|
Cryochemistry
Cryochemistry is the study of chemical interactions at temperatures below . It is derived from the Greek word ''cryos'', meaning 'cold'. It overlaps with many other sciences, including chemistry, cryobiology, condensed matter physics, and even astrochemistry. Cryochemistry has been a topic of interest since liquid nitrogen, which freezes at −210°C, became commonly available. Cryogenic-temperature chemical interactions are an important mechanism for studying the detailed pathways of chemical reactions by reducing the confusion introduced by thermal fluctuations. Cryochemistry forms the foundation for cryobiology, which uses slowed or stopped biological processes for medical and research purposes. Low temperature behaviours As a material cools, the relative motion of its component molecules/atoms decreases - its temperature decreases. Cooling can continue until all motion ceases, and its kinetic energy, or energy of motion, disappears. This condition is known as absolute zero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermochemistry
Thermochemistry is the study of the heat energy which is associated with chemical reactions and/or phase changes such as melting and boiling. A reaction may release or absorb energy, and a phase change may do the same. Thermochemistry focuses on the energy exchange between a system and its surroundings in the form of heat. Thermochemistry is useful in predicting reactant and product quantities throughout the course of a given reaction. In combination with entropy determinations, it is also used to predict whether a reaction is spontaneous or non-spontaneous, favorable or unfavorable. Endothermic process, Endothermic reactions absorb heat, while Exothermic process, exothermic reactions release heat. Thermochemistry coalesces the concepts of thermodynamics with the concept of energy in the form of chemical bonds. The subject commonly includes calculations of such quantities as heat capacity, heat of combustion, heat of formation, enthalpy, entropy, and Thermodynamic free energy, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), the latter being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible to extract energy as heat from a body at that temperature. Temperature is important in all fields of na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Helium
Liquid helium is a physical state of helium at very low temperatures at standard atmospheric pressures. Liquid helium may show superfluidity. At standard pressure, the chemical element helium exists in a liquid form only at the extremely low temperature of . Its boiling point and critical point depend on which isotope of helium is present: the common isotope helium-4 or the rare isotope helium-3. These are the only two stable isotopes of helium. See the table below for the values of these physical quantities. The density of liquid helium-4 at its boiling point and a pressure of one atmosphere (101.3 kilopascals) is about , or about one-eighth the density of liquid water. Liquefaction Helium was first liquefied on July 10, 1908, by the Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes at the University of Leiden in the Netherlands. At that time, helium-3 was unknown because the mass spectrometer had not yet been invented. In more recent decades, liquid helium has been used as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryobiology
Cryobiology is the branch of biology that studies the effects of low temperatures on living things within Earth's cryosphere or in science. The word cryobiology is derived from the Greek words κρῧος ryos "cold", βίος ios "life", and λόγος ogos "word". In practice, cryobiology is the study of biological material or systems at temperatures below normal. Materials or systems studied may include proteins, cells, tissues, organs, or whole organisms. Temperatures may range from moderately hypothermic conditions to cryogenic temperatures. Areas of study At least six major areas of cryobiology can be identified: 1) study of cold-adaptation of microorganisms, plants (cold hardiness), and animals, both invertebrates and vertebrates (including hibernation), 2) cryopreservation of cells, tissues, gametes, and embryos of animal and human origin for (medical) purposes of long-term storage by cooling to temperatures below the freezing point of water. This usually requires ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Chemistry
Physical chemistry is the study of macroscopic and microscopic phenomena in chemical systems in terms of the principles, practices, and concepts of physics such as motion, energy, force, time, thermodynamics, quantum chemistry, statistical mechanics, analytical dynamics and chemical equilibria. Physical chemistry, in contrast to chemical physics, is predominantly (but not always) a supra-molecular science, as the majority of the principles on which it was founded relate to the bulk rather than the molecular or atomic structure alone (for example, chemical equilibrium and colloids). Some of the relationships that physical chemistry strives to resolve include the effects of: # Intermolecular forces that act upon the physical properties of materials ( plasticity, tensile strength, surface tension in liquids). # Reaction kinetics on the rate of a reaction. # The identity of ions and the electrical conductivity of materials. # Surface science and electrochemistry of cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryogenics
In physics, cryogenics is the production and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures. The 13th IIR International Congress of Refrigeration (held in Washington DC in 1971) endorsed a universal definition of “cryogenics” and “cryogenic” by accepting a threshold of 120 K (or –153 °C) to distinguish these terms from the conventional refrigeration. This is a logical dividing line, since the normal boiling points of the so-called permanent gases (such as helium, hydrogen, neon, nitrogen, oxygen, and normal air) lie below 120K while the Freon refrigerants, hydrocarbons, and other common refrigerants have boiling points above 120K. The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology considers the field of cryogenics as that involving temperatures below -153 Celsius (120K; -243.4 Fahrenheit) Discovery of superconducting materials with critical temperatures significantly above the boiling point of nitrogen has provided new interest in reliable, low cost me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
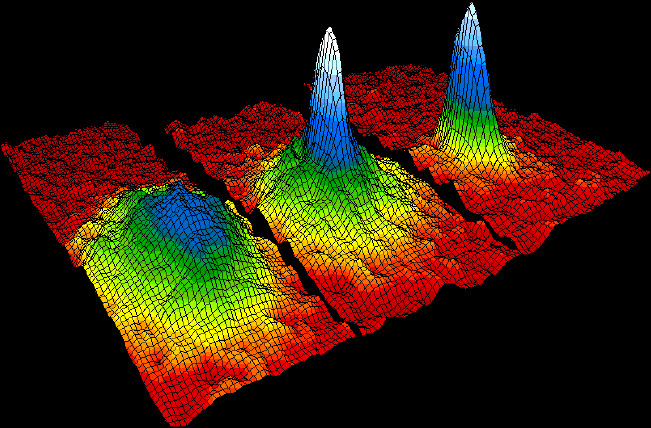
Bose–Einstein Condensate
In condensed matter physics, a Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) is a state of matter that is typically formed when a gas of bosons at very low densities is cooled to temperatures very close to absolute zero (−273.15 °C or −459.67 °F). Under such conditions, a large fraction of bosons occupy the lowest quantum state, at which point microscopic quantum mechanical phenomena, particularly wavefunction interference, become apparent macroscopically. A BEC is formed by cooling a gas of extremely low density (about 100,000 times less dense than normal air) to ultra-low temperatures. This state was first predicted, generally, in 1924–1925 by Albert Einstein following and crediting a pioneering paper by Satyendra Nath Bose on the new field now known as quantum statistics. In 1995, the Bose-Einstein condensate was created by Eric Cornell and Carl Wieman of the University of Colorado at Boulder using rubidium atoms; later that year, Wolfgang Ketterle of MIT prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent of quantum mechanics, describes many aspects of nature at an ordinary ( macroscopic) scale, but is not sufficient for describing them at small (atomic and subatomic) scales. Most theories in classical physics can be derived from quantum mechanics as an approximation valid at large (macroscopic) scale. Quantum mechanics differs from classical physics in that energy, momentum, angular momentum, and other quantities of a bound system are restricted to discrete values ( quantization); objects have characteristics of both particles and waves (wave–particle duality); and there are limit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
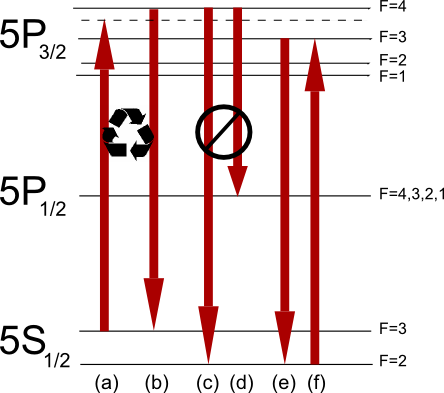
Doppler Cooling
Doppler cooling is a mechanism that can be used to trap and slow the motion of atoms to cool a substance. The term is sometimes used synonymously with laser cooling, though laser cooling includes other techniques. History Doppler cooling was simultaneously proposed by two groups in 1975, the first being David J. Wineland and Hans Georg Dehmelt and the second being Theodor W. Hänsch and Arthur Leonard Schawlow. It was first demonstrated by Wineland, Drullinger, and Walls in 1978 and shortly afterwards by Neuhauser, Hohenstatt, Toschek and Dehmelt. One conceptually simple form of Doppler cooling is referred to as optical molasses, since the dissipative optical force resembles the viscous drag on a body moving through molasses. Steven Chu, Claude Cohen-Tannoudji and William D. Phillips were awarded the 1997 Nobel Prize in Physics for their work in laser cooling and atom trapping. Brief explanation Doppler cooling involves light with frequency tuned slightly below an electro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Cooling
Laser cooling includes a number of techniques in which atoms, molecules, and small mechanical systems are cooled, often approaching temperatures near absolute zero. Laser cooling techniques rely on the fact that when an object (usually an atom) absorbs and re-emits a photon (a particle of light) its momentum changes. For an ensemble of particles, their thermodynamic temperature is proportional to the variance in their velocity. That is, more homogeneous velocities among particles corresponds to a lower temperature. Laser cooling techniques combine atomic spectroscopy with the aforementioned mechanical effect of light to compress the velocity distribution of an ensemble of particles, thereby cooling the particles. The 1997 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Claude Cohen-Tannoudji, Steven Chu, and William Daniel Phillips "for development of methods to cool and trap atoms with laser light". Methods The first example of laser cooling, and also still the most common method (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argon Fluorohydride
Argon fluorohydride (systematically named fluoridohydridoargon) or argon hydrofluoride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula HArF (also written ArHF). It is a compound of the chemical element argon. Discovery The discovery of this argon compound is credited to a group of Finnish scientists, led by Markku Räsänen. On 24 August 2000, in the journal ''Nature'', they announced their discovery of argon fluorohydride. This discovery caused the recognition that argon could form weakly bound compounds, even though it was not the first. Synthesis This chemical was synthesized by mixing argon and hydrogen fluoride on a caesium iodide surface at 8 K (−265 °C), and exposing the mixture to ultraviolet radiation. This caused the gases to combine. The infrared spectrum Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scale Of Temperature
Scale of temperature is a methodology of calibrating the physical quantity temperature in metrology. Empirical scales measure temperature in relation to convenient and stable parameters, such as the freezing and boiling point of water. Absolute temperature is based on thermodynamic principles: using the lowest possible temperature as the zero point, and selecting a convenient incremental unit. Celsius, Kelvin, and Fahrenheit are common temperature scales. Other scales used throughout history include Centigrade, Rankine, Rømer, Newton, Delisle, Réaumur, Gas Mark, Leiden and Wedgwood. Definition The zeroth law of thermodynamics describes thermal equilibrium between thermodynamic systems in form of an equivalence relation. Accordingly, all thermal systems may be divided into a quotient set, denoted as M. If the set M has the cardinality of c, then one can construct an injective function , by which every thermal system has a parameter associated with it such that when t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |