|
Cuthill–McKee Algorithm
In numerical linear algebra, the Cuthill–McKee algorithm (CM), named after Elizabeth Cuthill and James McKee,E. Cuthill and J. McKeethe bandwidth of sparse symmetric matrices''In Proc. 24th Nat. Conf. ACM, pages 157–172, 1969. is an algorithm to permute a sparse matrix that has a symmetric sparsity pattern into a band matrix form with a small bandwidth. The reverse Cuthill–McKee algorithm (RCM) due to Alan George and Joseph Liu is the same algorithm but with the resulting index numbers reversed. In practice this generally results in less fill-in than the CM ordering when Gaussian elimination is applied.J. A. George and J. W-H. Liu, Computer Solution of Large Sparse Positive Definite Systems, Prentice-Hall, 1981 The Cuthill McKee algorithm is a variant of the standard breadth-first search algorithm used in graph algorithms. It starts with a peripheral node and then generates levels R_i for i=1, 2,.. until all nodes are exhausted. The set R_ is created from set R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Can 73 Cm
{{disambiguation ...
Can may refer to: Containers * Aluminum can * Drink can * Oil can * Steel and tin cans * Trash can * Petrol can * Metal can (other) Music * Can (band), West Germany, 1968 ** ''Can'' (album), 1979 * Can (South Korean band) Other * Can (name), Turkish and Circassian given name and surname * Can (verb) * Canning of food * River Can, Essex, UK * Canada * Tomato can (sports idiom) See also * CAN (other) * Cann (other) * Cans (other) * Kan (other) Kan or KAN may refer to: Places * Kan (river), a tributary of the Yenisey in Russia * Kan District of Iran * Kan, Kyrgyzstan, a village in Batken Region * Mallam Aminu Kano International Airport, Kano, Nigeria, IATA code * Kannapolis (Amtrak sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph (discrete Mathematics)
In discrete mathematics, and more specifically in graph theory, a graph is a structure amounting to a set of objects in which some pairs of the objects are in some sense "related". The objects correspond to mathematical abstractions called '' vertices'' (also called ''nodes'' or ''points'') and each of the related pairs of vertices is called an ''edge'' (also called ''link'' or ''line''). Typically, a graph is depicted in diagrammatic form as a set of dots or circles for the vertices, joined by lines or curves for the edges. Graphs are one of the objects of study in discrete mathematics. The edges may be directed or undirected. For example, if the vertices represent people at a party, and there is an edge between two people if they shake hands, then this graph is undirected because any person ''A'' can shake hands with a person ''B'' only if ''B'' also shakes hands with ''A''. In contrast, if an edge from a person ''A'' to a person ''B'' means that ''A'' owes money to ''B'', th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix Theory
In mathematics, a matrix (plural matrices) is a rectangular array or table of numbers, symbols, or expressions, arranged in rows and columns, which is used to represent a mathematical object or a property of such an object. For example, \begin1 & 9 & -13 \\20 & 5 & -6 \end is a matrix with two rows and three columns. This is often referred to as a "two by three matrix", a "-matrix", or a matrix of dimension . Without further specifications, matrices represent linear maps, and allow explicit computations in linear algebra. Therefore, the study of matrices is a large part of linear algebra, and most properties and operations of abstract linear algebra can be expressed in terms of matrices. For example, matrix multiplication represents composition of linear maps. Not all matrices are related to linear algebra. This is, in particular, the case in graph theory, of incidence matrices, and adjacency matrices. ''This article focuses on matrices related to linear algebra, and, un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
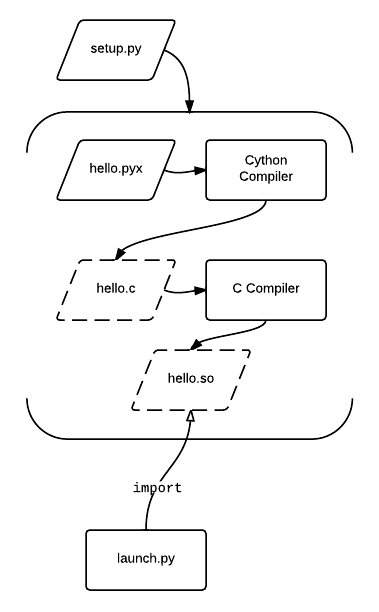
Cython
Cython () is a programming language that aims to be a superset of the Python programming language, designed to give C-like performance with code that is written mostly in Python with optional additional C-inspired syntax. Cython is a compiled language that is typically used to generate CPython extension modules. Annotated Python-like code is compiled to C or C++ then automatically wrapped in interface code, producing extension modules that can be loaded and used by regular Python code using the import statement, but with significantly less computational overhead at run time. Cython also facilitates wrapping independent C or C++ code into python-importable modules. Cython is written in Python and C and works on Windows, macOS, and Linux, producing source files compatible with CPython 2.6, 2.7, and 3.3 and later versions. Cython 3.0.0 is in development. Design Cython works by producing a standard Python module. However, the behavior differs from standard Python in that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SciPy
SciPy (pronounced "sigh pie") is a free and open-source Python library used for scientific computing and technical computing. SciPy contains modules for optimization, linear algebra, integration, interpolation, special functions, FFT, signal and image processing, ODE solvers and other tasks common in science and engineering. SciPy is also a family of conferences for users and developers of these tools: SciPy (in the United States), EuroSciPy (in Europe) and SciPy.in (in India). Enthought originated the SciPy conference in the United States and continues to sponsor many of the international conferences as well as host the SciPy website. The SciPy library is currently distributed under the BSD license, and its development is sponsored and supported by an open community of developers. It is also supported by NumFOCUS, a community foundation for supporting reproducible and accessible science. Components The SciPy package is at the core of Python's scientific computing capabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boost C++ Libraries
Boost is a set of libraries for the C++ programming language that provides support for tasks and structures such as linear algebra, pseudorandom number generation, multithreading, image processing, regular expressions, and unit testing. It contains 164 individual libraries (as of version 1.76). All of the Boost libraries are licensed under the Boost Software License, designed to allow Boost to be used with both free and proprietary software projects. Many of Boost's founders are on the C++ standards committee, and several Boost libraries have been accepted for incorporation into the C++ Technical Report 1, the C++11 standard (e.g. smart pointers, thread, regex, random, ratio, tuple) and the C++17 standard (e.g. filesystem, any, optional, variant, string_view). The Boost community emerged around 1998, when the first version of the standard was released. It has grown continuously since then and now plays a big role in the standardization of C++. Even though there is no formal r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph Bandwidth
In graph theory, the graph bandwidth problem is to label the vertices of a graph with distinct integers so that the quantity \max\ is minimized ( is the edge set of ). The problem may be visualized as placing the vertices of a graph at distinct integer points along the ''x''-axis so that the length of the longest edge is minimized. Such placement is called linear graph arrangement, linear graph layout or linear graph placement. The weighted graph bandwidth problem is a generalization wherein the edges are assigned weights and the cost function to be minimized is \max\. In terms of matrices, the (unweighted) graph bandwidth is the minimal bandwidth of a symmetric matrix which is an adjacency matrix of the graph. The bandwidth may also be defined as one less than the maximum clique size in a proper interval supergraph of the given graph, chosen to minimize its clique size . Bandwidth formulas for some graphs For several families of graphs, the bandwidth \varphi(G) is giv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Level Structure
In the mathematical subfield of graph theory a level structure of an undirected graph is a partition of the vertices into subsets that have the same distance from a given root vertex.. Definition and construction Given a connected graph ''G'' = (''V'', ''E'') with ''V'' the set of vertices and ''E'' the set of edges, and with a root vertex ''r'', the level structure is a partition of the vertices into subsets ''Li'' called levels, consisting of the vertices at distance ''i'' from ''r''. Equivalently, this set may be defined by setting ''L''0 = , and then, for ''i'' > 0, defining ''Li'' to be the set of vertices that are neighbors to vertices in ''L''''i'' − 1 but are not themselves in any earlier level. The level structure of a graph can be computed by a variant of breadth-first search: algorithm level-BFS(G, r): Q ← for ℓ from 0 to ∞: process(Q, ℓ) ''// the set Q holds all vertices at level ℓ'' mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degree (graph Theory)
In graph theory, the degree (or valency) of a vertex of a graph is the number of edges that are incident to the vertex; in a multigraph, a loop contributes 2 to a vertex's degree, for the two ends of the edge. The degree of a vertex v is denoted \deg(v) or \deg v. The maximum degree of a graph G, denoted by \Delta(G), and the minimum degree of a graph, denoted by \delta(G), are the maximum and minimum of its vertices' degrees. In the multigraph shown on the right, the maximum degree is 5 and the minimum degree is 0. In a regular graph, every vertex has the same degree, and so we can speak of ''the'' degree of the graph. A complete graph (denoted K_n, where n is the number of vertices in the graph) is a special kind of regular graph where all vertices have the maximum possible degree, n-1. In a signed graph, the number of positive edges connected to the vertex v is called positive deg(v) and the number of connected negative edges is entitled negative deg(v). Handshaking le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Vertex
This is a glossary of graph theory. Graph theory is the study of graphs, systems of nodes or vertices connected in pairs by lines or edges. Symbols A B C D E F G H I K L M N O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-tuple
In mathematics, a tuple is a finite ordered list (sequence) of elements. An -tuple is a sequence (or ordered list) of elements, where is a non-negative integer. There is only one 0-tuple, referred to as ''the empty tuple''. An -tuple is defined inductively using the construction of an ordered pair. Mathematicians usually write tuples by listing the elements within parentheses "" and separated by a comma and a space; for example, denotes a 5-tuple. Sometimes other symbols are used to surround the elements, such as square brackets " nbsp; or angle brackets "⟨ ⟩". Braces "" are used to specify arrays in some programming languages but not in mathematical expressions, as they are the standard notation for sets. The term ''tuple'' can often occur when discussing other mathematical objects, such as vectors. In computer science, tuples come in many forms. Most typed functional programming languages implement tuples directly as product types, tightly associated with algeb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertex (graph Theory)
In discrete mathematics, and more specifically in graph theory, a vertex (plural vertices) or node is the fundamental unit of which graphs are formed: an undirected graph consists of a set of vertices and a set of edges (unordered pairs of vertices), while a directed graph consists of a set of vertices and a set of arcs (ordered pairs of vertices). In a diagram of a graph, a vertex is usually represented by a circle with a label, and an edge is represented by a line or arrow extending from one vertex to another. From the point of view of graph theory, vertices are treated as featureless and indivisible objects, although they may have additional structure depending on the application from which the graph arises; for instance, a semantic network is a graph in which the vertices represent concepts or classes of objects. The two vertices forming an edge are said to be the endpoints of this edge, and the edge is said to be incident to the vertices. A vertex ''w'' is said to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |