|
Cutie (rivista)
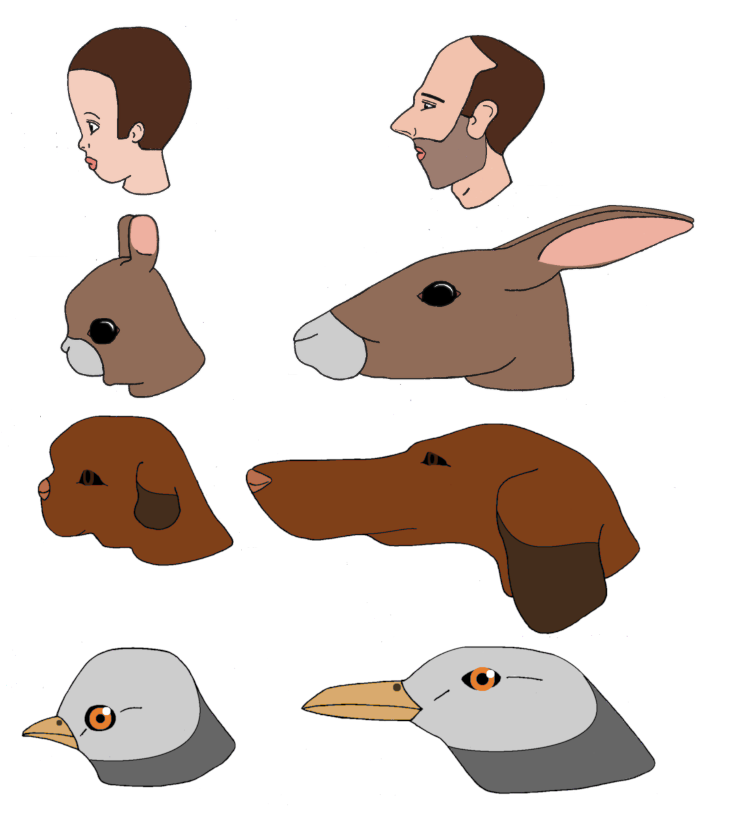
Cuteness is a subjective term describing a type of Physical attractiveness, attractiveness commonly associated with youth and Human physical appearance, appearance, as well as a scientific concept and analytical model in ethology, first introduced by Konrad Lorenz. Lorenz proposed the concept of baby schema (''Kindchenschema''), a set of facial and body features that make a creature appear "cute" and activate ("release") in others the motivation to care for it.Glocker ML, Langleben DD, Ruparel K, Loughead JW, Valdez JN, Griffin MD, Sachser N, Gur RC"Baby schema modulates the brain reward system in nulliparous women."''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences – U.S.A'' 2009 June 2;106(22):9115–9119. Cuteness may be ascribed to people as well as things that are regarded as attractive or charming. Juvenile traits Doug Jones, a visiting scholar in anthropology at Cornell University, said that the proportions of facial features change with age due to changes in hard t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Human Growth Skull Neoteny Cuteness Maturation
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1 million are insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a bilaterally symmetric body plan. The Bilateria include the protostomes, containing animals such as nematodes, arthropods, flatworms, annelids and molluscs, and the deuterostomes, containing the echinoderms and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anteroposterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toddler Boy
A toddler is a child approximately 12 to 36 months old, though definitions vary. The toddler years are a time of great cognitive, emotional and social development. The word is derived from "to toddle", which means to walk unsteadily, like a child of this age. Developmental milestones Toddler development can be broken down into a number of interrelated areas. There is reasonable consensus about what these areas may include: * Physical: growth or an increase in size. * Gross motor: the control of large muscles which enable walking, running, jumping and climbing. * Fine motor: the ability to control small muscles; enabling the toddler to feed themselves, draw and manipulate objects. * Vision: the ability to see near and far and interpret what is seen. * Hearing and speech: the ability to hear and receive information and listen (interpret), and the ability to understand and learn language and use it to communicate effectively. * Social: the ability to interact with the world throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kindchenschema - Mensch
Cuteness is a subjective term describing a type of Physical attractiveness, attractiveness commonly associated with youth and Human physical appearance, appearance, as well as a scientific concept and analytical model in ethology, first introduced by Konrad Lorenz. Lorenz proposed the concept of baby schema (''Kindchenschema''), a set of facial and body features that make a creature appear "cute" and activate ("release") in others the motivation to care for it.Glocker ML, Langleben DD, Ruparel K, Loughead JW, Valdez JN, Griffin MD, Sachser N, Gur RC"Baby schema modulates the brain reward system in nulliparous women."''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences – U.S.A'' 2009 June 2;106(22):9115–9119. Cuteness may be ascribed to people as well as things that are regarded as attractive or charming. Juvenile traits Doug Jones, a visiting scholar in anthropology at Cornell University, said that the proportions of facial features change with age due to changes in hard t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla ( cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together with Saur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |