|
Cutaneous B-cell Lymphoma
Cutaneous B-cell lymphomas constitute a group of diseases that occur less commonly than cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, and are characterized histologically by B-cells that appear similar to those normally found in germinal centers of lymph nodes. Conditions included in this group are: :* Primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type :* Primary cutaneous follicular lymphoma :* Primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma :* Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma :* Plasmacytoma :* Plasmacytosis See also * Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma * List of cutaneous conditions References External links Lymphoid-related cutaneous conditions Lymphoma {{Cutaneous-condition-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) is a class of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which is a type of cancer of the immune system. Unlike most non-Hodgkin lymphomas (which are generally B-cell-related), CTCL is caused by a mutation of T cells. The cancerous T cells in the body initially migrate to the skin, causing various lesions to appear. These lesions change shape as the disease progresses, typically beginning as what appears to be a rash which can be very itchy and eventually forming plaques and tumors before spreading to other parts of the body. Signs and symptoms The presentation depends if it is mycosis fungoides or Sézary syndrome, the most common, though not the only types. Among the symptoms for the aforementioned types are: enlarged lymph nodes, an enlarged liver and spleen, and non-specific dermatitis. Cause The cause of CTCL is unknown. Diagnosis A point-based algorithm for the diagnosis for early forms of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma was proposed by the International Socie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
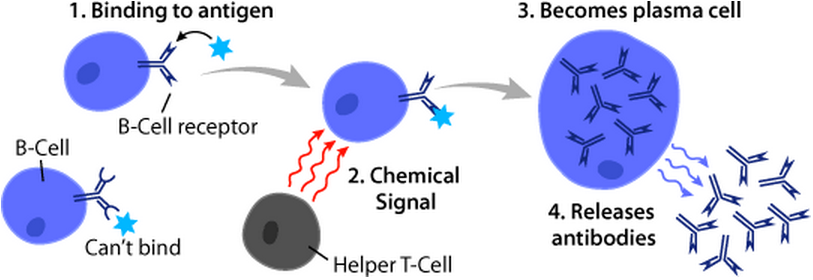
B-cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. Additionally, B cells present antigens (they are also classified as professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs)) and secrete cytokines. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the 'B' stands for bursa and not bone marrow as commonly believed. B cells, unlike the other two classes of lymphocytes, T cells a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germinal Center
Germinal centers or germinal centres (GCs) are transiently formed structures within B cell zone (follicles) in secondary lymphoid organs – lymph nodes, ileal Peyer's patches, and the spleen – where mature B cells are activated, proliferate, differentiate, and mutate their antibody genes (through somatic hypermutation aimed at achieving higher affinity) during a normal immune response; most of the germinal center B cells (BGC) are removed by tingible body macrophages. The B cells develop dynamically after the activation of follicular B cells by T-dependent antigen. As they undergo rapid and mutative cellular division, B cells of the germinal center's dark zone are known as centroblasts. Once these B cells have stopped proliferating and moved to the light zone, they are known as centrocytes, and are subjected to selection by follicular helper T (TFH) cells in the presence of follicular dendritic cells (FDCs). Germinal centers are an important part of the B cell humoral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymph Node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that include B and T cells. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system, acting as filters for foreign particles including cancer cells, but have no detoxification function. In the lymphatic system a lymph node is a secondary lymphoid organ. A lymph node is enclosed in a fibrous capsule and is made up of an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Lymph nodes become inflamed or enlarged in various diseases, which may range from trivial throat infections to life-threatening cancers. The condition of lymph nodes is very important in cancer staging, which decides the treatment to be used and determines the prognosis. Lymphadenopathy refers to glands that are enlarged or swollen. When inflamed or enlarged, lymph nodes can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Cutaneous Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma, Leg Type
Primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type (PCDLBCL-LT) (also termed PCDLBCL, leg type or primary cutaneous DLBCL, leg type) is a cutaneous lymphoma skin disease that occurs mostly in elderly females. In this disease, B cells (a type of lymphocyte) become malignant, accumulate in the dermis (i.e. the layer under the epidermis) and subcutaneous tissue below the dermis to form red and violaceous skin nodules and tumors. These lesions typically occur on the lower extremities but in uncommon cases may develop on the skin at virtually any other site. In ~10% of cases, the disease presents with one or more skin lesions none of which are on the lower extremities; the disease in these cases is sometimes regarded as a variant of PCDLBL, LT termed primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, other (PCDLBC-O). PCDLBCL, LT is a subtype of the diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCL) and has been thought of as a cutaneous counterpart to them. Like most variants and subtypes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Cutaneous Follicular Lymphoma
Primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma is a type of lymphoma. It was recognized as a distinct disease entity in the 2008 WHO classification. PCFCL had been previously conceived as a variant of follicular lymphoma (FL). Cause Unlike FL, PCFCL is not typically associated with t(14;18) translocation although presence of that translocation does not exclude PCFCL. It is usually not associated with overexpressed Bcl-2. PCFCL represents about 55% to 60% of primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas (PCBCL); primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell cell lymphoma, leg type are the other primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas. The cause of PCFCL is unknown. Treatment Surgical removal and/or radiotherapy is given for localized disease. Radiation using multiple radiation fields is given if the disease has wider extent with grouped lesions. For the less common situation of more extensive disease (still confined to skin), rituximab without chemotherapy is used. Intralesion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Cutaneous Marginal Zone Lymphoma
Primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphomas represent a heterogeneous group of diseases characterized by solitary or multiple dermal or subcutaneous nodules. Lymphomas included in this group are: :* Primary cutaneous immunocytoma :* Marginal zone B-cell lymphoma :* Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma See also * Cutaneous B-cell lymphoma * Skin lesion A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this s ... References Lymphoid-related cutaneous conditions Lymphoma {{Cutaneous-condition-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravascular Large B-cell Lymphoma
Intravascular lymphomas (IVL) are rare cancers in which malignant lymphocytes proliferate and accumulate within blood vessels. Almost all other tyes of lymphoma involve the proliferation and accumulation of malignant lymphocytes in lymph nodes, other parts of the lymphatic system (e.g. the spleen), and various non-lymphatic organs (e.g. bone marrow and liver) but not in blood vessels. IVL fall into three different forms based on the type of lymphocyte causing the disease. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma (IVBCL), which constitutes ~90% of all IVL, is a lymphoma of malignant B-cell lymphocytes as classified by the World Health Organization, 2016. The remaining IVL types, which have not yet been formally classified by the World Health Organization, are defined based mainly on case reports; these IVL are 1) intravascular NK-cell lymphoma (IVNKL) in which the malignant cells are a type of T cell lymphocyte termed natural killer cells (NK-cells) and 2) intravascular T-cell lymphoma ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmacytoma
Plasmacytoma is a plasma cell dyscrasia in which a plasma cell tumour grows within soft tissue or within the axial skeleton. The International Myeloma Working Group lists three types: solitary plasmacytoma of bone (SPB); extramedullary plasmacytoma (EP), and multiple plasmacytomas that are either primary or recurrent. The most common of these is SPB, accounting for 3–5% of all plasma cell malignancies. SPBs occur as lytic lesions within the axial skeleton and extramedullary plasmacytomas most often occur in the upper respiratory tract (85%), but can occur in any soft tissue. Approximately half of all cases produce paraproteinemia. SPBs and extramedullary plasmacytomas are mostly treated with radiotherapy, but surgery is used in some cases of extramedullary plasmacytoma. The skeletal forms frequently progress to multiple myeloma over the course of 2–4 years. Due to their cellular similarity, plasmacytomas have to be differentiated from multiple myeloma. For SPB and extramedu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmacytosis
Plasmacytosis is a condition in which there is an unusually large proportion of plasma cells in tissues, exudates, or blood. Plasmacytosis may be divided into two types—cutaneous and systemic—both of which have identical skin findings. Patients with plasmacytosis have been predominantly found to have lung infections (pneumonia, tuberculosis, abscess) whereas multiple myeloma is rarely found. See also * Cutaneous B-cell lymphoma * Multiple myeloma Multiple myeloma (MM), also known as plasma cell myeloma and simply myeloma, is a cancer of plasma cells, a type of white blood cell that normally produces antibodies. Often, no symptoms are noticed initially. As it progresses, bone pain, an ... * Plasmacytoma * Skin lesion References External links Lymphocytic disorders {{Dermatology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) is a class of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which is a type of cancer of the immune system. Unlike most non-Hodgkin lymphomas (which are generally B-cell-related), CTCL is caused by a mutation of T cells. The cancerous T cells in the body initially migrate to the skin, causing various lesions to appear. These lesions change shape as the disease progresses, typically beginning as what appears to be a rash which can be very itchy and eventually forming plaques and tumors before spreading to other parts of the body. Signs and symptoms The presentation depends if it is mycosis fungoides or Sézary syndrome, the most common, though not the only types. Among the symptoms for the aforementioned types are: enlarged lymph nodes, an enlarged liver and spleen, and non-specific dermatitis. Cause The cause of CTCL is unknown. Diagnosis A point-based algorithm for the diagnosis for early forms of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma was proposed by the International Socie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cutaneous Conditions
Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the body and composed of skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment. The skin weighs an average of four kilograms, covers an area of two square metres, and is made of three distinct layers: the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. The two main types of human skin are: glabrous skin, the hairless skin on the palms and soles (also referred to as the "palmoplantar" surfaces), and hair-bearing skin.Burns, Tony; ''et al''. (2006) ''Rook's Textbook of Dermatology CD-ROM''. Wiley-Blackwell. . Within the latter type, the hairs occur in structures called pilosebaceous units, each with hair follicle, sebaceous gland, and associated arrector pili muscle. In the embryo, the epidermis, hair, and glands form from the ectoderm, which is chemically influenced by the underlying mesoderm th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

