|
Cyber-utopianism
Cyber-utopianism, web-utopianism, digital utopianism, or utopian internet is a subcategory of technological utopianism and the belief that online communication helps bring about a more decentralized, democratic, and libertarian society. The desired values may also be privacy and anonymity, freedom of expression, access to culture and information or also socialist ideals leading to digital socialism. Origins The Californian Ideology is a set of beliefs combining bohemian and anti-authoritarian attitudes from the counterculture of the 1960s with techno-utopianism and support for neoliberal economic policies. These beliefs are thought by some to have been characteristic of the culture of the IT industry in Silicon Valley and the West Coast of the United States during the dot-com boom of the 1990s. Adam Curtis connects it to Ayn Rand's Objectivist philosophy in the film All Watched Over by Machines of Loving Grace (TV series). Such an ideology of digital utopianism fueled the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technological Utopianism
Technological utopianism (often called techno-utopianism or technoutopianism) is any ideology based on the premise that advances in science and technology could and should bring about a utopia, or at least help to fulfill one or another utopian ideal. A techno-utopia is therefore an ideal society, in which laws, government, and social conditions are solely operating for the benefit and well-being of all its citizens, set in the near- or far-future, as advanced science and technology will allow these ideal living standards to exist; for example, post-scarcity, Trans-human, transformations in human nature, the avoidance or prevention of suffering and even the immortality, end of death. Technological utopianism is often connected with other discourses presenting technologies as agents of social and cultural change, such as technological determinism or Imaginary (sociology)#Media imaginary, media imaginaries. A tech-utopia does not disregard any problems that technology may cause, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
File Sharing
File sharing is the practice of distributing or providing access to digital media, such as computer programs, multimedia (audio, images and video), documents or electronic books. Common methods of storage, transmission and dispersion include removable media, centralized servers on computer networks, Internet-based hyperlinked documents, and the use of distributed peer-to-peer networking. File sharing technologies, such as BitTorrent, are integral to modern media piracy, as well as the sharing of scientific data and other free content. History Files were first exchanged on removable media. Computers were able to access remote files using filesystem mounting, bulletin board systems (1978), Usenet (1979), and FTP servers (1970's). Internet Relay Chat (1988) and Hotline (1997) enabled users to communicate remotely through chat and to exchange files. The mp3 encoding, which was standardized in 1991 and substantially reduced the size of audio files, grew to widespread use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Californian Ideology
"The Californian Ideology" is a 1995 essay by English media theorists Richard Barbrook and Andy Cameron of the University of Westminster. Barbrook calls it a "critique of dotcom neoliberalism".Barbrook 2007Imaginary Futures: Other Works In the essay, Barbrook and Cameron argue that the rise of networking technologies in Silicon Valley in the 1990s was linked to American neoliberalism and a paradoxical hybridization of beliefs from the political left and right in the form of hopeful technological determinism. The essay was published in ''Mute'' magazineThe Californian Ideology, Barbrook, Cameron, 1995-09, Mute Vol 1 #3 CODE, , Mute, London, http://www.metamute.org/editorial/articles/californian-ideology in 1995 and later appeared on the '' nettime'' Internet mailing list. A revised version was published in ''Science as Culture'' in 1996. The essay has since been further revised and translated. Andrew Leonard of ''Salon'' called the essay "one of the most penetrating critiques of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Techno-utopianism
Technological utopianism (often called techno-utopianism or technoutopianism) is any ideology based on the premise that advances in science and technology could and should bring about a utopia, or at least help to fulfill one or another utopian ideal. A techno-utopia is therefore an ideal society, in which laws, government, and social conditions are solely operating for the benefit and well-being of all its citizens, set in the near- or far-future, as advanced science and technology will allow these ideal living standards to exist; for example, post-scarcity, Trans-human, transformations in human nature, the avoidance or prevention of suffering and even the immortality, end of death. Technological utopianism is often connected with other discourses presenting technologies as agents of social and cultural change, such as technological determinism or Imaginary (sociology)#Media imaginary, media imaginaries. A tech-utopia does not disregard any problems that technology may cause, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hospitality Exchange Service
Hospitality exchange services (hospitality exchange platforms, hospitality exchange networks or HospEx) are social networking services used for accommodation of travellers, where hosts do not receive payments. The relationships on homestay, hospitality exchange services are shaped by altruism and are related to the cyber-utopianism on the Web in its beginnings and to utopia in general. On HospEx, members typically create public profiles that describe themselves and their travel plans, and then searching for potential hosts or guests based on various criteria such as location, interests, and availability. Travelers connect with local hosts who are willing to offer free accommodation, meals, and/or other forms of hospitality during their trip. The concept of hospitality exchange has been around for a long time, with informal networks of travelers and hosts existing for decades. However, the advent of the internet and social media has made it much easier to connect with people from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ray Kurzweil
Raymond Kurzweil ( ; born February 12, 1948) is an American computer scientist, author, entrepreneur, futurist, and inventor. He is involved in fields such as optical character recognition (OCR), speech synthesis, text-to-speech synthesis, speech recognition technology and electronic keyboard instruments. He has written books on health technology, artificial intelligence (AI), transhumanism, the technological singularity, and futures studies, futurism. Kurzweil is a public advocate for the futurist and transhumanist movements and gives public talks to share his optimistic outlook on life extension technologies and the future of nanotechnology, robotics, and biotechnology. Kurzweil received the 1999 National Medal of Technology and Innovation, the United States' highest honor in technology, from President Bill Clinton in a White House ceremony. He received the $500,000 Lemelson–MIT Prize in 2001. He was elected a member of the National Academy of Engineering in 2001 for the app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extropianism
Extropianism, also referred to as the philosophy of extropy, is an "evolving framework of values and standards for continuously improving the human condition". Extropians believe that advances in science and technology will some day let people live indefinitely. An extropian may wish to contribute to this goal, e.g. by doing research and development or by volunteering to test new technology. Originated by a set of principles developed by the philosopher Max More in ''The Principles of Extropy'', extropian thinking places strong emphasis on rational thinking and on practical optimism. According to More, these principles "do not specify particular beliefs, technologies, or policies". Extropians share an optimistic view of the future, expecting considerable advances in computational power, life extension, nanotechnology and the like. Many extropians foresee the eventual realization of indefinite lifespans or immortality, and the recovery, thanks to future advances in biomedical t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Technology
Information technology (IT) is a set of related fields within information and communications technology (ICT), that encompass computer systems, software, programming languages, data processing, data and information processing, and storage. Information technology is an application of computer science and computer engineering. The term is commonly used as a synonym for computers and computer networks, but it also encompasses other information distribution technologies such as television and telephones. Several products or services within an economy are associated with information technology, including computer hardware, software, electronics, semiconductors, internet, Telecommunications equipment, telecom equipment, and e-commerce.. An information technology system (IT system) is generally an information system, a communications system, or, more specifically speaking, a Computer, computer system — including all Computer hardware, hardware, software, and peripheral equipment � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Sublime
The digital sublime is the mythologization of the impact of Computer, computers and cyberspace on human experiences of time, space and power. It is also known as cyber sublime or algorithmic sublime. It is a philosophical conception of emotions that captivate the collective conscience with the emergence of these new technologies and the promises and predictions that emerge from them. These emotions are the awe, the Surprise (emotion), astonishment, the rationality-subsuming Magnificence (history of ideas), glory, and the generally intense spiritual experience. This feeling is essentially provoked by intentionally black box, black-boxed algorithms or by the lack of knowledge about algorithms. The sublime can be either utopian or dystopian depending on the individual's interpretation of their emotional response. The utopian interpretation of the digital sublime is known as digital utopianism and the dystopian is referred to as digital dystopia. Classical notion of the sublime Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW or simply the Web) is an information system that enables Content (media), content sharing over the Internet through user-friendly ways meant to appeal to users beyond Information technology, IT specialists and hobbyists. It allows documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet according to specific rules of the HTTP, Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). The Web was invented by English computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee while at CERN in 1989 and opened to the public in 1993. It was conceived as a "universal linked information system". Documents and other media content are made available to the network through web servers and can be accessed by programs such as web browsers. Servers and resources on the World Wide Web are identified and located through character strings called uniform resource locators (URLs). The original and still very common document type is a web page formatted in Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). This markup lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Democracy
Direct democracy or pure democracy is a form of democracy in which the Election#Electorate, electorate directly decides on policy initiatives, without legislator, elected representatives as proxies, as opposed to the representative democracy model which occurs in the majority of established democracies. The theory and practice of direct democracy and participation as its common characteristic constituted the core of the work of many theorists, philosophers, politicians, and social critics, among whom the most important are Jean-Jacques Rousseau, John Stuart Mill, and G. D. H. Cole, G.D.H. Cole. Overview In direct democracy the people decide on policies without any intermediary or representative, whereas in a representative democracy people vote for representatives who then enact policy initiatives. Depending on the particular system in use, direct democracy might entail passing executive decisions, the use of sortition, making laws, directly electing or dismissing officials, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
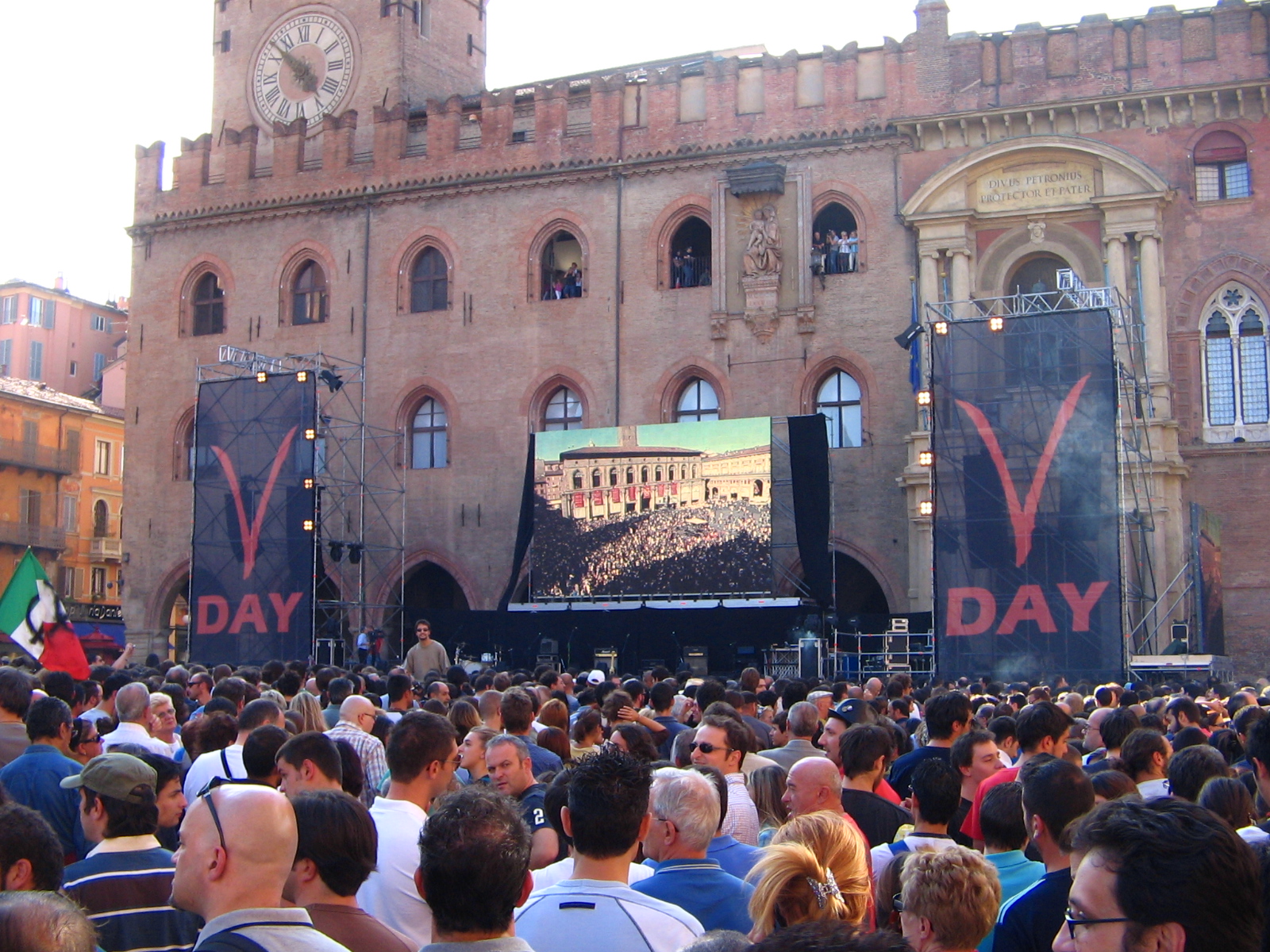
Five Star Movement
The Five Star Movement ( , M5S) is a political party in Italy, led by Giuseppe Conte. It was launched on 4 October 2009 by Beppe Grillo, a political activist and comedian, and Gianroberto Casaleggio, a web strategist. The party is primarily described as populist of the syncretic kind, due to its long-time indifference to the left–right political spectrum. The party has been a proponent of green politics and direct democracy, as well as progressivism, social democracy and left-wing populism. During an online vote held in November 2024, party members decided to identify as "independent progressives". In the 2013 general election, the M5S obtained 25.6% of the vote, but rejected a proposed coalition government with the centre-left Democratic Party (PD) and joined the opposition. In 2016 M5S' Chiara Appendino and Virginia Raggi were elected mayors of Turin and Rome, respectively. The M5S supported the successful "no" vote in the 2016 constitutional referendum. In the 2018 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |