|
Cutan (soil)
Cutans are the modification of the soil texture, or soil structure, at natural surfaces (particle, pore, or ped) in soil materials due to illuviation. Cutans are oriented deposits which can be composed of any of the component substances of the soil material. Cutans are common features in soil and represent focuses of chemical and biological reactions. Cutans may include clay skins or coatings of silica, sesquioxide, manganese, ferromanganese, soil organic matter or carbonate.{{cite web , url = http://home.entouch.net/dmd/paleosol.htm , title = Paleosols , author = Jonathan Clark , accessdate = 2006-10-17 , url-status = dead , archiveurl = https://web.archive.org/web/20061026205314/http://home.entouch.net/dmd/paleosol.htm , archivedate = 2006-10-26 Clay skins are also called argillans, and soil horizons with sufficient clay illuviation are termed argillic horizons. Significance Cutans provide physical evidence, observable in the field, as to the degree and nature of pedoge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Texture
Soil texture is a classification instrument used both in the field and laboratory to determine soil classes based on their physical texture. Soil texture can be determined using qualitative methods such as texture by feel, and quantitative methods such as the hydrometer method based on Stokes' law. Soil texture has agricultural applications such as determining crop suitability and to predict the response of the soil to environmental and management conditions such as drought or calcium (lime) requirements. Soil texture focuses on the particles that are less than two millimeters in diameter which include sand, silt, and clay. The USDA soil taxonomy and WRB soil classification systems use 12 textural classes whereas the UK-ADAS system uses 11.''Soil Science Division Staff. 2017. Soil survey sand. C. Ditzler, K. Scheffe, and H.C. Monger (eds.). USDA Handbook 18. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C.'' These classifications are based on the percentages of sand, silt, and clay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid (H2CO3), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word ''carbonate'' may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate group C(=O)(O–)2. The term is also used as a verb, to describe carbonation: the process of raising the concentrations of carbonate and bicarbonate ions in water to produce carbonated water and other carbonated beverageseither by the addition of carbon dioxide gas under pressure or by dissolving carbonate or bicarbonate salts into the water. In geology and mineralogy, the term "carbonate" can refer both to carbonate minerals and carbonate rock (which is made of chiefly carbonate minerals), and both are dominated by the carbonate ion, . Carbonate minerals are extremely varied and ubiquitous in chemically precipitated sedimentary rock. The most common are calcite or calcium carbonate, CaCO3, the chief constituent of limestone (as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
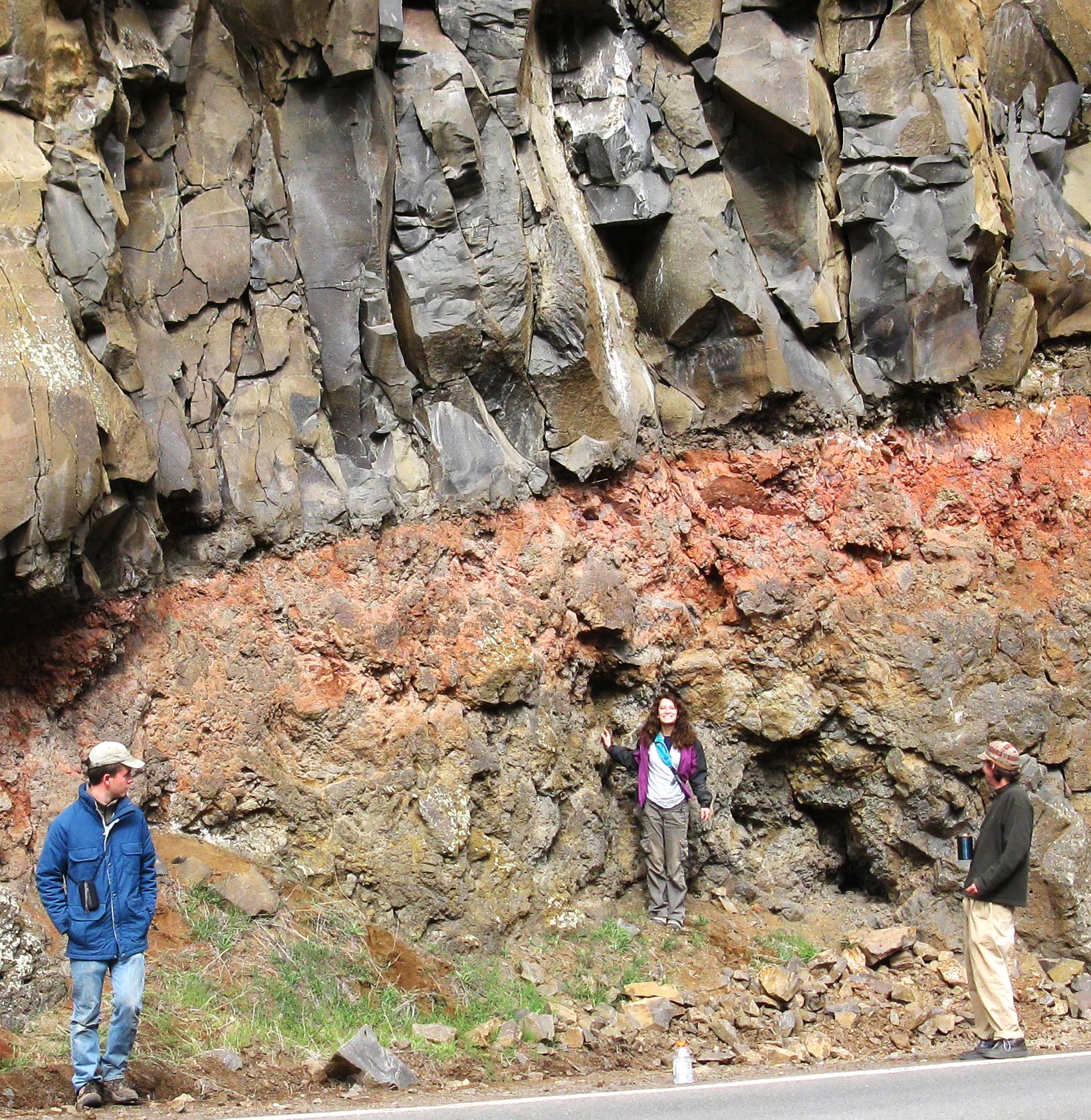
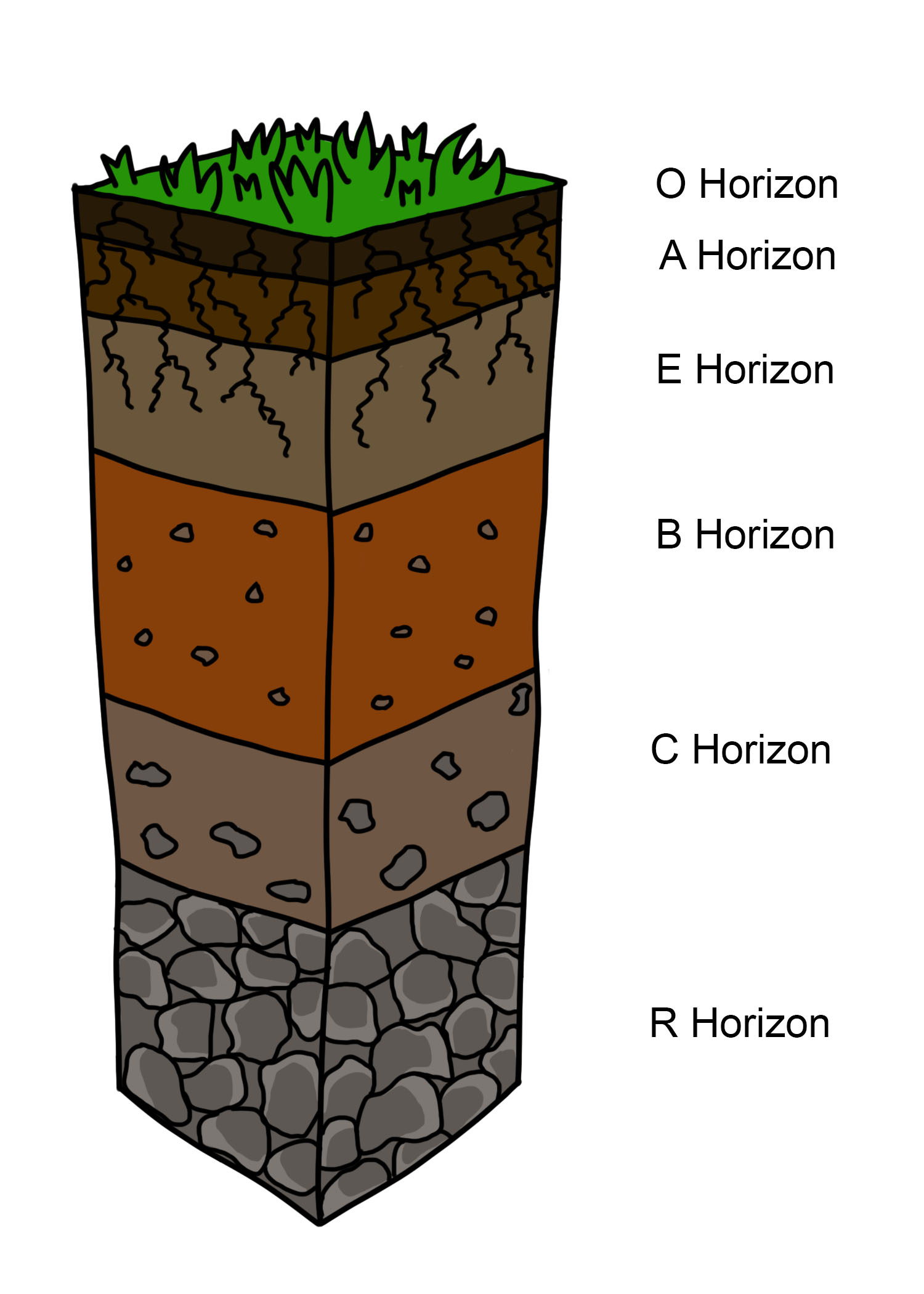
Soil Profile
A soil horizon is a layer parallel to the soil surface whose physical, chemical and biological characteristics differ from the layers above and beneath. Horizons are defined in many cases by obvious physical features, mainly colour and texture. These may be described both in absolute terms (particle size distribution for texture, for instance) and in terms relative to the surrounding material, i.e. 'coarser' or 'sandier' than the horizons above and below. The identified horizons are indicated with symbols, which are mostly used in a hierarchical way. Master horizons (main horizons) are indicated by capital letters. Suffixes, in form of lowercase letters and figures, further differentiate the master horizons. There are many different systems of horizon symbols in the world. No one system is more correct—as artificial constructs, their utility lies in their ability to accurately describe local conditions in a consistent manner. Due to the different definitions of the horizon symb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfisols
Alfisols are a soil order in USDA soil taxonomy. Alfisols form in semi-arid to humid areas, typically under a hardwood forest cover. They have a clay-enriched subsoil and relatively high native fertility. "Alf" refers to aluminium (Al) and iron (Fe). Because of their productivity and abundance, Alfisols represent one of the more important soil orders for food and fiber production. They are widely used both in agriculture and forestry, and are generally easier to keep fertile than other humid-climate soils, though those in Australia and Africa are still very deficient in nitrogen and available phosphorus. Those in monsoonal tropical regions, however, have a tendency to acidify when heavily cultivated, especially when nitrogenous fertilizers are used. In the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB), most Alfisols are classified as Luvisols or Lixisols, but some are classed as Retisols or Nitisols. Aqualfs are mainly Stagnosols or Planosols. Alfisols with a natric horizon are m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleopedology
Paleopedology (palaeopedology in the United Kingdom) is the discipline that studies soils of past geological eras, from quite recent (Quaternary) to the earliest periods of the Earth's history. Paleopedology can be seen either as a branch of soil science (pedology) or of paleontology, since the methods it uses are in many ways a well-defined combination of the two disciplines. History Paleopedology's earliest developments arose from observations in Scotland circa 1795 whereby it was found that some soils in cliffs appeared to be remains of a former exposed land surface. During the nineteenth century there were many other finds of former soils throughout Europe and North America. However, most of this was only found in the search for animal and/or plant fossils and it was not until soil science first developed that buried soils of past geological ages were considered of any value. It was only when the first relationships between soils and climate were observed in the steppes of Russ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Morphology
Soil morphology is the study of the formation and description of soil types within various soil horizons. C.F. Marbut championed reliance on soil morphology instead of on theories of pedogenesis for soil classification because theories of soil genesis are both ephemeral and dynamic. Observable attributes typically analyzed in the field include the composition, form, soil structure and organization of the soil. Color of the base soil and features such as mottling, distribution of roots and pores, consistency of the soil and evidence of mineral presence also contribute to the classification. The observations are typically performed on a soil profile in order to analyze the various soil horizons. A profile is a vertical cut, two-dimensional, in the soil and bounds one side of a pedon. A pedon is the smallest unit, containing all soil horizons. Pedons are typically 1 square meter on top and capture the lateral range of variability of the soil down to the bedrock. Soil horizons Soi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedogenesis
Soil formation, also known as pedogenesis, is the process of soil genesis as regulated by the effects of place, environment, and history. Biogeochemical processes act to both create and destroy order (anisotropy) within soils. These alterations lead to the development of layers, termed soil horizon, distinguished by differences in color, structure, texture, and chemistry. These features occur in patterns of soil type distribution, forming in response to differences in soil forming factors. Pedogenesis is studied as a branch of pedology, the study of soil in its natural environment. Other branches of pedology are the study of soil morphology, and soil classification. The study of pedogenesis is important to understanding soil distribution patterns in current ( soil geography) and past (paleopedology) geologic periods. Overview Soil develops through a series of changes. The starting point is weathering of freshly accumulated parent material. A variety of soil microbes (bacteria, ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Horizons
A soil horizon is a layer parallel to the soil surface whose physical, chemical and biological characteristics differ from the layers above and beneath. Horizons are defined in many cases by obvious physical features, mainly colour and texture. These may be described both in absolute terms (particle size distribution for texture, for instance) and in terms relative to the surrounding material, i.e. 'coarser' or 'sandier' than the horizons above and below. The identified horizons are indicated with symbols, which are mostly used in a hierarchical way. Master horizons (main horizons) are indicated by capital letters. Suffixes, in form of lowercase letters and figures, further differentiate the master horizons. There are many different systems of horizon symbols in the world. No one system is more correct—as artificial constructs, their utility lies in their ability to accurately describe local conditions in a consistent manner. Due to the different definitions of the horizon symb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Organic Matter
Soil organic matter (SOM) is the organic matter component of soil, consisting of plant and animal detritus at various stages of decomposition, cells and tissues of soil microbes, and substances that soil microbes synthesize. SOM provides numerous benefits to the physical and chemical properties of soil and its capacity to provide regulatory ecosystem services. SOM is especially critical for soil functions and quality. The benefits of SOM result from a number of complex, interactive, edaphic factors; a non-exhaustive list of these benefits to soil function includes improvement of soil structure, aggregation, water retention, soil biodiversity, absorption and retention of pollutants, buffering capacity, and the cycling and storage of plant nutrients. SOM increases soil fertility by providing cation exchange sites and being a reserve of plant nutrients, especially nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and sulfur (S), along with micronutrients, which the mineralization of SOM slowly release ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Structure
Soil structure describes the arrangement or the way of soil in the solid parts of the soil and of the pore space located between them. It is determined by how individual soil granules clump, bind together, and aggregate, resulting in the arrangement of soil pores between them. Soil has a major influence on water and air movement, biological activity, root growth and seedling emergence. There are several different types of soil structure. It is inherently a dynamic and complex system that is affected by different factors. Overview Soil structure describes the arrangement of the solid parts of the soil and of the pore spaces located between them (Marshall & Holmes, 1979). Aggregation is the result of the interaction of soil particles through rearrangement, flocculation and cementation. It is enhanced by: the precipitation of oxides, hydroxides, carbonates and silicates; the products of biological activity (such as biofilms, fungal hyphae and glycoproteins); ionic bridging between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferromanganese
Ferromanganese is a ferroalloy with high manganese content (high-carbon ferromanganese can contain as much as 80% Mn by weight). It is made by heating a mixture of the oxides MnO2 and Fe2O3, with carbon (usually as coal and coke) in either a blast furnace or an electric arc furnace-type system, called a submerged arc furnace. The oxides undergo carbothermal reduction in the furnaces, producing the ferromanganese. Ferromanganese is used as a deoxidizer for steel. A North American standard specification is ASTM A99. The ten grades covered under this specification includes; *Standard ferromanganese *Medium-carbon ferromanganese *Low-carbon ferromanganese A similar material is a pig iron with high content of manganese, is called spiegeleisen, or specular pig iron. History 350px, lang=en, Evolution of global manganese production, by processes. In 1856, Robert Forester Mushet "used manganese to improve the ability of steel produced by the Bessemer process to withstand rolling and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy uses, particularly in stainless steels. It improves strength, workability, and resistance to wear. Manganese oxide is used as an oxidising agent; as a rubber additive; and in glass making, fertilisers, and ceramics. Manganese sulfate can be used as a fungicide. Manganese is also an essential human dietary element, important in macronutrient metabolism, bone formation, and free radical defense systems. It is a critical component in dozens of proteins and enzymes. It is found mostly in the bones, but also the liver, kidneys, and brain. In the human brain, the manganese is bound to manganese metalloproteins, most notably glutamine synthetase in astrocytes. Manganese was first isolated in 1774. It is familiar in the laboratory in the form of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |