|
Crow (missile)
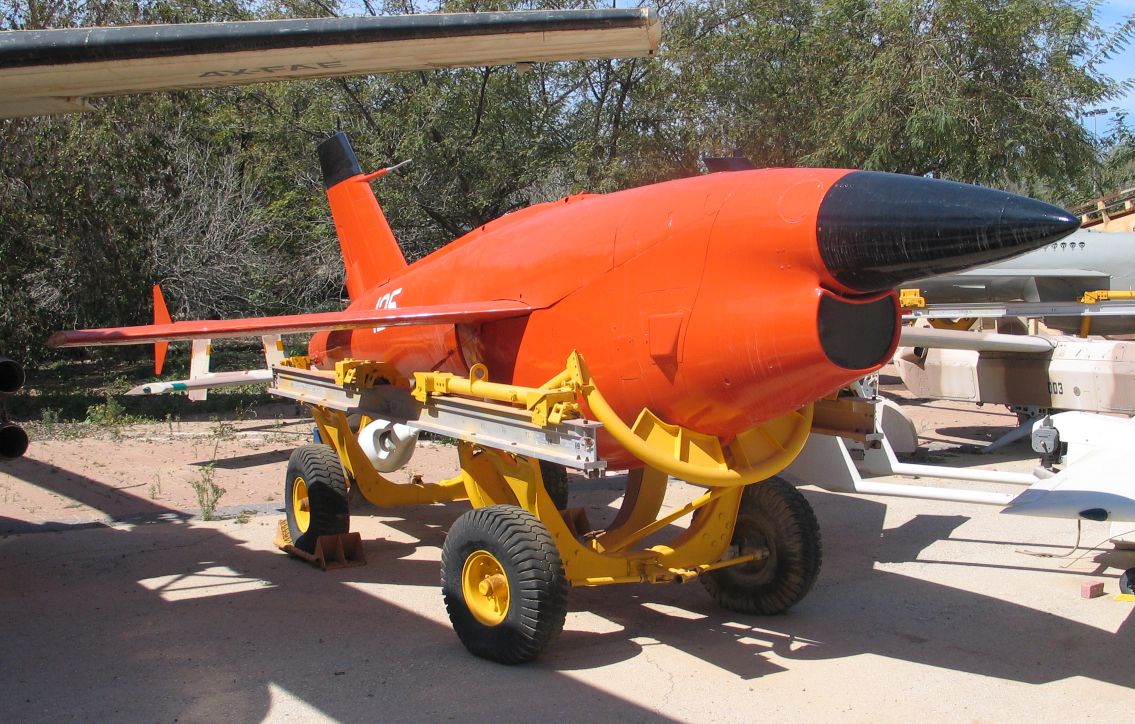
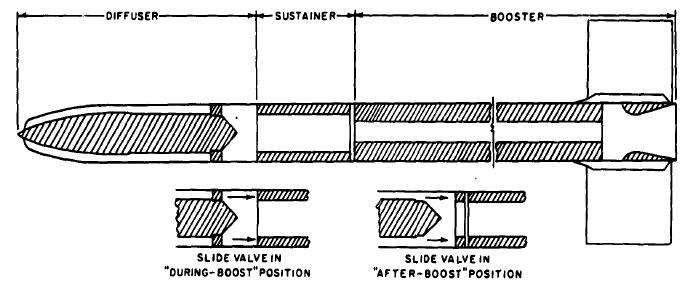
The Creative Research On Weapons or Crow program was an experimental missile project developed by the United States Navy's Naval Air Missile Test Center during the late 1950s. Intended to evaluate the solid-fueled integral rocket/ramjet (SFIRR) method of propulsion as well as solid-fueled ramjet engines, flight tests were conducted during the early 1960s with mixed success. Development and RARE Studies of the rocket-ramjet and solid-fueled ramjet concepts began at the U.S. Navy's Naval Air Missile Test Center — later the Naval Missile Center — at Point Mugu, California in 1956, with the intent of increasing the range of small air-to-air missiles through using the combined ramjet and rocket propulsion system with solid fuels only. Following extensive ground testing, the concept was considered promising enough for a flight-test vehicle to be constructed to fully evaluate the new engine.Parsch 2004 The first flight test vehicle, known as Ram Air Rocket Engine or RARE, was deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II
The McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II is an American tandem two-seat, twin-engine, all-weather, long-range supersonic jet interceptor and fighter-bomber originally developed by McDonnell Aircraft for the United States Navy.Swanborough and Bowers 1976, p. 301. Proving highly adaptable, it entered service with the Navy in 1961 before it was adopted by the United States Marine Corps and the United States Air Force, and by the mid-1960s it had become a major part of their air arms. Phantom production ran from 1958 to 1981 with a total of 5,195 aircraft built, making it the most produced American supersonic military aircraft in history, and cementing its position as an iconic combat aircraft of the Cold War."F-4 Phantoms Phabulous 40th" Boeing. Retrieved : 27 November 2012. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projectile Motion
Projectile motion is a form of motion experienced by an object or particle (a projectile) that is projected in a gravitational field, such as from Earth's surface, and moves along a curved path under the action of gravity only. In the particular case of projectile motion of Earth, most calculations assume the effects of air resistance are passive and negligible. The curved path of objects in projectile motion was shown by Galileo to be a parabola, but may also be a straight line in the special case when it is thrown directly upwards. The study of such motions is called ballistics, and such a trajectory is a ballistic trajectory. The only force of mathematical significance that is actively exerted on the object is gravity, which acts downward, thus imparting to the object a downward acceleration towards the Earth’s center of mass. Because of the object's inertia, no external force is needed to maintain the horizontal velocity component of the object's motion. Taking other force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Missiles
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a particular factor is manipulated. Experiments vary greatly in goal and scale but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results. There also exist natural experimental studies. A child may carry out basic experiments to understand how things fall to the ground, while teams of scientists may take years of systematic investigation to advance their understanding of a phenomenon. Experiments and other types of hands-on activities are very important to student learning in the science classroom. Experiments can raise test scores and help a student become more engaged and interested in the material they are learning, especially when used over time. Experiments can vary from personal and informal natural comparisons (e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold War Missiles Of The United States
Cold is the presence of low temperature, especially in the atmosphere. In common usage, cold is often a subjective perception. A lower bound to temperature is absolute zero, defined as 0.00K on the Kelvin scale, an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale. This corresponds to on the Celsius scale, on the Fahrenheit scale, and on the Rankine scale. Since temperature relates to the thermal energy held by an object or a sample of matter, which is the kinetic energy of the random motion of the particle constituents of matter, an object will have less thermal energy when it is colder and more when it is hotter. If it were possible to cool a system to absolute zero, all motion of the particles in a sample of matter would cease and they would be at complete rest in the classical sense. The object could be described as having zero thermal energy. Microscopically in the description of quantum mechanics, however, matter still has zero-point energy even at absolute zero, because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BrahMos
The BrahMos (also designated as PJ-10)India Displays Big Missiles at Defense Show . ''Aviation International News''. 19 April 2018. is a medium-range stealth supersonic cruise missile that can be launched from submarine, ships, airplanes or land, notably being the fastest supersonic cruise missile in the world at the time of introducing. It is a joint-venture between the |
AQM-127 SLAT
The AQM-127 Supersonic Low-Altitude Target (SLAT) was a target drone developed during the 1980s by Martin Marietta for use by the United States Navy. Derived from Martin Marietta's work on the cancelled ASALM missile, SLAT proved to have severe difficulties in flight testing, and the project was cancelled during 1991. Design and development Development of what became the YAQM-127 was initiated in 1983 following the cancellation of the BQM-111 Firebrand. A replacement for the MQM-8 Vandal target drone was still required, and a specification was developed for a target drone, capable of being recovered via parachute and reused, for launch from a variety of aircraft.Parsch and Caston 2006 Bids for the contract were submitted by Martin Marietta, Ling-Temco-Vought, and Teledyne Ryan, with the Martin Marietta design being judged the winner of the design competition in September 1984. Derived from the cancelled Advanced Strategic Air-Launched Missile developed by Martin Marietta for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASALM
The Advanced Strategic Air-Launched Missile (ASALM) was a medium-range strategic missile program, developed in the late 1970s for the United States Air Force. Intended for use in both the air-to-surface and anti- AWACS roles, the missile's development reached the stage of propulsion-system tests before being cancelled in 1980. Design and development Development of the Advanced Strategic Air-Launched Missile was initiated in 1976.Parsch 2003 The ASALM was intended to replace the AGM-69 SRAM in United States Air Force service, providing improved speed and range over the earlier missile, as well as improved performance against hardened targets.Gunston 1983, p.88. In addition, the requirement specified that the ASALM should be capable of operating in a secondary air-to-air mode against AWACS radar-warning aircraft. Martin Marietta and McDonnell Douglas submitted proposals for the contract, the former's design using a Marquardt propulsion system; the latter's, one developed by Unite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Fuel Ducted Ramjet
Solid Fuel Ducted Ramjet (SFDR) is a missile propulsion system currently being developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation of India. The project aims to develop critical technologies required in the propulsion systems of future Indian long range air-to-air missiles. Description The Solid Fuel Ducted Ramjet is a missile propulsion system that includes a thrust modulated ducted rocket with a reduced smoke nozzle-less missile booster. The thrust modulation in the system is achieved using a hot gas flow controller. The system utilises a solid fuelled air-breathing ramjet engine. It is an extremely long-range missile with a projected range of 350 km. As per International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS), this kind of propulsion system drastically enhances the range with higher average speed. The missiles which use such system are also able to carry larger payload due to absence of an oxidiser. Unlike solid-propellant rocket, the Ramjet takes up oxygen fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Target Drone
A target drone is an unmanned aerial vehicle, generally remote controlled, usually used in the training of anti-aircraft crews. One of the earliest drones was the British DH.82 Queen Bee, a variant of the Tiger Moth trainer aircraft operational from 1935. Its name led to the present term "drone". In their simplest form, target drones often resemble radio-controlled model aircraft. More modern drones may use countermeasures, radar, and similar systems to mimic manned aircraft. More advanced drones are made from large, older missiles which have had their warheads removed. In the United Kingdom, obsolete Royal Air Force and Royal Navy jet and propeller-powered aircraft (such as the Fairey Firefly, Gloster Meteor and de Havilland Sea Vixen used at RAE Llanbedr between the 1950s and 1990s) have also been modified into remote-controlled drones, but such modifications are costly. With a much larger budget, the U.S. military has been more likely to convert retired aircraft or olde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air-to-air Missile
The newest and the oldest member of Rafael's Python family of AAM for comparisons, Python-5 (displayed lower-front) and Shafrir-1 (upper-back) An air-to-air missile (AAM) is a missile fired from an aircraft for the purpose of destroying another aircraft. AAMs are typically powered by one or more rocket motors, usually solid fueled but sometimes liquid fueled. Ramjet engines, as used on the Meteor, are emerging as propulsion that will enable future medium-range missiles to maintain higher average speed across their engagement envelope. Air-to-air missiles are broadly put in two groups. Those designed to engage opposing aircraft at ranges of less than 16 km are known as short-range or "within visual range" missiles (SRAAMs or WVRAAMs) and are sometimes called "dogfight" missiles because they are designed to optimize their agility rather than range. Most use infrared guidance and are called heat-seeking missiles. In contrast, medium- or long-range missiles (MRAAMs or L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrionics
Astrionics is the science and technology of the development and application of electronic systems, subsystems, and components used in spacecraft. The electronic systems on-board a spacecraft are embedded systems and include attitude determination and control, communications, command and telemetry, and computer systems. Sensors refers to the electronic components on board a spacecraft. For engineers one of the most important considerations that must be made in the design process is the environment in which the spacecraft systems and components must operate and endure. The challenges of designing systems and components for the space environment include more than the fact that space is a vacuum. Attitude determination and control Overview One of the most vital roles electronics and sensors play in a mission and performance of a spacecraft is to determine and control its attitude, or how it is oriented in space. The orientation of a spacecraft varies depending on the mission. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)