|
Cross-check
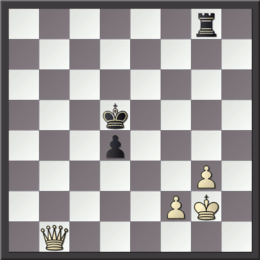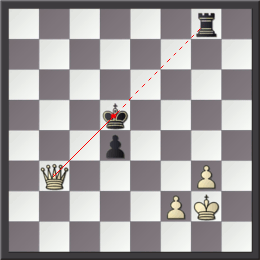
In chess, a cross-check is a tactic in which a check is played in response to a check, especially when the original check is blocked by a piece that itself either delivers check or reveals a discovered check from another piece. Sometimes the term is extended to cover cases in which the king moves out of check and reveals a discovered check from another piece (this is also known as a ''royal check''); it does not generally apply to cases where the original checking piece is captured. The cross-check is an essential tactic in winning some endgames such as those with two queens versus one, or a queen and pawn versus a queen. In these cases, the defense usually tries for a perpetual check and sometimes the stronger side can stop it only by a cross-check. Examples A cross-check occurs from time to time in games. It is an essential tactic in winning endgames such as two queens versus one queen, or queen and pawn versus queen, where it is used to stop a series of checks from the op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Check (chess)
In chess and similar games, check is a condition that occurs when a player's king is under threat of on the opponent's next turn. A king so threatened is said to be in check. A player must get out of check if possible by moving the king to a safe square, interposing a piece between the threatening piece and the king, or capturing the threatening piece. If the player cannot get out of check by any of these options, the game ends in checkmate, and the player loses. Players cannot make any move that puts their own king in check. Many chess variants feature check, such as shogi, xiangqi, and janggi. Overview A check is the result of a move that places the opposing king under an immediate threat of capture by one (or occasionally two) of the player's pieces. Making a move that checks is sometimes called "giving check". Even if a piece is pinned against the player's own king, it may still give check. For example, in the diagrammed position, White has just played Be4+, simultane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess Terminology
This glossary of chess explains commonly used terms in chess, in alphabetical order. Some of these terms have their own pages, like ''fork'' and ''pin''. For a list of unorthodox chess pieces, see Fairy chess piece; for a list of terms specific to chess problems, see Glossary of chess problems; for a list of named opening lines, see List of chess openings; for a list of chess-related games, see List of chess variants. A B , "lightning"] A #fast chess, fast form of chess with a very short time limit, usually three or five minutes per player for the entire game. With the advent of electronic chess clocks, the time remaining is often incremented by one or two seconds per move.Schiller 2003, p. 398 C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess Tactics
In chess, a tactic is a sequence of moves that each makes one or more immediate threats ─ that is, a Check (chess), check, a Glossary of chess#material, material threat, a Checkmate, checkmating sequence threat, or the threat of another tactic ─ which culminates in the opponent being unable to respond to all of the threats without conceding an immediate benefit to the opponent. Most often, the immediate benefit takes the form of a material advantage or checkmating attack; however, some tactics are used for defensive purposes and can salvage material that would otherwise be lost, or to induce stalemate in an otherwise lost position. Tactics are usually contrasted with Chess strategy, strategy, whereby the individual moves by themselves don't make indefensible threats, and the cumulative advantage of the moves takes longer to be capitalised on. In rough terms, the dichotomy can be summarised as tactics concerning short-term play and strategy concerning long-term play. Examples of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen And Pawn Versus Queen Endgame
The queen and pawn versus queen endgame is a chess endgame in which both sides have a queen and one side has a pawn, which one tries to promote. It is very complicated and difficult to play. Cross-checks are often used as a device to win the game by forcing the exchange of queens. It is almost always a draw if the defending king is in front of the pawn. Karsten Müller and Frank Lamprecht say that this endgame occurs quite frequently but Mark Dvoretsky says that it occurs quite seldom. This is the second most common "piece and pawn versus piece" endgame, next to the rook and pawn versus rook endgame. History Before about 1940 all that was known about this endgame was based on some superficial analysis of a few positions from the time of Philidor (1726–95). Analysts gradually started to analyze the endgame. The endgame occurred in a 1944 game between Botvinnik and Ravinsky (below) and much analysis followed. Paul Keres published a large amount of analysis in 1947–49. This a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Chess Terms
This glossary of chess explains commonly used terms in chess, in alphabetical order. Some of these terms have their own pages, like ''fork'' and ''pin''. For a list of unorthodox chess pieces, see Fairy chess piece; for a list of terms specific to chess problems, see Glossary of chess problems; for a list of named opening lines, see List of chess openings; for a list of chess-related games, see List of chess variants. A B , "lightning"] A #fast chess, fast form of chess with a very short time limit, usually three or five minutes per player for the entire game. With the advent of electronic chess clocks, the time remaining is often incremented by one or two seconds per move.Schiller 2003, p. 398 C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess Tactic
In chess, a tactic is a sequence of moves that each makes one or more immediate threats ─ that is, a check, a material threat, a checkmating sequence threat, or the threat of another tactic ─ which culminates in the opponent being unable to respond to all of the threats without conceding an immediate benefit to the opponent. Most often, the immediate benefit takes the form of a material advantage or checkmating attack; however, some tactics are used for defensive purposes and can salvage material that would otherwise be lost, or to induce stalemate in an otherwise lost position. Tactics are usually contrasted with strategy, whereby the individual moves by themselves don't make indefensible threats, and the cumulative advantage of the moves takes longer to be capitalised on. In rough terms, the dichotomy can be summarised as tactics concerning short-term play and strategy concerning long-term play. Examples of strategic advantages are weaknesses in, compromised pawn structure i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess
Chess is a board game for two players, called White and Black, each controlling an army of chess pieces in their color, with the objective to checkmate the opponent's king. It is sometimes called international chess or Western chess to distinguish it from related games, such as xiangqi (Chinese chess) and shogi (Japanese chess). The recorded history of chess goes back at least to the emergence of a similar game, chaturanga, in seventh-century India. The rules of chess as we know them today emerged in Europe at the end of the 15th century, with standardization and universal acceptance by the end of the 19th century. Today, chess is one of the world's most popular games, played by millions of people worldwide. Chess is an abstract strategy game that involves no hidden information and no use of dice or cards. It is played on a chessboard with 64 squares arranged in an eight-by-eight grid. At the start, each player controls sixteen pieces: one king, one queen, two rooks, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fork (chess)
In chess, a fork is a tactic in which a piece multiple enemy pieces simultaneously. The attacker usually aims to capture one of the forked pieces. The defender often cannot counter every threat. A fork is most effective when it is forcing, such as when the king is put in check. A fork is a type of . Terminology A fork is an example of a . The type of fork is named after the type of forking piece. For example, a fork by a knight is a knight fork. The attacked pieces are ''forked''. If the King is one of the attacked pieces, the term ''absolute fork'' is sometimes used. A fork not involving the enemy king is in contrast a ''relative fork''. A fork of the king and queen, the highest material-gaining fork possible, is sometimes called a ''royal fork''. A fork of the enemy king, queen, and one (or both) rooks is sometimes called a ''grand fork''. A knight fork of the enemy king, queen, and possibly other pieces is sometimes called a ''family fork'' or ''family check''. Strategy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pawn (chess)
The pawn (♙, ♟) is the most numerous and weakest piece in the game of chess. It may move one vacant square directly forward, it may move two vacant squares directly forward on its first move, and it may capture one square diagonally forward. Each player begins a game with eight pawns, one on each square of their second . The white pawns start on a2 through h2; the black pawns start on a7 through h7. Individual pawns are referred to by the on which they stand. For example, one speaks of "White's f-pawn" or "Black's b-pawn". Alternatively, they can be referred to by the piece which stood on that file at the beginning of the game, e.g. "White's king bishop's pawn" or "Black's queen knight's pawn". It is also common to refer to a rook's pawn, meaning any pawn on the a- or h-files, a knight's pawn (on the b- or g-files), a bishop's pawn (on the c- or f-files), a queen's pawn (on the d-file), a king's pawn (on the e-file), and a central pawn (on the d- or e-files). The pawn histori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Checkmate
Checkmate (often shortened to mate) is any game position in chess and other chess-like games in which a player's king is in check (threatened with ) and there is no possible escape. Checkmating the opponent wins the game. In chess, the king is never actually captured—the player loses as soon as the player's king is checkmated. In formal games, it is usually considered good etiquette to resign an inevitably lost game before being checkmated. If a player is not in check but has no legal move, then it is '' stalemate'', and the game immediately ends in a draw. A checkmating move is recorded in algebraic notation using the hash symbol "#", for example: 34.Qg3#. Examples A checkmate may occur in as few as two moves on one side with all of the pieces still on the board (as in Fool's mate, in the opening phase of the game), in a middlegame position (as in the 1956 game called the Game of the Century between Donald Byrne and Bobby Fischer), or after many moves with as few as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endgame Tablebase
An endgame tablebase is a computerized database that contains precalculated exhaustive analysis of chess endgame positions. It is typically used by a computer chess engine during play, or by a human or computer that is retrospectively analysing a game that has already been played. The tablebase contains the game-theoretical value (win, loss, or draw) in each possible position, and how many moves it would take to achieve that result with perfect play. Thus, the tablebase acts as an oracle, always providing the optimal moves. Typically the database records each possible position with certain pieces remaining on the board, and the best moves with White to move and with Black to move. Tablebases are generated by retrograde analysis, working backward from a checkmated position. By 2005, all chess positions with up to six pieces, including the two kings, had been solved. By August 2012, tablebases had solved chess for almost every position with up to seven pieces, but the positio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess Problem Terminology
This glossary of chess problems explains commonly used terms in chess problems, in alphabetical order. For a list of unorthodox pieces used in chess problems, see Fairy chess piece; for a list of terms used in chess is general, see Glossary of chess; for a list of chess-related games, see List of chess variants. A B C D E F G H I K L M N O P R S T U V W Z Notes References * * * * External links Problemesiscontains a glossary and list of themes {{Glossaries of sports Problems A problem is a difficulty which may be resolved by problem solving. Problem(s) or The Problem may also refer to: People * Pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |