|
CubicWeb
CubicWeb is a free and open-source semantic web application framework, licensed under the LGPL. It is written in Python. It has been an open free software project since October 2008, but the project began in 2000 and was initially developed by Logilab for internal uses such as intranet, bug tracker and forge applications. As of 2012, CubicWeb is being used in large-scale semantic web and linked open data applications and international corporations. Concepts The framework is entirely driven by a data model. Once the data model is defined, one gets a functional web application and can further customize the views (by default it provides a set of default views for each type of data). A cube is a reusable component defining specific features. For example, a cubforgeallows one to create one's own forge and the forge cube reuses the cubes comment, file, email, etc. Interesting general purpose cubes include dbpedia and openlibrary. The framework has been translated to English, F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mulgara (software)
Mulgara is a triplestore and fork of the original Kowari project. It is open-source, scalable, and transaction-safe. Mulgara instances can be queried via the iTQL query language and the SPARQL query language. History Kowari was first made available for download in beta form on October 26, 2003. In April 2004, Tucana Technologies Inc demonstrated the Tucana Knowledge Server (TKS), a proprietary RDF database relying on Kowari as the basis. A steady number of releases occurred throughout 2004, includinan1.1 pre-release The development of TKS stalled due to difficulties with funding at the end of 2004, while the development of Kowari continued on. In September 2005, Tucana was bought by Northrop Grumman. In January 2006, Northrop Grumman threatened a Kowari developer with legal action if he released any new version of Kowari. As a consequence, Kowari was forked in July 2006. It was renamed to Mulgara as Northrop Grumman owned the Kowari trademark. All development on Kowari has stop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sesame (framework)
Eclipse RDF4J (formerly OpenRDF Sesame) is an open-source framework for storing, querying, and analysing RDF data. It was created by the Dutch software company Aduna as part of "On-To-Knowledge", a semantic web project that ran from 1999 to 2002. It contains implementations of an in-memory triplestore and an on-disk triplestore, along with two separate Servlet packages that can be used to manage and provide access to these triplestores, on a permanent server. The RDF4J Rio (RDF Input/Output) package contains a simple API for Java-based RDF parsers and writers. Parsers and writers for popular RDF serialisations are distributed along with RDF4J, and users can easily extend the list by putting their parsers and writers on the Java classpath when running their application. RDF4J supports two query languages: SPARQL and SeRQL. RDF4J's RDF database API differs from comparable solutions in that it offers a stackable interface through which functionality can be added, and the storage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Python (programming Language)
Python is a high-level, general-purpose programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation. Python is dynamically-typed and garbage-collected. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including structured (particularly procedural), object-oriented and functional programming. It is often described as a "batteries included" language due to its comprehensive standard library. Guido van Rossum began working on Python in the late 1980s as a successor to the ABC programming language and first released it in 1991 as Python 0.9.0. Python 2.0 was released in 2000 and introduced new features such as list comprehensions, cycle-detecting garbage collection, reference counting, and Unicode support. Python 3.0, released in 2008, was a major revision that is not completely backward-compatible with earlier versions. Python 2 was discontinued with version 2.7.18 in 2020. Python consistently ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LDAP
The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP ) is an open, vendor-neutral, industry standard application protocol for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services over an Internet Protocol (IP) network. Directory services play an important role in developing intranet and Internet applications by allowing the sharing of information about users, systems, networks, services, and applications throughout the network. As examples, directory services may provide any organized set of records, often with a hierarchical structure, such as a corporate email directory. Similarly, a telephone directory is a list of subscribers with an address and a phone number. LDAP is specified in a series of Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) Standard Track publications called Request for Comments (RFCs), using the description language ASN.1. The latest specification is Version 3, published aRFC 4511ref name="gracion Gracion.com. Retrieved on 2013-07-17. (a road map to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Python (programming Language) Web Frameworks
Python may refer to: Snakes * Pythonidae, a family of nonvenomous snakes found in Africa, Asia, and Australia ** ''Python'' (genus), a genus of Pythonidae found in Africa and Asia * Python (mythology), a mythical serpent Computing * Python (programming language), a widely used programming language * Python, a native code compiler for CMU Common Lisp * Python, the internal project name for the PERQ 3 computer workstation People * Python of Aenus (4th-century BCE), student of Plato * Python (painter), (ca. 360–320 BCE) vase painter in Poseidonia * Python of Byzantium, orator, diplomat of Philip II of Macedon * Python of Catana, poet who accompanied Alexander the Great * Python Anghelo (1954–2014) Romanian graphic artist Roller coasters * Python (Efteling), a roller coaster in the Netherlands * Python (Busch Gardens Tampa Bay), a defunct roller coaster * Python (Coney Island, Cincinnati, Ohio), a steel roller coaster Vehicles * Python (automobile maker), an Australian car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RDFLib
RDFLib is a Python library for working with RDF, a simple yet powerful language for representing information. This library contains parsers/serializers for almost all of the known RDF serializations, such as RDF/XML, Turtle, N-Triples, & JSON-LD, many of which are now supported in their updated form (e.g. Turtle 1.1). The library also contains both in-memory and persistent Graph back-ends for storing RDF information and numerous convenience functions for declaring graph namespaces, lodging SPARQL queries and so on. It is in continuous development with the most recent stable releaserdflib 6.1.1having been released on 20 December 2021. It was originally created by Daniel Krech with the first release in November, 2002. A number of other Python projects use rdflib for RDF manipulation, including: OWL-RL- A simple implementation of the OWL2 RL Profile (reasoning engine) pySHACL- a Python SHACL validator pyLDAPI- an add-on module for the Python Flask web framework used to delive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jena (framework)
Apache Jena is an open source Semantic Web framework for Java. It provides an API to extract data from and write to RDF graphs. The graphs are represented as an abstract "model". A model can be sourced with data from files, databases, URLs or a combination of these. A model can also be queried through SPARQL 1.1. Jena is similar to RDF4J (formerly OpenRDF Sesame); though, unlike RDF4J, Jena provides support for OWL (Web Ontology Language). The framework has various internal reasoners and the Pellet reasoner (an open source Java OWL-DL reasoner) can be set up to work in Jena. Jena supports serialisation of RDF graphs to: *a relational database *RDF/XML *Turtle *TriG * Notation 3 * JSON-LD Versions After Apache integration Jena was integrated as a project under the umbrella of The Apache Software Foundation in April 2012, after having been in the Apache Incubator since November 2010. Before Apache integration Jena was created by HP Labs and was on SourceForge since 2001, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
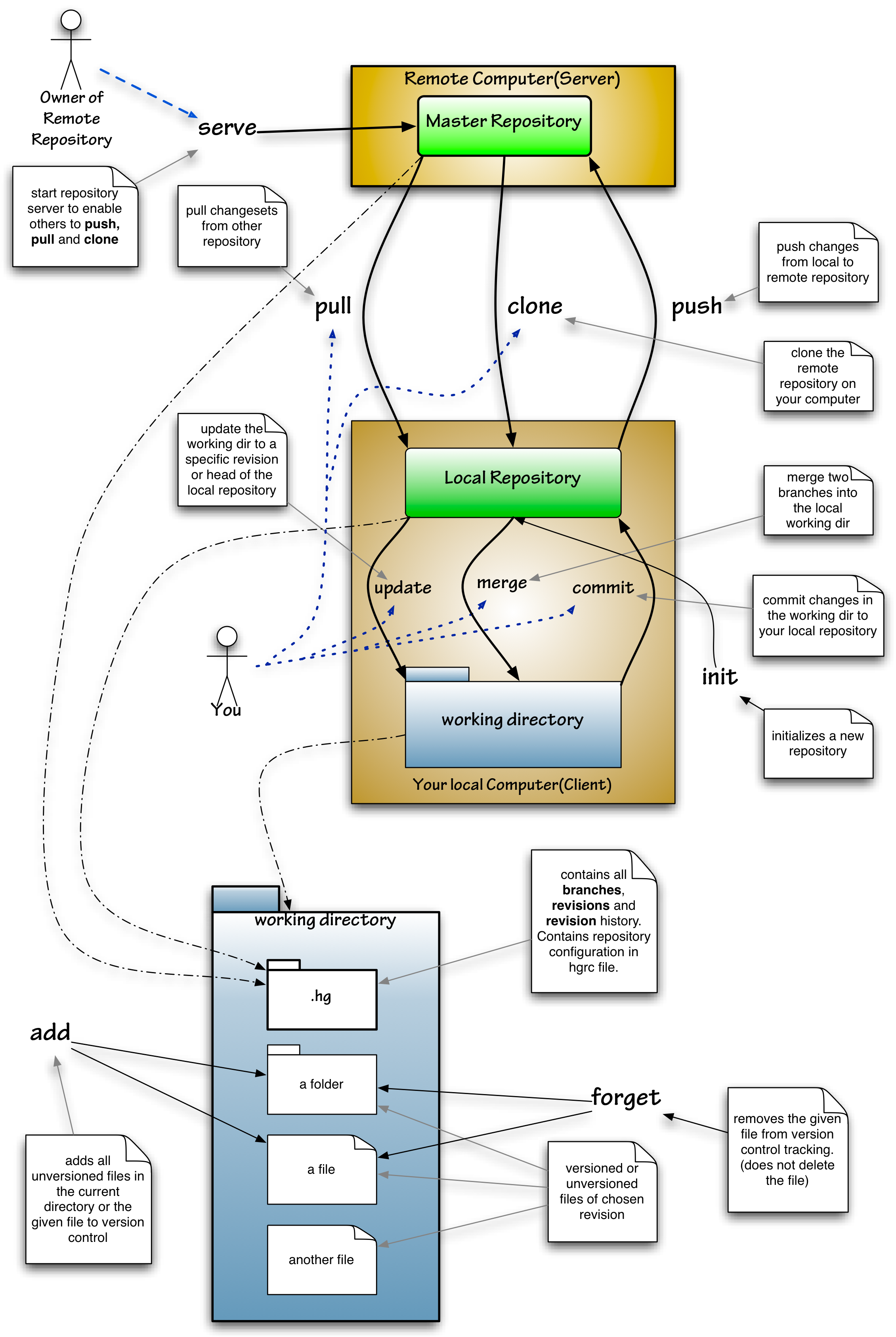
Mercurial
Mercurial is a distributed revision control tool for software developers. It is supported on Microsoft Windows and Unix-like systems, such as FreeBSD, macOS, and Linux. Mercurial's major design goals include high performance and scalability, decentralization, fully distributed collaborative development, robust handling of both plain text and binary files, and advanced branching and merging capabilities, while remaining conceptually simple. It includes an integrated web-interface. Mercurial has also taken steps to ease the transition for users of other version control systems, particularly Subversion. Mercurial is primarily a command-line driven program, but graphical user interface extensions are available, e.g. TortoiseHg, and several IDEs offer support for version control with Mercurial. All of Mercurial's operations are invoked as arguments to its driver program hg (a reference to Hg – the chemical symbol of the element mercury). Olivia Mackall originated Mercu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subversion (software)
Apache Subversion (often abbreviated SVN, after its command name ''svn'') is a software versioning and revision control system distributed as open source under the Apache License. Software developers use Subversion to maintain current and historical versions of files such as source code, web pages, and documentation. Its goal is to be a mostly compatible successor to the widely used Concurrent Versions System (CVS). The open source community has used Subversion widely: for example, in projects such as Apache Software Foundation, Free Pascal, FreeBSD, SourceForge, and from 2006 to 2019, GCC. CodePlex was previously a common host for Subversion repositories. Subversion was created by CollabNet Inc. in 2000, and is now a top-level Apache project being built and used by a global community of contributors. History CollabNet founded the Subversion project in 2000 as an effort to write an open-source version-control system which operated much like CVS but which fixed the bugs a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resource Description Framework
The Resource Description Framework (RDF) is a World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) standard originally designed as a data model for metadata. It has come to be used as a general method for description and exchange of graph data. RDF provides a variety of syntax notations and data serialization formats with Turtle (Terse RDF Triple Language) currently being the most widely used notation. RDF is a directed graph composed of triple statements. An RDF graph statement is represented by: 1) a node for the subject, 2) an arc that goes from a subject to an object for the predicate, and 3) a node for the object. Each of the three parts of the statement can be identified by a URI. An object can also be a literal value. This simple, flexible data model has a lot of expressive power to represent complex situations, relationships, and other things of interest, while also being appropriately abstract. RDF was adopted as a W3C recommendation in 1999. The RDF 1.0 specification was published in 2004, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unix-like
A Unix-like (sometimes referred to as UN*X or *nix) operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, although not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification. A Unix-like application is one that behaves like the corresponding Unix command or shell. Although there are general philosophies for Unix design, there is no technical standard defining the term, and opinions can differ about the degree to which a particular operating system or application is Unix-like. Some well-known examples of Unix-like operating systems include Linux and BSD. These systems are often used on servers, as well as on personal computers and other devices. Many popular applications, such as the Apache web server and the Bash shell, are also designed to be used on Unix-like systems. One of the key features of Unix-like systems is their ability to support multiple users and processes simultaneously. This allows users to run mult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |