|
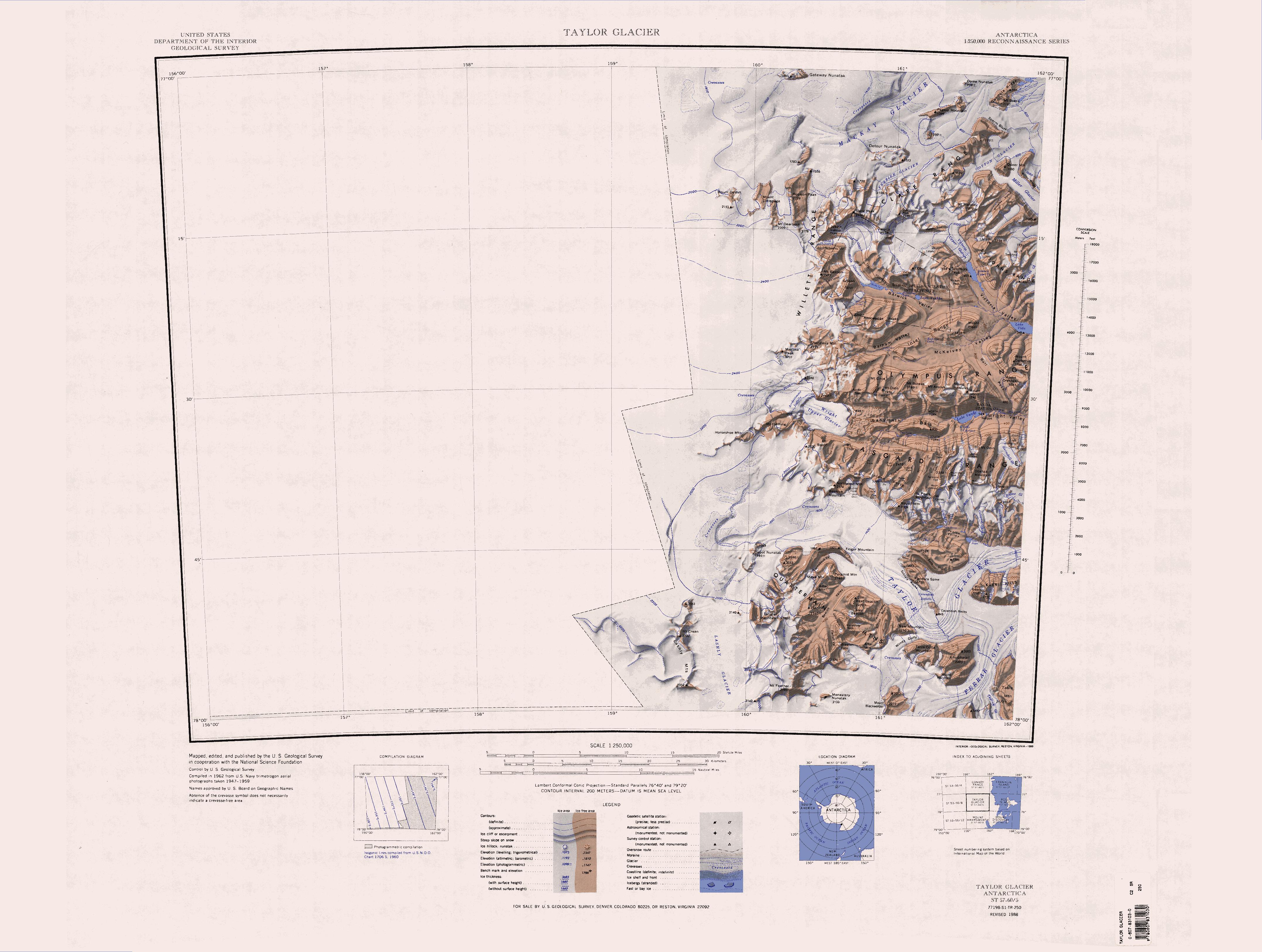
Cruzen Range
The Cruzen Range () is a mountain range that rises to in Vashka Crag and extends west to east for between Salyer Ledge and Nickell Peak in the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Victoria Land, Antarctica. The range is bounded to north, east, south and west by the Clare Range, Victoria Valley, Barwick Valley, and the Webb Glacier. Name The Cruzen Range was named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAP) in 2005 after Rear Admiral Richard H. Cruzen, commander of Task Force 68 during the U.S. Navy Antarctic Developments Project, 1946-47 (Operation Highjump). Location The Cruzen Range was formerly the southern part of the Clare Range, to the north. It is separated from the Clare Range by Webb Cirque which holds the névé at the head of the Webb Glacier to the northwest, and Victoria Upper Névé that feeds Victoria Upper Glacier to the northeast. The two are separated by a ridge leading south from Parker Mesa to The Fortress. To the south the range is bounded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Webb Cirque
Barwick Valley is an ice-free valley north of Apocalypse Peaks, extending from Webb Glacier to Victoria Valley in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (VUWAE) (1958–59) for R.E. Barwick, summer biologist with the New Zealand party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (1956–58) who worked in this area in 1957–58 and as a member of the VUWAE, 1958–59. Antarctic Specially Protected Area An area of 480 km2, comprising parts of both Barwick Valley and the adjacent Balham Valley, is protected under the Antarctic Treaty System as Antarctic Specially Protected Area An Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) is an area on the continent of Antarctica, or on nearby islands, which is protected by scientists and several different international bodies. The protected areas were established in 1961 under the Antarct ... (ASPA) No.123 because it is one of the least disturbed or contaminated of the McMu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LaBelle Valley
Barwick Valley is an ice-free valley north of Apocalypse Peaks, extending from Webb Glacier to Victoria Valley in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (VUWAE) (1958–59) for R.E. Barwick, summer biologist with the New Zealand party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (1956–58) who worked in this area in 1957–58 and as a member of the VUWAE, 1958–59. Antarctic Specially Protected Area An area of 480 km2, comprising parts of both Barwick Valley and the adjacent Balham Valley, is protected under the Antarctic Treaty System as Antarctic Specially Protected Area An Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) is an area on the continent of Antarctica, or on nearby islands, which is protected by scientists and several different international bodies. The protected areas were established in 1961 under the Antarct ... (ASPA) No.123 because it is one of the least disturbed or contaminated of the McMu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Vashka
Barwick Valley is an ice-free valley north of Apocalypse Peaks, extending from Webb Glacier to Victoria Valley in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (VUWAE) (1958–59) for R.E. Barwick, summer biologist with the New Zealand party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (1956–58) who worked in this area in 1957–58 and as a member of the VUWAE, 1958–59. Antarctic Specially Protected Area An area of 480 km2, comprising parts of both Barwick Valley and the adjacent Balham Valley, is protected under the Antarctic Treaty System as Antarctic Specially Protected Area An Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) is an area on the continent of Antarctica, or on nearby islands, which is protected by scientists and several different international bodies. The protected areas were established in 1961 under the Antarct ... (ASPA) No.123 because it is one of the least disturbed or contaminated of the McMu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria University Of Wellington Antarctic Expedition
The Antarctic Research Centre (ARC) is part of the School of Geography, Environment and Earth Sciences at Victoria University of Wellington. Its mission is to research "Antarctic climate history and processes, and their influence on the global climate system. The current director of the Antarctic Research Centre is Associate Professor Robert McKay. Directors * 1972 - 2007: Professor Peter Barrett * 2008 - 2016: Professor Tim Naish * 2017 - 2019: Professor Andrew Mackintosh * 2020 - Present: Professor Robert McKay History In December 1957, geology students Barrie McKelvey and Peter Webb along with biologist Ron Balham conducted an expedition to the then unexplored McMurdo Dry Valleys via the Royal New Zealand Navy Antarctic support ship HMNZS ''Endeavour''. This expedition formed the basic for the annual Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expeditions, which continue to the present day. Since this first expedition, over 400 staff and students have travelled to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beacon Sandstone
The Beacon Supergroup is a geological formation exposed in Antarctica and deposited from the Devonian to the Triassic (). The unit was originally described as either a formation or sandstone, and upgraded to group and supergroup as time passed. It contains a sandy member known as the Beacon Heights Orthoquartzite. Overview The base of the Beacon Supergroup is marked by an unconformity and is composed of the Devonian Taylor Group, a quartzose sandstone sequence; and the Late Carboniferous to Early Jurassic Victoria Group, consisting of glacial beds, sandstone, shale, conglomerate, and coal. The Beacon Sandstone was named by Hartley T. Ferrar during Scott's Discovery Expedition (1901–1904), using the Beacon Heights survey points as reference. '' Glossopteris'' fossils dated the sandstone to the Permian and linked the lithology to similar sequences on neighboring continents. Generally flat lying, the supergroup is up to 3.2 km thick and is fairly continuous from south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parker Mesa
Clare Range () is the range extending west-southwest from Sperm Bluff to the Willett Range on the south side of Mackay Glacier Mackay Glacier () is a large glacier in Victoria Land, descending eastward from the Antarctic polar plateau, between the Convoy Range and Clare Range, into the southern part of Granite Harbour. It was discovered by the South Magnetic Pole party o ..., in Victoria Land. It was circumnavigated in 1957 by the New Zealand Northern Survey Party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (1956–58), and named by them after Clare College, Cambridge, England. References * Mountain ranges of Victoria Land Scott Coast {{ScottCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Upper Glacier
Victoria Upper Glacier () is a glacier occupying the upper northwest end of Victoria Valley in Antarctica. It is a retreating glacier. The Victoria Valley is the northernmost of the McMurdo Dry Valleys. Melt water from the glacier feeds the Victoria River and on from there to Lake Vida Lake Vida is a hypersaline lake in Victoria Valley, the northernmost of the large McMurdo Dry Valleys, on the continent of Antarctica. It is isolated under year-round ice cover, and is considerably more saline than seawater. It came to public at .... It was named by the Victoria University Wellington Antarctic Expedition (1958–59) for their Alma Mater, which sponsored the expedition. In 2003, it was renamed from Upper Victoria Glacier to be consistent with Victoria Lower Glacier. Heaphy Spur divides the head of Victoria Upper Glacier. References Glaciers of Victoria Land McMurdo Dry Valleys {{McMurdoDryValleys-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Upper Névé
Victoria Valley is one of the larger McMurdo Dry Valleys in Antarctica. Lake Vida is the largest lake of the valley. The Victoria River drains the Victoria Upper Glacier, with Upper Victoria Lake just below it and northwest of Lake Vida, into Vida Lake on its western side. Lake Thomas Lake Thomas is a meltwater lake that is circumscribed on the northwest and northeast sides by Robertson Ridge and Clark Glacier (Antarctica), Clark Glacier, in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for ... is east of Lake Vida. See also * Dry Valleys Geology Valleys of Victoria Land McMurdo Dry Valleys {{McMurdoDryValleys-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Land
Victoria Land is a region in eastern Antarctica which fronts the western side of the Ross Sea and the Ross Ice Shelf, extending southward from about 70°30'S to 78°00'S, and westward from the Ross Sea to the edge of the Antarctic Plateau. It was discovered by Captain James Clark Ross in January 1841 and named after Queen Victoria. The rocky promontory of Minna Bluff is often regarded as the southernmost point of Victoria Land, and separates the Scott Coast to the north from the Hillary Coast of the Ross Dependency to the south. The region includes ranges of the Transantarctic Mountains and the McMurdo Dry Valleys (the highest point being Mount Abbott in the Northern Foothills), and the flatlands known as the Labyrinth. The Mount Melbourne is an active volcano in Victoria Land. Early explorers of Victoria Land include James Clark Ross and Douglas Mawson. In 1979, scientists discovered a group of 309 meteorites in Antarctica, some of which were found near the Allan Hills in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Highjump
Operation HIGHJUMP, officially titled The United States Navy Antarctic Developments Program, 1946–1947, (also called Task Force 68), was a United States Navy (USN) operation to establish the Antarctic research base Little America IV. The operation was organized by Rear Admiral Richard E. Byrd, Jr., USN (Ret), Officer in Charge, Task Force 68, and led by Rear Admiral Ethan Erik Larson, USN, Commanding Officer, Task Force 68. Operation HIGHJUMP commenced 26 August 1946 and ended in late February 1947. Task Force 68 included 4,700 men, 13 ships, and 33 aircraft. HIGHJUMP's objectives, according to the U.S. Navy report of the operation, were: # Training personnel and testing equipment in frigid conditions; # Consolidating and extending the United States' sovereignty over the largest practicable area of the Antarctic continent (publicly denied as a goal before the expedition ended); # Determining the feasibility of establishing, maintaining, and utilizing bases in the Antarctic an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_in_Antartica_1947.jpg)