|
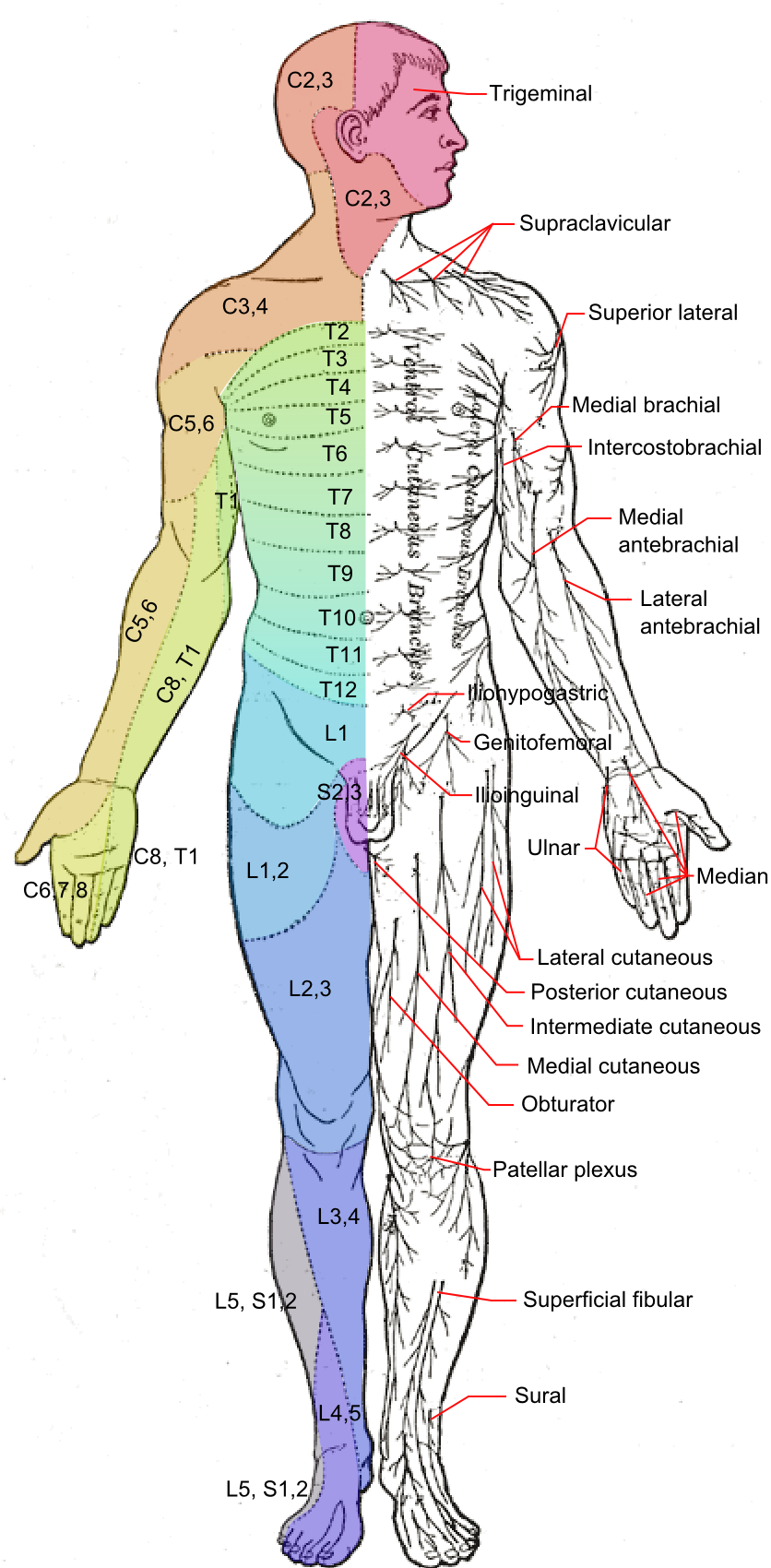
Cutaneous Nerves
A cutaneous nerve is a nerve that provides nerve supply to the skin. Human anatomy In human anatomy, cutaneous nerves are primarily responsible for providing sensory innervation to the skin. In addition to sympathetic and autonomic afferent (sensory) fibers, most cutaneous nerves also contain sympathetic efferent (visceromotor) fibers, which innervate cutaneous blood vessels, sweat glands, and the arrector pilli muscles of hair follicles. These structures are important to the sympathetic nervous response. There are many cutaneous nerves in the human body, only some of which are named. Some of the larger cutaneous nerves are as follows: Upper body * In the arm (proper) ** Superior lateral cutaneous nerve of arm (Superior LCNOA) ** Inferior lateral cutaneous nerve of arm (Inferior LCNOA) ** Posterior cutaneous nerve of arm (PCNOA) ** Medial cutaneous nerve of arm (MCNOA) * In the forearm ** Lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm (LCNOF) ** Posterior cutaneous nerve of forearm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system. A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses called action potentials that are transmitted along each of the axons to peripheral organs or, in the case of sensory nerves, from the periphery back to the central nervous system. Each axon, within the nerve, is an extension of an individual neuron, along with other supportive cells such as some Schwann cells that coat the axons in myelin. Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the endoneurium. The axons are bundled together into groups called fascicles, and each fascicle is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the perineurium. Finally, the entire nerve is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the epineurium. Nerve cells (often called neurons) are f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Cutaneous Nerve Of Thigh
The lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh (also called the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve) is a cutaneous nerve of the thigh. It originates from the dorsal divisions of the second and third lumbar nerves from the lumbar plexus. It passes under the inguinal ligament to reach the thigh. It supplies sensation to the skin on the lateral part of the thigh by an anterior branch and a posterior branch. The lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh can be investigated using ultrasound. Local anaesthetic can be injected around the nerve for skin grafts and surgery around the outer thigh. Nerve compression (usually around the inguinal ligament) can cause meralgia paraesthetica. Structure The lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh is a nerve of the lumbar plexus. It arises from the dorsal divisions of the second and third lumbar nerves (L2-L3). It passes through psoas major muscle, and emerges from its lateral border. It crosses the iliacus muscle obliquely, toward the anterior superior iliac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Auricular Nerve
The great auricular nerve is a cutaneous nerve of the head. It originates from the cervical plexus, with branches of spinal nerves C2 and C3. It provides sensory nerve supply to the skin over the parotid gland and the mastoid process of the temporal bone, and surfaces of the outer ear. Pain resulting from parotitis is caused by an impingement on the great auricular nerve. Structure The great auricular nerve is the largest of the ascending branches of the cervical plexus. It arises from the second and third cervical nerves. It winds around the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, and, after perforating the deep fascia, ascends upon that muscle beneath the platysma muscle to the parotid gland. Here, it divides into an anterior and a posterior branch. Branches * The anterior branch (ramus anterior; facial branch) is distributed to the skin of the face over the parotid gland. It communicates with the facial nerve inside the parotid gland. * The posterior branch ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraclavicular Nerves
The supraclavicular nerves (descending branches) arise from the third and fourth cervical nerves. They emerge beneath the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoideus (sternocleidomastoid muscle), and descend in the posterior triangle of the neck beneath the platysma muscle and the deep cervical fascia. Together, they innervate skin over the shoulder. The supraclavicular nerve can be blocked during shoulder surgery. Branches The supraclavicular nerves arise from C3 and C4 spinal nerve roots. Near the clavicle, the supraclavicular nerves perforate the fascia and the platysma muscle to become cutaneous. They are arranged, according to their position, into three groups—anterior, middle, and posterior. Medial supraclavicular nerve The medial supraclavicular nerves or ''anterior supraclavicular nerves'' (nn. supraclaviculares anteriores; suprasternal nerves) cross obliquely over the external jugular vein and the clavicular and sternal heads of the sternocleidomastoideus, and supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auriculotemporal Nerve
The auriculotemporal nerve is a branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3) that runs with the superficial temporal artery and vein, and provides sensory innervation to various regions on the side of the head. Structure Origin The auriculotemporal nerve arises from the mandibular nerve (CN V3). The mandibular nerve is a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V), and the mandibular nerve exits the skull through the foramen ovale.Gray's Anatomy for Students, 2nd edition (2010), Drake Vogel and Mitchell, Elseview These roots encircle the middle meningeal artery (a branch of the mandibular part of the maxillary artery, which is in turn a terminal branch of the external carotid artery). The roots encompass the middle meningeal artery then converge to form a single nerve. Course The auriculotemporal nerve passes between the neck of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament. It gives off parotid branches and then turns superiorly, posterior to its head and moving anteriorly, giv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buccal Nerve
The buccal nerve (long buccal nerve) is a nerve in the face. It is a branch of the mandibular nerve (which is itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve) and transmits sensory information from skin over the buccal membrane (in general, the cheek) and from the second and third molar teeth. Not to be confused with the buccal branch of the facial nerve which transmits motor information to the buccinator muscle. Structure The buccal nerve courses between the two heads of the lateral pterygoid muscle, underneath the tendon of the temporalis muscle. It then runs under the masseter muscle, anterior to the ramus of the mandible. It connects with the buccal branches of the facial nerve on the surface of the buccinator muscle. It gives off many significant branches. Relations The facial nerve (CN VII) also has buccal branches, which carry motor innervation to the buccinator muscle, a muscle of facial expression. This follows from the trigeminal (V3) supplying all muscles of mastication and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mental Nerve
The mental nerve is a sensory nerve of the face. It is a branch of the posterior trunk of the inferior alveolar nerve, itself a branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3), itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It provides sensation to the front of the chin and the lower lip, as well as the gums of the anterior mandibular (lower) teeth. It can be blocked with local anaesthesia for procedures on the chin, lower lip, and mucous membrane of the inner cheek. Problems with the nerve cause chin numbness. Structure The mental nerve is a branch of the posterior trunk of the inferior alveolar nerve. This is a branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3), itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It emerges from the mental foramen in the mandible. It divides into three branches beneath the depressor anguli oris muscle. One branch descends to the skin of the chin. Two branches ascend to the skin and mucous membrane of the lower lip. These branches communicate freely with the facial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infraorbital Nerve
The infraorbital nerve is a branch of the maxillary nerve, itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It travels through the orbit and enters the infraorbital canal to exit onto the face through the infraorbital foramen. It provides sensory innervation to the skin and mucous membranes around the middle of the face. Structure The infraorbital nerve is a branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2), itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It travels with the infraorbital artery and vein. It branches from the maxillary nerve in the pterygopalatine fossa and travels through the inferior orbital fissure to enter the orbit. It runs anteriorly along the floor of the orbit in the infraorbital groove to the infraorbital canal of the maxilla. Within the infraorbital canal it has three branches, the posterior superior alveolar nerve, middle superior alveolar nerve and anterior superior alveolar nerve. After traversing the canal it emerges onto the anterior surface of the maxilla thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraorbital Nerve
The supraorbital nerve is one of two branches of the frontal nerve, itself a branch of the ophthalmic nerve. The other branch of the frontal nerve is the supratrochlear nerve. Structure The supraorbital nerve branches from the frontal nerve midway between the base and apex of the orbit. It travels anteriorly above the levator palpebrae superioris and exits the orbit through the supraorbital foramen (or notch) in the superior margin orbit. It exits the orbit lateral to the supratrochlear nerve. It then ascends onto the forehead beneath the corrugator supercilii and frontalis muscles and divides into a medial branch and lateral branch. Function The supraorbital nerve provides sensory innervation to the skin of the lateral forehead and upper eyelid, as well as the conjunctiva of the upper eyelid and mucosa of the frontal sinus The frontal sinuses are one of the four pairs of paranasal sinuses that are situated behind the brow ridges. Sinuses are mucosa-lined airspaces within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsal Cutaneous Branches
The torso or trunk is an anatomical term for the central part, or the core, of the body of many animals (including humans), from which the head, neck, limbs, tail and other appendages extend. The tetrapod torso — including that of a human — is usually divided into the ''thoracic'' segment (also known as the upper torso, where the forelimbs extend), the ''abdominal'' segment (also known as the "mid-section" or "midriff"), and the ''pelvic'' and '' perineal'' segments (sometimes known together with the abdomen as the lower torso, where the hindlimbs extend). Anatomy Major organs In humans, most critical organs, with the notable exception of the brain, are housed within the torso. In the upper chest, the heart and lungs are protected by the rib cage, and the abdomen contains most of the organs responsible for digestion: the stomach, which breaks down partially digested food via gastric acid; the liver, which respectively produces bile necessary for digestion; the large and smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Cutaneous Branches Of Torso
The intercostal nerves are part of the somatic nervous system, and arise from the anterior rami of the thoracic spinal nerves from T1 to T11. The intercostal nerves are distributed chiefly to the thoracic pleura and abdominal peritoneum, and differ from the anterior rami of the other spinal nerves in that each pursues an independent course without plexus formation. The first two nerves supply fibers to the upper limb and thorax; the next four distribute to the walls of the thorax; the lower five supply the walls of the thorax and abdomen. The 7th intercostal nerve end at the xyphoid process of the sternum. The 10th intercostal nerve terminates at the navel. The 12th ( subcostal) thoracic is distributed to the walls of the abdomen and groin. Each of these fibers contains around 1300 axons. Unlike the nerves from the autonomic nervous system that innervate the visceral pleura of the thoracic cavity, the intercostal nerves arise from the somatic nervous system. This enables them to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventral Cutaneous Branches
The torso or trunk is an anatomical term for the central part, or the core, of the body of many animals (including humans), from which the head, neck, limbs, tail and other appendages extend. The tetrapod torso — including that of a human — is usually divided into the ''thoracic'' segment (also known as the upper torso, where the forelimbs extend), the ''abdominal'' segment (also known as the "mid-section" or "midriff"), and the ''pelvic'' and '' perineal'' segments (sometimes known together with the abdomen as the lower torso, where the hindlimbs extend). Anatomy Major organs In humans, most critical organs, with the notable exception of the brain, are housed within the torso. In the upper chest, the heart and lungs are protected by the rib cage, and the abdomen contains most of the organs responsible for digestion: the stomach, which breaks down partially digested food via gastric acid; the liver, which respectively produces bile necessary for digestion; the large and smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |