|
Cygnus OB2-8A
Cygnus OB2 #8A is a double-lined spectroscopic binary located near the centre of the Cygnus OB2 association located 5,500 light years away. Discovery Until 1951 Cyg OB2 #8 had been known only as an anonymous catalogue entry in the Bonner Durchmusterung. Then it was identified as one of several highly luminous hot stars close together in Cygnus. Despite being commonly referred to as Schulte #8A, the number 8 was first published in an earlier paper. Schulte identified the grouping as a massive stellar association and split star #8 into four components, including #8A. System The Cygnus OB2 #8A system contains two massive luminous O class stars in a 21.9 day orbit. The primary is a supergiant and the secondary is a giant star. The two stars are not thought to be exchanging mass and their luminosity classes match the main sequence turnoff in the Cyg OB2 association at around O6. The nearby stars Cyg OB2 #8B, #8C, and #8D, originally thought to be a single star, are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bica2 HST
Bica may refer to: * Bica (coffee), a type of coffee beverage originally from Portugal * Bica, Cluj, one of 6 villages comprising the Mănăstireni commune in Cluj County, Romania * Bica-Q, a trade name of the antiandrogen bicalutamide * Fazenda da Bica, a region of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil * Quinta da Bica, a ''quinta'' (estate) near Seia, Beira region, Portugal * Bicalutamide, a drug used to treat prostate cancer and in feminizing hormone therapy People * Bica (footballer) (Marcus Di Giuseppe, born 1972), Brazilian footballer * Camillo Mac Bica (born 1947), American philosopher, poet, activist, and author * Carlos Bica (active from 1998), Portuguese jazz bassist * José Bica (born 2003), Portuguese footballer * Sergio Bica (born 1983), Uruguayan footballer * Adrian Bică Bădan (born 1988), Romanian footballer BICA * Bahamas Institute of Chartered Accountants, a professional association * Banque Internationale pour la Centrafrique, a bank * BICA Honduras, a non-profit environmental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1RXS
1RXS is an acronym which is the prefix used for the First ROSAT X-ray Survey (1st ROSAT X-ray Survey). This is a catalogue of astronomical objects that were visible in the X-ray spectrum from the ROSAT satellite, in the field of X-ray astronomy. Examinations of 1RXS has shown that many sources can be identified, such as old neutron star A neutron star is the gravitationally collapsed Stellar core, core of a massive supergiant star. It results from the supernova explosion of a stellar evolution#Massive star, massive star—combined with gravitational collapse—that compresses ...s, while other entries are "intriguing", according to one researcher. See also * 1RXS J160929.1−210524, example References External links Catalog site Astronomical surveys X-ray astronomy ROSAT objects {{spacecraft-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O-type Giants
Type 0 or Type O may refer to: Type 0 Aircraft *Type 0 Carrier Fighter Mitsubishi A6M, a Japanese fighter aircraft *Type 0 Observation Seaplane Mitsubishi F1M, a Japanese reconnaissance seaplane *Type 0 Reconnaissance Seaplane Aichi E13A, a Japanese reconnaissance seaplane *Type 0 Small Reconnaissance Seaplane Yokosuka E14Y, a Japanese submarine-based reconnaissance seaplane *Type 0 Transport Showa/Nakajima L2D, a Japanese transport aircraft Watercraft *Type-0 heavy lift vessel Dockwise Vanguard, a semi-submersible heavy lift ship Entertainment * ''Final Fantasy Type-0'', a video game Science *Glycogen storage disease type 0, a disease *Type 0 civilization in the Kardashev scale of technological advancement *Type-0 language or Recursively enumerable language in the Chomsky hierarchy of formal languages *Type 0 string theory, a model of string theory Type O *Type O in the ABO blood group system *an O-type star **an O-type main-sequence star **an O-type giant star **a subdwarf O s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical X-ray Sources
Astrophysical X-ray sources are astronomical objects with physical properties which result in the emission of X-rays. Several types of astrophysical objects emit X-rays. They include galaxy clusters, black holes in active galactic nucleus, active galactic nuclei (AGN), galactic objects such as supernova remnants, stars, and binary stars containing a white dwarf (cataclysmic variable stars and super soft X-ray sources), neutron star or black hole (X-ray binaries). Some Solar System bodies emit X-rays, the most notable being the Moon, although most of the X-ray brightness of the Moon arises from reflected solar X-rays. Furthermore, celestial entities in space are discussed as celestial X-ray sources. The origin of all observed astronomical X-ray sources is in, near to, or associated with a coronal cloud or gas at coronal cloud temperatures for however long or brief a period. A combination of many unresolved X-ray sources is thought to produce the observed X-ray background. The X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emission-line Stars
A spectral line is a weaker or stronger region in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum. It may result from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used to identify atoms and molecules. These "fingerprints" can be compared to the previously collected ones of atoms and molecules, and are thus used to identify the atomic and molecular components of stars and planets, which would otherwise be impossible. Types of line spectra Spectral lines are the result of interaction between a quantum system (usually atoms, but sometimes molecules or atomic nuclei) and a single photon. When a photon has about the right amount of energy (which is connected to its frequency) to allow a change in the energy state of the system (in the case of an atom this is usually an electron changing orbitals), the photon is absorbed. Then the energy will be spontaneously re-emitted, either as one photon at the same f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
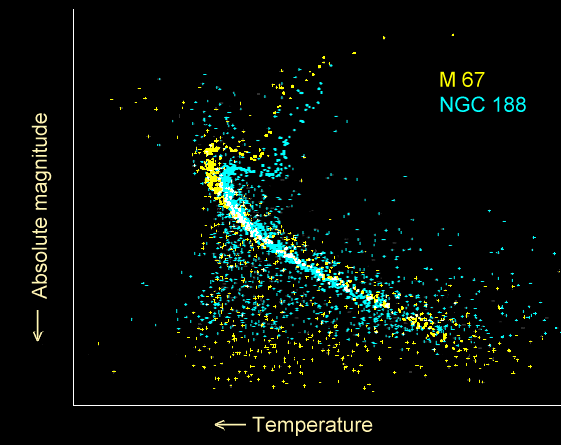
Main Sequence Turnoff
The turnoff point for a star refers to the point on the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram where it leaves the main sequence after its main fuel is exhaustedthe main sequence turnoff. By plotting the turnoff points of individual stars in a star cluster one can Main sequence#Evolutionary_tracks, estimate the cluster's age. Stars with no turnoff point Red dwarfs, also referred to as classM stars, are stars of . They have sufficient mass to sustain hydrogen-to-helium Nuclear fusion, fusion via the proton–proton chain reaction, but they do not have sufficient mass to create the temperatures and pressures necessary to fuse helium into carbon, nitrogen or oxygen (see CNO cycle). However, all their hydrogen is available for fusion, and low temperature and pressure means a lifetime measured in trillions of years. For example, the lifespan of a star of 0.1 solar masses is six trillion years. This lifespan greatly exceeds the current age of the universe, therefore all red dwarfs are main sequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Star
A giant star has a substantially larger radius and luminosity than a main-sequence (or ''dwarf'') star of the same surface temperature. They lie above the main sequence (luminosity class V in the Yerkes spectral classification) on the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram and correspond to luminosity classes II and III. The terms ''giant'' and ''dwarf'' were coined for stars of quite different luminosity despite similar temperature or spectral type (namely K and M) by Ejnar Hertzsprung in 1905 or 1906. Giant stars have radii up to a few hundred times the Sun and luminosities over 10 times that of the Sun. Stars still more luminous than giants are referred to as supergiants and hypergiants. A hot, luminous main-sequence star may also be referred to as a giant, but any main-sequence star is properly called a dwarf, regardless of how large and luminous it is. Formation A star becomes a giant after all the hydrogen available for fusion at its core has been depleted and, as a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supergiant
Supergiants are among the most massive and most luminous stars. Supergiant stars occupy the top region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram, with absolute visual magnitudes between about −3 and −8. The temperatures of supergiant stars range from about 3,400 K to over 20,000 K. Definition The title ''supergiant'', as applied to a star, does not have a single concrete definition. The term ''giant star'' was first coined by Hertzsprung when it became apparent that the majority of stars fell into two distinct regions of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram. One region contained larger and more luminous stars of spectral types A to M, which received the name ''giant''. Subsequently, as they lacked any measurable parallax, it became apparent that some of these stars were significantly larger and more luminous than the bulk, and the term ''super-giant'' arose, quickly adopted as ''supergiant''. Supergiants with spectral classes of O to A are typically referred to as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Association
A stellar association is a very loose star cluster, looser than both open clusters and globular clusters. Stellar associations will normally contain from 10 to 100 or more visible stars. An association is primarily identified by commonalities in its member stars' movement vectors, ages, and chemical compositions. These shared features indicate that the members share a common origin. Nevertheless, they have become gravitationally unbound, unlike star clusters, and the member stars will drift apart over millions of years, becoming a moving group as they scatter throughout their neighborhood within the galaxy. Stellar associations were discovered by Victor Ambartsumian in 1947. The conventional name for an association uses the names or abbreviations of the constellation (or constellations) in which they are located; the association type, and, sometimes, a numerical identifier. Types Victor Ambartsumian first categorized stellar associations into two groups, OB and T, based on the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectroscopic Binary
A binary star or binary star system is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved as separate stars using a telescope, in which case they are called ''visual binaries''. Many visual binaries have long orbital periods of several centuries or millennia and therefore have orbits which are uncertain or poorly known. They may also be detected by indirect techniques, such as spectroscopy (''spectroscopic binaries'') or astrometry (''astrometric binaries''). If a binary star happens to orbit in a plane along our line of sight, its components will eclipse and transit each other; these pairs are called ''eclipsing binaries'', or, together with other binaries that change brightness as they orbit, ''photometric binaries''. If components in binary star systems are close enough, they can gravitationally distort each other's outer stellar atmospheres. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guide Star Catalog
The Guide Star Catalog (GSC), also known as the ''Hubble Space Telescope, Guide Catalog'' (''HSTGC''), is a star catalog compiled to support the Hubble Space Telescope with targeting off-axis stars. GSC-I contained approximately 20,000,000 stars with apparent magnitudes of 6 to 15. GSC-II contains 945,592,683 stars out to magnitude 21. As far as possible, binary stars and non-stellar objects have been excluded or flagged as not meeting the requirements of Fine Guidance Sensors. This is the first full sky star catalog created specifically for navigation in outer space. History Version 1.0 The first version of this catalog was published in 1989. The first catalog was created by digitizing photographic plates produced by the Palomar Schmidt Quick-V survey for the northern hemisphere and the UK Schmidt SERC-J survey for the southern hemisphere. This catalog contains objects in the magnitude range 7-16 and the classification was biased to prevent the use of a non-stellar object as a gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalog Of Stellar Identification
The Catalog of Stellar Identifications (CSI) is a star catalog which was constructed to facilitate cross-referencing between different star catalogs. It contains designations and basic data for, as of 1983, approximately 440,000 stars, and was created by merging the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory Star Catalog, the Henry Draper Catalogue, the AGK2/3, the Cape Photographic Catalogue, the Cape Zone Catalogue, the Yale Zone Catalogue, the Cape Catalogue of Faint Stars, and the Boss General Catalogue. It contains stellar coordinates, magnitudes, spectral types, proper motions, and cross-references to designations in the previously mentioned catalogs. It also gives cross-references to many other catalogues, such as the Index Catalogue of Visual Double Stars, which have been linked to the CSI. The CSI eventually became part of the SIMBAD SIMBAD (the Set of Identifications, Measurements and Bibliography for Astronomical Data) is an astronomy, astronomical database of objec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |