|
Crowmarsh Gifford
Crowmarsh Gifford, commonly known as Crowmarsh, is a village in the civil parish of Crowmarsh in South Oxfordshire. It is beside the River Thames opposite the market town of Wallingford, the two linked by Wallingford Bridge. Crowmarsh parish also includes the hamlet of Newnham Murren, which is now merged with the village; the hamlet of Mongewell, and the village of North Stoke to the south. History After the Norman Conquest of England most of the land was granted to Walter Giffard, later Earl of Buckingham. It later came into the possession of William Marshal, 1st Earl of Pembroke and remained with his heirs until passing back to the Crown. Nearby Newnham Manor was originally granted by William the Conqueror to Miles Crispin, but by 1428 was owned by Thomas Chaucer, son of the poet Geoffrey Chaucer. After his death it was passed to his daughter Alice, wife of William de la Pole, 4th Earl of Suffolk. Other land was granted to Battle Abbey. The Church of England parish churc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crowmarsh
Crowmarsh is a fairly large, mostly rural civil parish in South Oxfordshire, England east and southeast of the town of Wallingford on the opposite bank of the River Thames and may also refer to its larger district council ward which extends to Ipsden and Nuffield. Formation and constituent settlements The civil parish was formed on 1 April 1932 by the amalgamation of four existing parishes. The four parishes retain their individual identities. Crowmarsh Gifford and Newnham Murren are contiguous villages divided by ''The Street'', the road which leads to Wallingford Bridge. In the south of the parish are the hamlet-size villages of North Stoke and Mongewell. Governance As a civil parish, Crowmarsh has three tiers of local government. The lowest tier is Crowmarsh Parish Council, which has responsibility for minor matters such as allotments, open spaces and community halls. The parish council has 12 members, elected for a four-year term. The middle level is South Oxford ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William The Conqueror
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first House of Normandy, Norman List of English monarchs#House of Normandy, king of England, reigning from 1066 until his death in 1087. A descendant of Rollo, he was Duke of Normandy from 1035 onward. By 1060, following a long struggle to establish his throne, his hold on Normandy was secure. In 1066, following the death of Edward the Confessor, William invaded England, leading an army of Normans to victory over the Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon forces of Harold Godwinson at the Battle of Hastings, and suppressed subsequent English revolts in what has become known as the Norman Conquest. The rest of his life was marked by struggles to consolidate his hold over England and his continental lands, and by difficulties with his eldest son, Robert Curthose. William was the son of the unmarried Duke Robert I of Normandy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
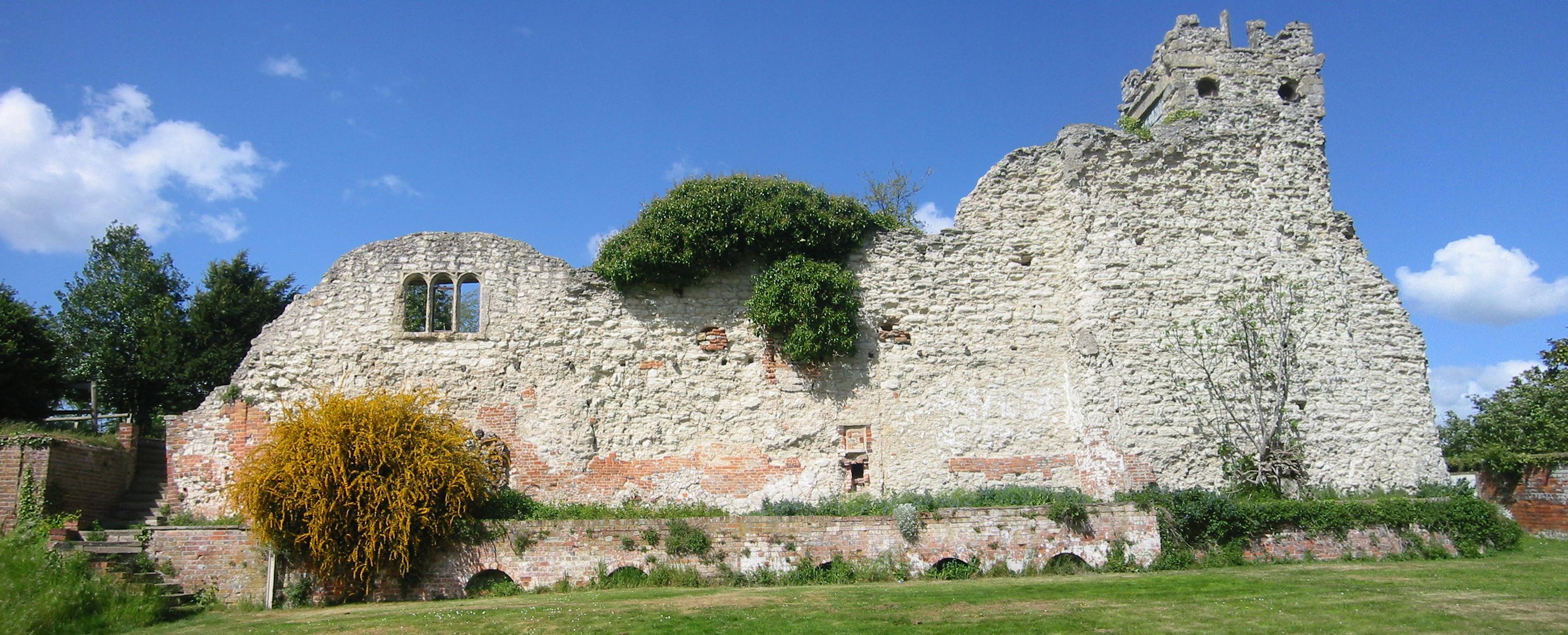
Wallingford Castle
Wallingford Castle was a major medieval castle situated in Wallingford in the English county of Oxfordshire (historically Berkshire), adjacent to the River Thames. Established in the 11th century as a motte-and-bailey design within an Anglo-Saxon ''burgh'', it grew to become what historian Nicholas Brooks has described as "one of the most powerful royal castles of the 12th and 13th centuries". Held for the Empress Matilda during the civil war years of the Anarchy, it survived multiple sieges and was never taken. Over the next two centuries it became a luxurious castle, used by royalty and their immediate family. After being abandoned as a royal residence by Henry VIII, the castle fell into decline. Refortified during the English Civil War, it was eventually slighted, i.e. deliberately destroyed, after being captured by Parliamentary forces after a long siege. The site was subsequently left relatively undeveloped, and the limited remains of the castle walls and the considerable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Of England
Stephen (1092 or 1096 – 25 October 1154), often referred to as Stephen of Blois, was King of England from 22 December 1135 to his death in 1154. He was Count of Boulogne '' jure uxoris'' from 1125 until 1147 and Duke of Normandy from 1135 until 1144. His reign was marked by the Anarchy, a civil war with his cousin and rival, the Empress Matilda, whose son, Henry II, succeeded Stephen as the first of the Angevin kings of England. Stephen was born in the County of Blois in central France as the fourth son of Stephen-Henry, Count of Blois, and Adela, daughter of William the Conqueror. His father died while Stephen was still young, and he was brought up by his mother. Placed into the court of his uncle Henry I of England, Stephen rose in prominence and was granted extensive lands. He married Matilda of Boulogne, inheriting additional estates in Kent and Boulogne that made the couple one of the wealthiest in England. Stephen narrowly escaped drowning with Henry I's son, William ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transept
A transept (with two semitransepts) is a transverse part of any building, which lies across the main body of the building. In cruciform churches, a transept is an area set crosswise to the nave in a cruciform ("cross-shaped") building within the Romanesque and Gothic Christian church architectural traditions. Each half of a transept is known as a semitransept. Description The transept of a church separates the nave from the sanctuary, apse, choir, chevet, presbytery, or chancel. The transepts cross the nave at the crossing, which belongs equally to the main nave axis and to the transept. Upon its four piers, the crossing may support a spire (e.g., Salisbury Cathedral), a central tower (e.g., Gloucester Cathedral) or a crossing dome (e.g., St Paul's Cathedral). Since the altar is usually located at the east end of a church, a transept extends to the north and south. The north and south end walls often hold decorated windows of stained glass, such as rose windows, in sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Architecture
The term Norman architecture is used to categorise styles of Romanesque architecture developed by the Normans in the various lands under their dominion or influence in the 11th and 12th centuries. In particular the term is traditionally used for English Romanesque architecture. The Normans introduced large numbers of castles and fortifications including Norman keeps, and at the same time monasteries, abbeys, churches and cathedrals, in a style characterised by the usual Romanesque rounded arches (particularly over windows and doorways) and especially massive proportions compared to other regional variations of the style. Origins These Romanesque styles originated in Normandy and became widespread in northwestern Europe, particularly in England, which contributed considerable development and where the largest number of examples survived. At about the same time, a Norman dynasty that ruled in Sicily produced a distinctive variation–incorporating Byzantine and Saracen influen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baptismal Font
A baptismal font is an article of church furniture used for baptism. Aspersion and affusion fonts The fonts of many Christian denominations are for baptisms using a non-immersive method, such as aspersion (sprinkling) or affusion (pouring). The simplest of these fonts has a pedestal (about tall) with a holder for a basin of water. The materials vary greatly consisting of carved and sculpted marble, wood, or metal. The shape can vary. Many are eight-sided as a reminder of the new creation and as a connection to the practice of circumcision, which traditionally occurs on the eighth day. Some are three-sided as a reminder of the Holy Trinity: Father, Son, and Holy Spirit. Fonts are often placed at or near the entrance to a church's nave to remind believers of their baptism as they enter the church to pray, since the rite of baptism served as their initiation into the Church. In many churches of the Middle Ages and Renaissance there was a special chapel or even a separate build ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chancel
In church architecture, the chancel is the space around the altar, including the choir and the sanctuary (sometimes called the presbytery), at the liturgical east end of a traditional Christian church building. It may terminate in an apse. Overview The chancel is generally the area used by the clergy and choir during worship, while the congregation is in the nave. Direct access may be provided by a priest's door, usually on the south side of the church. This is one definition, sometimes called the "strict" one; in practice in churches where the eastern end contains other elements such as an ambulatory and side chapels, these are also often counted as part of the chancel, especially when discussing architecture. In smaller churches, where the altar is backed by the outside east wall and there is no distinct choir, the chancel and sanctuary may be the same area. In churches with a retroquire area behind the altar, this may only be included in the broader definition of chancel. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Magdalene
Mary Magdalene (sometimes called Mary of Magdala, or simply the Magdalene or the Madeleine) was a woman who, according to the four canonical gospels, traveled with Jesus as one of his followers and was a witness to crucifixion of Jesus, his crucifixion and Resurrection of Jesus, resurrection. She is mentioned by name twelve times in the canonical gospels, more than most of the Apostles in the New Testament, apostles and more than any other woman in the gospels, other than Jesus' family. Mary's epithet ''Magdalene'' may mean that she came from the town of Magdala, a fishing town on the western shore of the Sea of Galilee in Roman Judea. The Gospel of Luke Luke 8, chapter 8 lists Mary Magdalene as one of the women who traveled with Jesus and helped support his ministry "out of their resources", indicating that she was probably wealthy. The same passage also states that seven demons Exorcism, had been driven out of her, a statement which is repeated in Mark 16. In all the four can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Of England Parish Church
A parish church in the Church of England is the church which acts as the religious centre for the people within each Church of England parish (the smallest and most basic Church of England administrative unit; since the 19th century sometimes called the ecclesiastical parish, to avoid confusion with the civil parish which many towns and villages have). Parishes in England In England, there are parish churches for both the Church of England and the Roman Catholic Church. References to a "parish church", without mention of a denomination, will, however, usually be to those of the Church of England due to its status as the Established Church. This is generally true also for Wales, although the Church in Wales is dis-established. The Church of England is made up of parishes, each one forming part of a diocese. Almost every part of England is within both a parish and a diocese (there are very few non-parochial areas and some parishes not in dioceses). These ecclesiastical parishes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
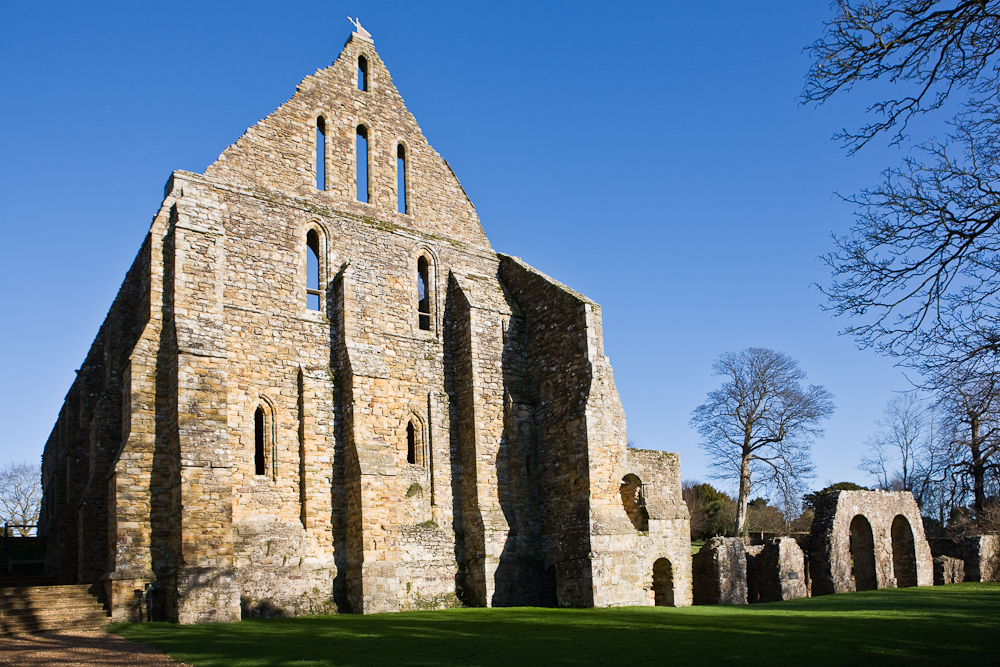
Battle Abbey
Battle Abbey is a partially ruined Benedictine abbey in Battle, East Sussex, England. The abbey was built on the site of the Battle of Hastings and dedicated to St Martin of Tours. It is a Scheduled Monument. The Grade I listed site is now operated by English Heritage as 1066 Battle of Hastings, Abbey and Battlefield, which includes the abbey buildings and ruins, a visitor centre with a film and exhibition about the battle, audio tours of the battlefield site, and the monks' gatehouse with recovered artefacts. The visitor centre includes a children's discovery room and a café, and there is an outdoor-themed playground. The triple light window depicting the life of St John and the crucifixion of Jesus is claimed to have once adorned Battle Abbey which dates from 1045, removed during the Cromwell era to protect it from destruction. The legend goes that it was hidden for many years until it was transported to Tasmania to be fitted to the eastern end of the Buckland Church.” ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William De La Pole, 1st Duke Of Suffolk
William de la Pole, 1st Duke of Suffolk, (16 October 1396 – 2 May 1450), nicknamed Jackanapes, was an English magnate, statesman, and military commander during the Hundred Years' War. He became a favourite of the weak king Henry VI of England, and consequently a leading figure in the English government where he became associated with many of the royal government's failures of the time, particularly on the war in France. Suffolk also appears prominently in Shakespeare's '' Henry VI'', parts 1 and 2. He fought in the Hundred Years' War and participated in campaigns of Henry V, and then continued to serve in France for King Henry VI. He was one of the English commanders at the failed Siege of Orléans. He favoured a diplomatic rather than military solution to the deteriorating situation in France, a stance which would later resonate well with King Henry VI. Suffolk became a dominant figure in the government, and was at the forefront of the main policies conducted during t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |