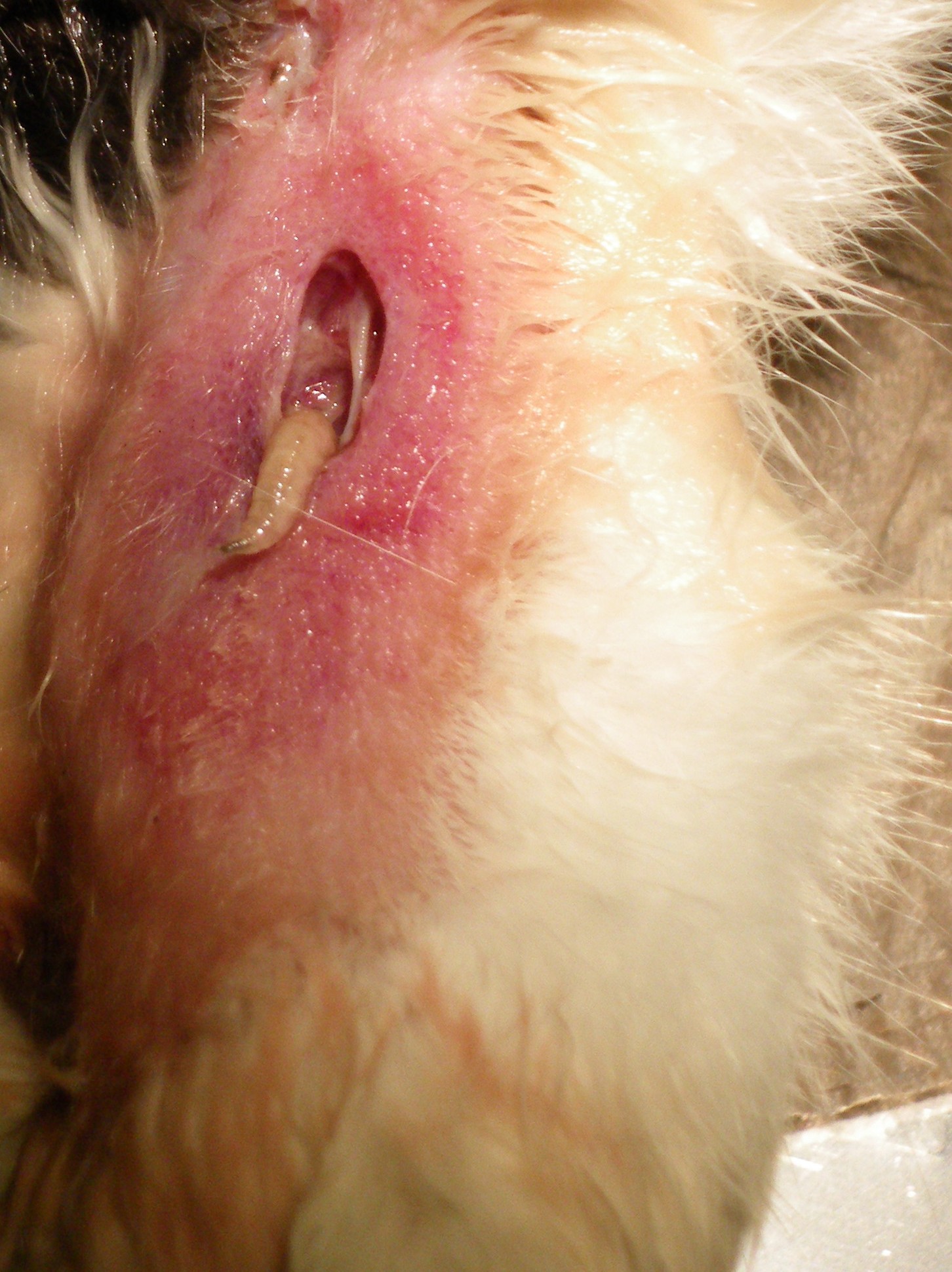
Maggot
A maggot is the larva of a fly (order Diptera); it is applied in particular to the larvae of Brachycera flies, such as houseflies, cheese flies, and blowflies, rather than larvae of the Nematocera, such as mosquitoes and crane flies. Entomology "Maggot" is not a technical term and should not be taken as such; in many standard textbooks of entomology, it does not appear in the index at all. In many non-technical texts, the term is used for insect larvae in general. Other sources have coined their own definitions; for example: "The term applies to a grub when all trace of limbs has disappeared" and "Applied to the footless larvae of Diptera".Smith, John. BExplanation of terms used in entomology Brooklyn Entomological Society, 1906. Additionally, in ''Flies: The Natural History and Diversity of Diptera'', the author claims maggots "are larvae of higher Brachycera ( Cyclorrhapha)." Maggot-like fly larvae are of significance in ecology and medicine; among other roles, var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants and algae, also in plastids such as chloroplasts. Human mitochondrial DNA was the first significant part of the human genome to be sequenced. This sequencing revealed that the human mtDNA includes 16,569 base pairs and encodes 13 proteins. Since animal mtDNA evolves faster than nuclear genetic markers, it represents a mainstay of phylogenetics and evolutionary biology. It also permits an examination of the relatedness of populations, and so has become important in anthropology and biogeography. Origin Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA are thought to be of separate evolutionary origin, with the mtDNA being derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maggot Therapy
Maggot therapy (also known as larval therapy) is a type of biotherapy involving the introduction of live, disinfected maggots (fly larvae) into non-healing skin and soft-tissue wounds of a human or other animal for the purpose of cleaning out the necrotic (dead) tissue within a wound, (debridement) and disinfection. There is evidence that maggot therapy may help with wound healing. Medical uses Maggot therapy improves healing in chronic ulcers. In diabetic foot ulcers there is tentative evidence of benefit. A Cochrane review of methods for the debridement of venous leg ulcers found maggot therapy to be broadly as effective as most other methods, but the study also noted that the quality of data was poor. In 2004, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) cleared maggots from common green bottle fly for use as a "medical device" in the US for the purpose of treatment of: * Non-healing necrotic skin and soft tissue wounds * Pressure ulcers * Venous stasis ulcers * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necrotic
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated digestion of cell components. In contrast, apoptosis is a naturally occurring programmed and targeted cause of cellular death. While apoptosis often provides beneficial effects to the organism, necrosis is almost always detrimental and can be fatal. Cellular death due to necrosis does not follow the apoptotic signal transduction pathway, but rather various receptors are activated and result in the loss of cell membrane integrity and an uncontrolled release of products of cell death into the extracellular space. This initiates in the surrounding tissue an inflammatory response, which attracts leukocytes and nearby phagocytes which eliminate the dead cells by phagocytosis. However, microbial damaging substances released by leukocytes would crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myiasis
Myiasis is the parasitic infestation of the body of a live animal by fly larvae (maggots) which grow inside the host while feeding on its tissue. Although flies are most commonly attracted to open wounds and urine- or feces-soaked fur, some species (including the most common myiatic flies—the botfly, blowfly, and screwfly) can create an infestation even on unbroken skin and have been known to use moist soil and non-myiatic flies (such as the common housefly) as vector agents for their parasitic larvae. Because some animals (particularly non-native domestic animals) cannot react as effectively as humans to the causes and effects of myiasis, such infestations present a severe and continuing problem for livestock industries worldwide, causing severe economic losses where they are not mitigated by human action. Although typically a far greater issue for animals, myiasis is also a relatively frequent disease for humans in rural tropical regions where myiatic flies thrive, and of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calliphora
''Calliphora'' is a genus of blow flies, also known as bottle flies, found in most parts of the world, with the highest diversity in Australia. The most widespread species in North America area ''Calliphora livida'', '' C. vicina'', and '' C. vomitoria''. ''Calliphora'', meaning "bearer of beauty", was first formally named in 1830 by Jean-Baptiste Robineau-Desvoidy. It is the type genus of the family Calliphoridae. Description Adults of ''Calliphora'' have a grey or black thorax, the colour dulled by a heavy microtomentum. The abdomen is metallic blue (rarely purple or green) and sometimes also dulled by microtomentum. The suprasquamal ridge is bare or with inconspicuous fine setae only. The first flagellomere of the antenna is more than twice the length of the pedicel. Larvae have two posterior spiracles with a thick and unbroken peritreme, and (like other Calliphoridae larvae) containing straight slits. There is an accessory sclerite A sclerite (Greek , ', meaning " har ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucilia (fly)
''Lucilia'' is a genus of blow flies in the family Calliphoridae. Various species in this genus are commonly known as green bottle flies. Species Genus: ''Lucilia'' Robineau-Desvoidy, 1830 *'' Lucilia adisoemartoi'' Kurahashi, 1988 *'' Lucilia aestuans'' Robineau-Desvoidy, 1863 *'' Lucilia affinis'' Robineau-Desvoidy, 1863 *'' Lucilia agilis'' Robineau-Desvoidy, 1863 *'' Lucilia albofasciata'' Macquart & Berthelot, 1839 *'' Lucilia ampullacea'' Villeneuve, 1922 *''Lucilia andrewsi'' Senior-White, 1940 *''Lucilia angustifrons'' Ye, 1983 *''Lucilia angustifrontata'' Ye, 1992 *''Lucilia appendicifera'' Fan, 1965 *''Lucilia arrogans'' Robineau-Desvoidy, 1863 *''Lucilia arvensis'' Robineau-Desvoidy, 1863 *''Lucilia aurata'' Robineau-Desvoidy, 1863 *''Lucilia aureovultu'' Theowald, 1957 *''Lucilia azurea'' Meigen, 1838 *''Lucilia bazini'' Séguy, 1934 *''Lucilia bismarckensis'' Kurahashi, 1987 *'' Lucilia bufonivora'' Moniez, 1876 *''Lucilia caerulea'' Robineau-Desvoidy, 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decomposition
Decomposition or rot is the process by which dead organic substances are broken down into simpler organic or inorganic matter such as carbon dioxide, water, simple sugars and mineral salts. The process is a part of the nutrient cycle and is essential for recycling the finite matter that occupies physical space in the biosphere. Bodies of living organisms begin to decompose shortly after death. Animals, such as worms, also help decompose the organic materials. Organisms that do this are known as decomposers or detritivores. Although no two organisms decompose in the same way, they all undergo the same sequential stages of decomposition. The science which studies decomposition is generally referred to as ''taphonomy'' from the Greek word ''taphos'', meaning tomb. Decomposition can also be a gradual process for organisms that have extended periods of dormancy. One can differentiate abiotic decomposition from biotic decomposition (biodegradation). The former means "the degradation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)