|
Cyclone Hary
Very Intense Tropical Cyclone Hary was the strongest tropical cyclone in the 2001–02 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season. Developing on March 5 from the monsoon trough, the storm initially moved generally to the west and gradually intensified. With favorable conditions, Hary quickly intensified on March 7, developing an eye and well-defined outflow. After reaching an initial peak, the cyclone briefly weakened due to an eyewall replacement cycle, by which time the storm turned southwestward toward Madagascar. Hary re-intensified and attained peak winds of on March 10 just offshore eastern Madagascar, which made it the first very intense tropical cyclone since 2000. After peaking, Hary weakened due to land interaction, and it struck Madagascar southeast of Antalaha. It was turning south over land, and as a result it quickly moved offshore. There were three deaths in the country, one of which from electrocution. There was locally heavy crop damage, and four brid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa across the Mozambique Channel. At Madagascar is the world's List of island countries, second-largest island country, after Indonesia. The nation is home to around 30 million inhabitants and consists of the island of Geography of Madagascar, Madagascar (the List of islands by area, fourth-largest island in the world), along with numerous smaller peripheral islands. Following the prehistoric breakup of the supercontinent Gondwana, Madagascar split from the Indian subcontinent around 90 million years ago, allowing native plants and animals to evolve in relative isolation. Consequently, Madagascar is a biodiversity hotspot; over 90% of wildlife of Madagascar, its wildlife is endemic. Human settlement of Madagascar occurred during or befo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
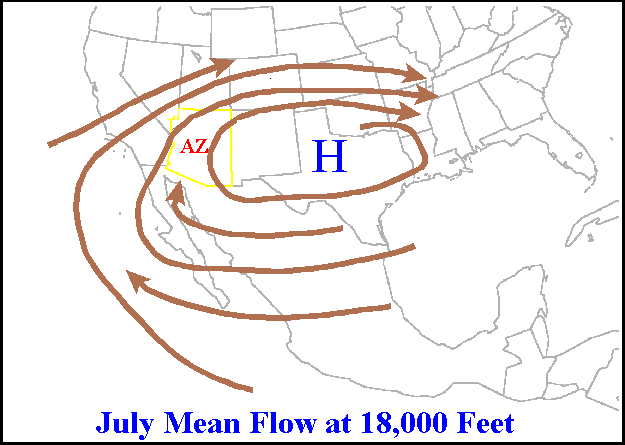
Ridge (meteorology)
A ridge or barometric ridge is a term in meteorology describing an elongated area of relatively high atmospheric pressure compared to the surrounding environment, without being a closed circulation. It is associated with an area of maximum anticyclonic curvature of wind flow. The ridge originates in the center of an anticyclone and sandwiched between two low-pressure areas, and the locus of the maximum curvature is called the ''ridge line''. This phenomenon is the opposite of a trough. Description Ridges can be represented in two ways: * On surface weather maps, the pressure isobars form contours where the maximum pressure is found along the axis of the ridge. * In upper-air maps, geopotential height isohypses form similar contours where the maximum defines the ridge. Related weather Given the direction of the winds around an anticyclonic circulation and the fact that weather systems move from west to east: *ahead of an upper-ridge, the airflow that comes from the polar regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westerlies
The westerlies, anti-trades, or prevailing westerlies, are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude. They originate from the high-pressure areas in the horse latitudes and trend towards the poles and steer extratropical cyclones in this general manner. Tropical cyclones which cross the subtropical ridge axis into the westerlies recurve due to the increased westerly flow. The winds are predominantly from the southwest in the Northern Hemisphere and from the northwest in the Southern Hemisphere. The westerlies are strongest in the winter hemisphere and times when the pressure is lower over the poles, while they are weakest in the summer hemisphere and when pressures are higher over the poles. The westerlies are particularly strong, especially in the Southern Hemisphere (called also 'Brave West winds' at striking Chile, Tasmania and New Zealand), in areas where land is absent, because land amplifies the flow pattern, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
40th Parallel South
The 40th parallel south is a circle of latitude that is 40 degrees south of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses the Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean, Australasia, the Pacific Ocean and South America. Its long oceanic stretches are the northern domain of the Roaring Forties. On 21 June 2018, the sun is at 26.17° in the sky and at 73.83° on 21 December, in King Island, Tasmania, which is near the 40th parallel. The maximum altitude of the Sun is > 35.00º in April and > 28.00º in May. Around the world Starting at the Prime Meridian and heading eastwards, the parallel 40° south passes through: : See also *39th parallel south * 41st parallel south *Roaring Forties *Project Loon Loon LLC was an Alphabet Inc. subsidiary working on providing Internet access to rural and remote areas. The company used high-altitude balloons in the stratosphere at an altitude of to to create an aerial wireless network with up to 1 Mbi ... References {{geographical coordinates, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Île Amsterdam
Île Amsterdam (), also known as Amsterdam Island and New Amsterdam (''Nouvelle-Amsterdam''), is an island of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands in the southern Indian Ocean that together with neighbouring Île Saint-Paul to the south forms one of the five districts of the territory. The island is roughly equidistant to the land masses of Madagascar, Australia, and Antarctica – as well as the British Indian Ocean Territory and the Cocos (Keeling) Islands (about from each). The research station at Martin-de-Viviès, first called ''Camp Heurtin'' and then ''La Roche Godon'', is the only settlement on the island and is the seasonal home to about thirty researchers and staff studying biology, meteorology, and geomagnetics. History The first person known to have sighted the island was the Spanish explorer Juan Sebastián de Elcano, on 18 March 1522, during his circumnavigation of the world. Elcano did not give the island a name. On 17 June 1633, Dutch mariner Anthonie va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Île Sainte-Marie
Nosy Boraha , previously known as Sainte-Marie, main town Ambodifotatra, is an island off the east coast of Madagascar. The island forms an administrative district within Analanjirofo Region, and covers an area of 222 km2. It has a population estimated at 30,000. Sainte-Marie Island is known for its authentic and preserved character, its whale watching, its beautiful beaches, its romantic history and the kindness of its inhabitants. Administration The island is organized as the city (''commune urbaine'') and district of Nosy Boraha in Analanjirofo Region. *1 town hall *17 fokontany (villages) *1 deputy Population The Betsimisaraka are the largest ethnic group on the island, though there had been a long history of mixed marriages, including with pirates in the 17th century. Transport infrastructure *1 international airport in the South (inaugurated 2015) *1 commercial port (Ilot Madame) *1 passenger port (Ambodifotatra) Ferries leave from Soanierana Ivongo and Mahambo, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landfall (meteorology)
Landfall is the event of a storm moving over land after being over water. More broadly, and in relation to human travel, it refers to 'the first land that is reached or seen at the end of a journey across the sea or through the air, or the fact of arriving there. Tropical cyclone A tropical cyclone is classified as making landfall when the center of the storm moves across the coast; in a relatively strong tropical cyclone, this is when the eye moves over land. This is where most of the damage occurs within a mature tropical cyclone, such as a typhoon or hurricane, as most of the damaging aspects of these systems are concentrated near the eyewall. Such effects include the peaking of the storm surge, the core of strong winds coming ashore, and heavy flooding rains. These coupled with high surf can cause major beach erosion. When a tropical cyclone makes landfall, the eye usually closes in upon itself due to negative environmental factors over land, such as friction with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapid Deepening
In meteorology, rapid intensification is a situation where a tropical cyclone intensifies dramatically in a short period of time. The United States National Hurricane Center defines rapid intensification as an increase in the maximum sustained winds of a tropical cyclone of at least in a 24-hour period. Necessary conditions External In order for rapid intensification to occur, several conditions must be in place. Water temperatures must be extremely warm (near or above ), and water of this temperature must be sufficiently deep such that waves do not churn deeper cooler waters up to the surface. Wind shear must be low; when wind shear is high, the convection and circulation in the cyclone will be disrupted. Dry air can also limit the strengthening of tropical cyclones. Internal Usually, an anticyclone in the upper layers of the troposphere above the storm must also be present for extremely low surface pressures to develop. This is because air must be converging towards the low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Sustained Winds
The maximum sustained wind associated with a tropical cyclone is a common indicator of the intensity of the storm. Within a mature tropical cyclone, it is found within the eyewall at a distance defined as the radius of maximum wind, or RMW. Unlike gusts, the value of these winds are determined via their sampling and averaging the sampled results over a period of time. Wind measuring has been standardized globally to reflect the winds at above the Earth's surface, and the maximum sustained wind represents the highest average wind over either a one-minute (US) or ten-minute time span (see the definition, below), anywhere within the tropical cyclone. Surface winds are highly variable due to friction between the atmosphere and the Earth's surface, as well as near hills and mountains over land. Over the ocean, satellite imagery determines the value of the maximum sustained winds within a tropical cyclone. Land, ship, aircraft reconnaissance observations, and radar imagery can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
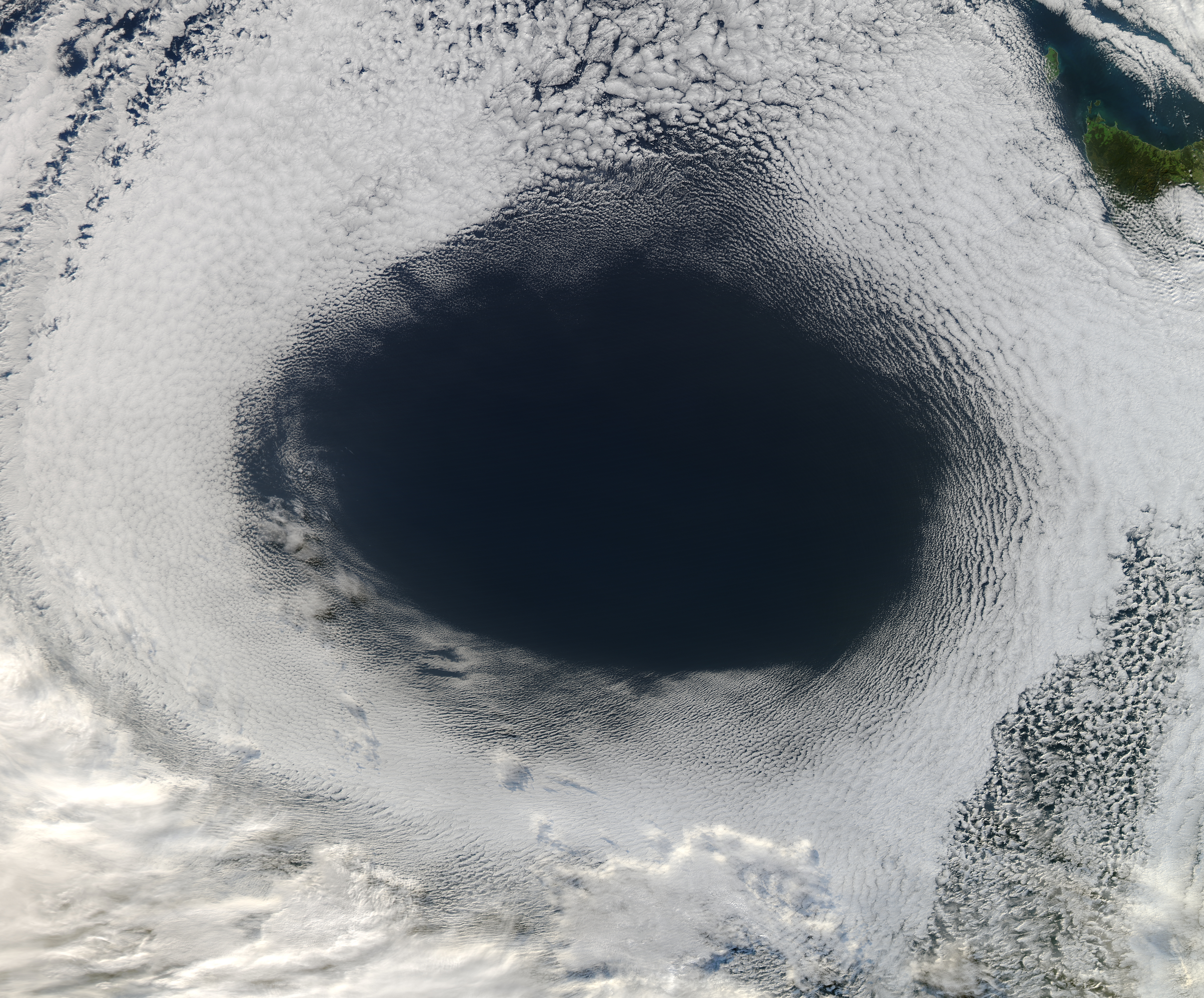
Central Dense Overcast
The central dense overcast, or CDO, of a tropical cyclone or strong subtropical cyclone is the large central area of thunderstorms surrounding its circulation center, caused by the formation of its eyewall. It can be round, angular, oval, or irregular in shape. This feature shows up in tropical cyclones of tropical storm or hurricane strength. How far the center is embedded within the CDO, and the temperature difference between the cloud tops within the CDO and the cyclone's eye, can help determine a tropical cyclone's intensity with the Dvorak technique. Locating the center within the CDO can be a problem with strong tropical storms and minimal hurricanes as its location can be obscured by the CDO's high cloud canopy. This center location problem can be resolved through the use of microwave satellite imagery. After a cyclone strengthens to around hurricane intensity, an eye appears at the center of the CDO, defining its center of low pressure and its cyclonic wind field. Tropic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticyclone
An anticyclone is a weather phenomenon defined as a large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure, clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to a cyclone). Effects of surface-based anticyclones include clearing skies as well as cooler, drier air. Fog can also form overnight within a region of higher pressure. Mid-tropospheric systems, such as the subtropical ridge, deflect tropical cyclones around their periphery and cause a temperature inversion inhibiting free convection near their center, building up surface-based haze under their base. Anticyclones aloft can form within warm-core lows such as tropical cyclones, due to descending cool air from the backside of upper troughs such as polar highs, or from large-scale sinking such as a subtropical ridge. The evolution of an anticyclone depends upon variables such as its size, intensity, and extent of moist con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |