|
Cross-cultural Capital
In management and organizational studies disciplines, cross-cultural capital (CCC) is the aggregate set of knowledge, skills, abilities and psychological dispositions that gives individuals competitive advantage in interacting, working, and managing in culturally diverse environments. It is considered a facet of human capital. Cross-cultural capital is conceived as a broad construct and it is composed of both dispositional (or, more trait-like) and experience-based elements (more statelike), including personality dispositions (e.g., openness to experience), values and beliefs (e.g.,pro-diversity beliefs), cognitive style (cognitive flexibility) and acquired specific skills (e.g., mastery of several languages) as well as of relevant experiences (e.g., traveling, living and working in different countries; growing up in a multicultural environment). Some scholars include cultural intelligence (CQ) as one of the state-like components of cross-cultural capital. This corresponds to Ang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychological
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between the natural and social sciences. Psychologists seek an understanding of the emergent properties of brains, linking the discipline to neuroscience. As social scientists, psychologists aim to understand the behavior of individuals and groups.Fernald LD (2008)''Psychology: Six perspectives'' (pp.12–15). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.Hockenbury & Hockenbury. Psychology. Worth Publishers, 2010. Ψ (''psi''), the first letter of the Greek word ''psyche'' from which the term psychology is derived (see below), is commonly associated with the science. A professional practitioner or researcher involved in the discipline is called a psychologist. Some psychologists can also be classified as behavioral or cognitive scientists. Some psycholog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
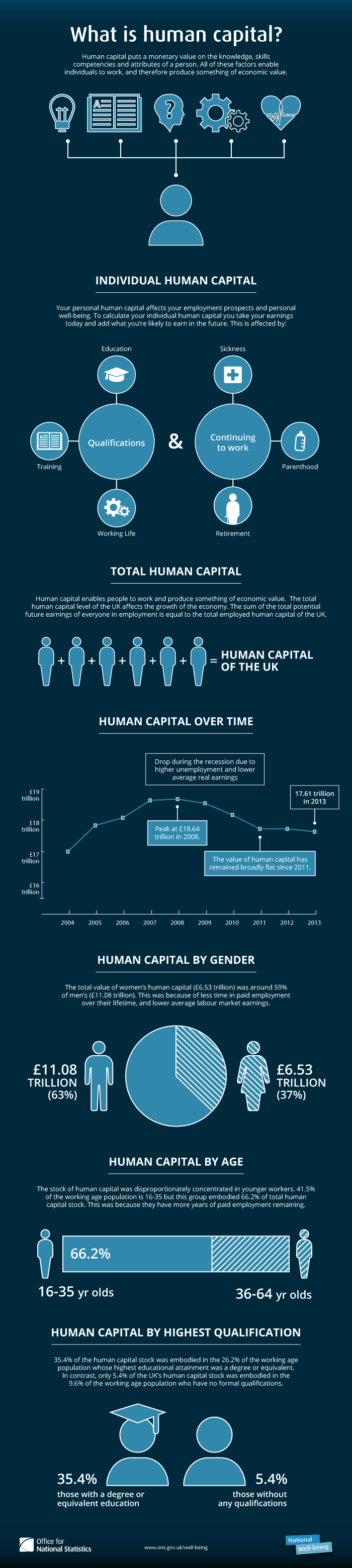
Human Capital
Human capital is a concept used by social scientists to designate personal attributes considered useful in the production process. It encompasses employee knowledge, skills, know-how, good health, and education. Human capital has a substantial impact on individual earnings. Research indicates that human capital investments have high economic returns throughout childhood and young adulthood. Companies can invest in human capital, for example, through education and training, enabling improved levels of quality and production. As a result of his conceptualization and modeling work using Human Capital as a key factor, the 2018 Nobel Prize for Economics was jointly awarded to Paul Romer, who founded the modern innovation-driven approach to understanding economic growth. In the recent literature, the new concept of task-specific human capital was coined in 2004 by Robert Gibbons, an economist at MIT, and Michael Waldman, an economist at Cornell University. The concept emphasizes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Flexibility
Cognitive flexibility is an intrinsic property of a cognitive system often associated with the mental ability to adjust its activity and content, switch between different task rules and corresponding behavioral responses, maintain multiple concepts simultaneously and shift internal attention between them. The term ''cognitive flexibility'' is traditionally used to refer to one of the executive functions. In this sense, it can be seen as neural underpinnings of adaptive and flexible behavior. Most flexibility tests were developed under this assumption several decades ago. Nowadays, cognitive flexibility can also be referred to as a set of properties of the brain that facilitate flexible yet relevant switching between functional brain states. Cognitive flexibility varies during the lifespan of an individual. In addition, certain conditions such as obsessive–compulsive disorder are associated with reduced cognitive flexibility. Since cognitive flexibility is a vital component of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van Dyne
Van Dyne is a Dutch surname. Notable people with the name include: * George Van Dyne (1933–1981), pioneer of systems ecology * Janet van Dyne, a fictional superhero appearing in Marvel Comics * Van Dyne, Wisconsin, unincorporated census-designated place in Fond du Lac County, Wisconsin * Van Dyne Civic Building, historic courthouse building located in Bradford County, Pennsylvania * Van Dyne Crotty, American uniform laundering and rental company * Vernon Van Dyne, distinguished U.S. Army Officer See also * Dyne The dyne (symbol: dyn; ) is a derived unit of force specified in the centimetre–gram–second (CGS) system of units, a predecessor of the modern SI. History The name dyne was first proposed as a CGS unit of force in 1873 by a Committee of ..., a unit of force {{Surname Dutch-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomological Network
A nomological network (or nomological net) is a representation of the concepts (construct (philosophy of science), constructs) of interest in a study, their observable manifestations, and the interrelationships between these. The term "nomological" derives from the Greek language, Greek, meaning "lawful", or in philosophy of science terms, "law-like". It was Lee J. Cronbach, Cronbach and Paul E. Meehl, Meehl's view of construct validity that in order to provide Scientific method, evidence that a Measurement, measure has construct validity, a nomological network must be developed for its measure. The necessary elements of a nomological network are: * At least two construct (philosophy of science), constructs; * One or more theory, theoretical propositions, specifying wikt:Special:Search/linkage, linkages between constructs, for example: "As age increases, memory loss increases". * 1:1 correspondence, Correspondence Operator (mathematics), rules, allowing each construct to be measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Intelligence
Cultural intelligence or cultural quotient (CQ) is the ability to relate and work effectively across cultures, bearing similarity to the term cultural agility. The term has been used in business, education, government, and academic research contexts. Originally, the term cultural intelligence and the abbreviation "CQ" was developed in research by Christopher Earley (2002) and Earley and Soon Ang (2003). During the same period, researchers David Thomas and Kerr Inkson worked on a complementary framework of CQ as well. A few years later, Ang Soon and Linn Van Dyne worked on a scale development of the CQ construct as a research-based way of measuring and predicting intercultural performance. The term is relatively recent: early definitions and studies of the concepts were given by P. Christopher Earley and Soon Ang in the book ''Cultural Intelligence: Individual Interactions Across Cultures'' (2003) and more fully developed later by David Livermore in the book, ''Leading with Cultura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communication Apprehension
Communication apprehension is a degree or measure of the anxiety triggered by the real or anticipated communication act, as defined by James C. McCroskey. The fear of judgment from the audience and self-image is what fuels the anxiety. Communication apprehension, CA, can cause a variety of involuntary responses such as "stomach butterflies" which is your body shutting the digestive system down and going into the fight-or-flight response, shaking, nausea, sweating, forgetting the information, among many others. The term communication apprehension is usually connected with stage fright; however, this response is not necessarily connected with a delivery on a stage or in front of a large audience. This anxiety can be caused by any of the four forms of communication: interpersonal, group, public, and mass communication. The most common and reliable test used to measure an individual's CA level when exposed to these forms of communication is called the Personal Report of Communication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat whereas the latter is defined as the emotional response to a real threat. It is often accompanied by nervous behavior such as pacing back and forth, somatic complaints, and rumination. Anxiety is a feeling of uneasiness and worry, usually generalized and unfocused as an overreaction to a situation that is only subjectively seen as menacing. It is often accompanied by muscular tension, restlessness, fatigue, inability to catch one's breath, tightness in the abdominal region, nausea, and problems in concentration. Anxiety is closely related to fear, which is a response to a real or perceived immediate threat (fight or flight response); anxiety involves the expectation of future threat including dread. People facing anxiety may withdraw fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |