|
Crisp Maltings
CRISP may refer to: * Center for Research in Security and Privacy, largest research center for IT security in Europe * C-language Reduced Instruction Set Processor, an AT&T microprocessor design * Chesapeake Regional Information System for our Patients, a health information exchange in Maryland, US * Computer Registration Involving Student Participation, online course registration system designed by Bernard Galler * Computer Retrieval of Information on Scientific Projects, a database of biomedical research projects funded by the U.S. government * Construction Research and Innovation Strategy Panel, a construction industry study group in the United Kingdom * Coral Reef Initiative for the South Pacific, a French inter-ministerial project founded in 2002 * Cross-industry standard process for data mining (CRISP-DM), a data mining process model * Cross Registry Information Service Protocol WHOIS (pronounced as the phrase "who is") is a query and response protocol that is widely use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center For Research In Security And Privacy
ATHENE, formerly Center for Research in Security and Privacy (CRISP), is the national research center for IT security and privacy in Germany and the largest research center for IT security in Europe. The research center is located in Darmstadt and deals with key issues of IT security in the digitization of government, business and society. ATHENE established a new research area in IT security research, the IT security of large systems, which is the focus of its research. Up to now, isolated aspects such as individual protocols or encryption methods have mostly been investigated. Research into the IT security of large systems should lead to a measurable increase in IT security. The research spectrum ranges from basic research to application. Director of ATHENE is Michael Waidner. Organisation ATHENE is an institution of the Fraunhofer Society and an alliance of the Fraunhofer Institute for Secure Information Technology (Fraunhofer SIT), the Fraunhofer Institute for Computer Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Security
Computer security, cybersecurity (cyber security), or information technology security (IT security) is the protection of computer systems and networks from attack by malicious actors that may result in unauthorized information disclosure, theft of, or damage to hardware, software, or data, as well as from the disruption or misdirection of the services they provide. The field has become of significance due to the expanded reliance on computer systems, the Internet, and wireless network standards such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, and due to the growth of smart devices, including smartphones, televisions, and the various devices that constitute the Internet of things (IoT). Cybersecurity is one of the most significant challenges of the contemporary world, due to both the complexity of information systems and the societies they support. Security is of especially high importance for systems that govern large-scale systems with far-reaching physical effects, such as power distribution, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-language Reduced Instruction Set Processor
The AT&T Hobbit is a microprocessor design that AT&T Corporation developed in the early 1990s. It was based on the company's CRISP (C-language Reduced Instruction Set Processor) design, which in turn grew out of the C Machine design by Bell Labs of the late 1980s. All were optimized for running code compiled from the C programming language. The design concentrates on fast instruction decoding, indexed array access, and procedure calls. Its processor is partially RISC-like. The project ended in 1994 because the Hobbit failed to achieve commercially viable sales. History CRISP was produced in 1987, largely for experimental purposes. Apple Computer approached AT&T and paid it to develop a newer version of the CRISP suitable for low-power use in the Newton handheld computer. The result is the Hobbit, which was initially produced as the 92010 in 1992 with a 3 KB instruction buffer and the 92020 in 1994 with 6 KB. Several support chips were produced: * AT&T 92011 System M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chesapeake Regional Information System For Our Patients
The Chesapeake Regional Information System for our Patients (CRISP) is a nonprofit organization created to function as Maryland's state-designated health information exchange (HIE), by the Maryland Health Care Commission. CRISP currently serves as the HIE for Maryland and the District of Columbia. CRISP is advised by a wide range of stakeholders who are responsible for healthcare throughout the region. Health information exchange allows clinical information to move electronically among disparate health information systems. The goal of the HIE is to deliver the right health information to the right place at the right time – providing safer, timelier, efficient, effective, equitable, patient centered care. In doing so, CRISP offers a suite of tools aimed at improving the facilitation of care for their service region's providers. CRISP was created by Johns Hopkins Medicine, MedStar Health, the University of Maryland Medical System and Erickson Retirement Communities, and receives inp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard Galler
Bernard A. Galler ( in Chicago – in Ann Arbor, Michigan) was an American mathematician and computer scientist at the University of Michigan who was involved in the development of large-scale operating systems and computer languages including the MAD programming language and the Michigan Terminal System operating system. Education and career Galler attended the University of Chicago where he earned a B.Sc. in mathematics at the University of Chicago (1947), followed by a M.Sc. from UCLA and a Ph.D. from the University of Chicago (1955), advised by Paul Halmos and Marshall Stone. He joined the mathematics department at the University of Michigan (1955) where he taught the first programming course (1956) using an IBM 704. Galler helped to develop the computer language called the Michigan Algorithm Decoder (1959-) in use at several universities. He formed the Communication Sciences dept (1965), renamed Computer Sciences (CS), which became the Computer and Communications (CCS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Retrieval Of Information On Scientific Projects
The CRISP (Computer Retrieval of Information on Scientific Projects) system at NIH has been replaced by the RePORT Expenditures and Results (RePORTER) query tool. CRISP was a fully searchable database of biomedical research projects funded by the U.S. government. It covers projects going back to 1972 and records name and abstract of the project, the principal investigator and the involved institution. The database is maintained by the Office of Extramural Research at the National Institutes of Health. To facilitate indexing and searching, CRISP also contains a thesaurus and controlled vocabulary for terms used in biological and medical Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practic ... research. Each project is assigned three keywords from the thesaurus. All users, including the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Construction Research And Innovation Strategy Panel
The Construction Research and Innovation Strategy Panel (CRISP) was an initiative established in 1995 to identify and prioritise the research needs of the construction industry of the United Kingdom. It operated through a series of Task Groups, each dealing with a particular research topic, and each of which produced a report published on the CRISP website. Collated recommendations were passed to appropriate funding bodies. In 2005, CRISP was absorbed into the National Platform for the Built Environment. History In 1995, CRISP was given responsibility for advising the then Department of the Environment on priorities for research and innovation, and was based at the Building Research Establishment in Garston, Hertfordshire, near Watford. Operation between 1998 and 2003 From 1998 Davis Langdon Consultancy provided management support. Between 1998 and 2002, 13 Task Groups covering topics such as ''design'', ''sustainable construction'', ''performance'' and ''value'' produced 233 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coral Reef Initiative For The South Pacific
Coral Reef Initiative for the South Pacific (CRISP) is a French inter-ministerial project founded in 2002. Its aims focus on developing a vision for the future for coral reef eco-systems and the communities that depend on them within the French overseas territories and Pacific Island developing countries. Programme coordination is provided by the CRISP Coordination Unit and a programme manager who is supported by scientific counselors. The programme is hosted by the Secretariat of the Pacific Community who is located in Nouméa, New-Caledonia. CRISP is under the institutional protection from the Pacific Community and the South Pacific Regional Environment Programme. It is a regional initiative that promotes the protection and sustainable management of the coral reefs of the Pacific island states. History During the French-Oceania Summit of 2003, French President Jacques Chirac promoted the idea of bringing together Oceania participants to work towards sustainable development of the P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
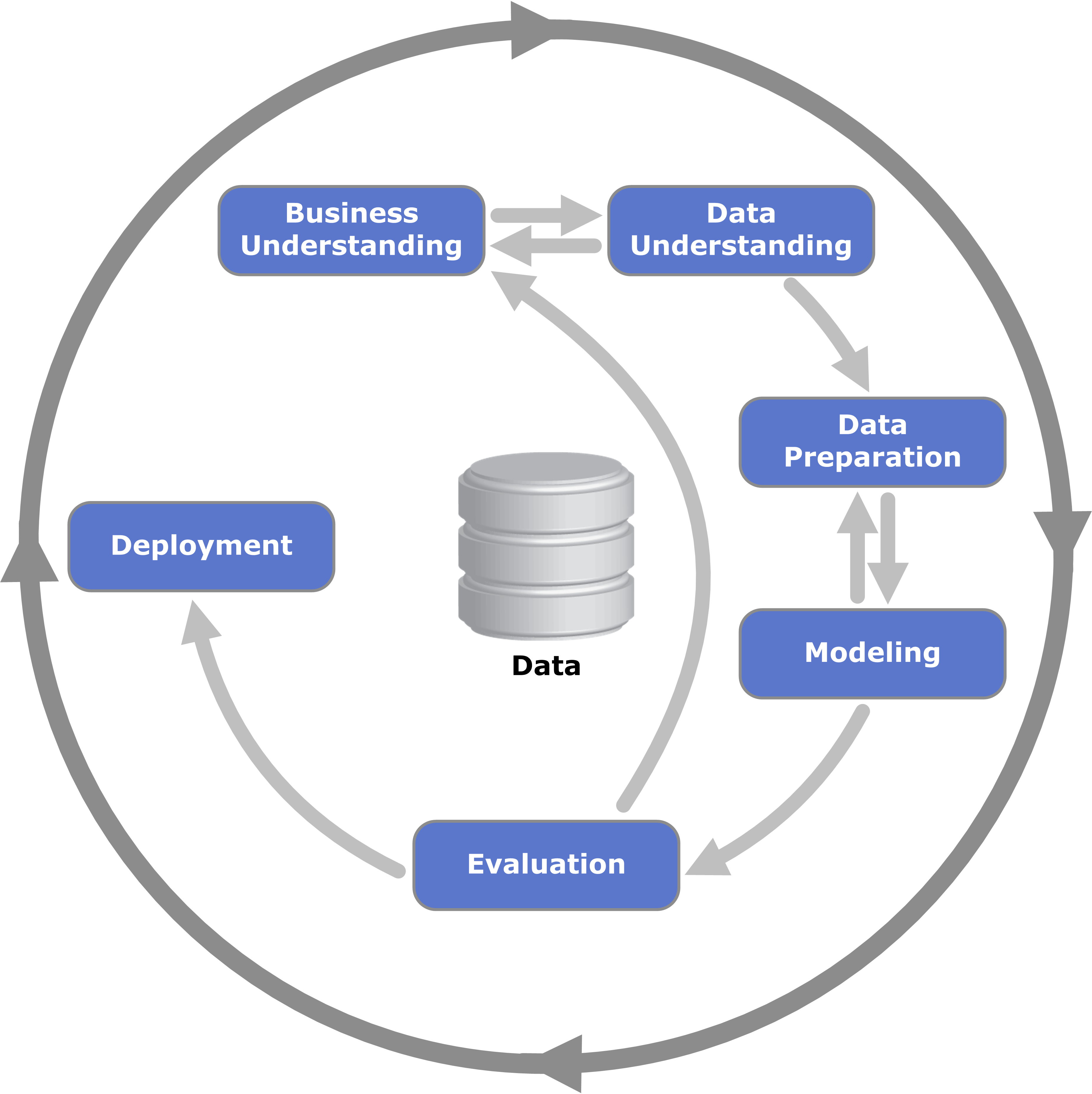
Cross-industry Standard Process For Data Mining
Cross-industry standard process for data mining, known as CRISP-DM,Shearer C., ''The CRISP-DM model: the new blueprint for data mining'', J Data Warehousing (2000); 5:13—22. is an open standard process model that describes common approaches used by data mining experts. It is the most widely-used analytics model. In 2015, IBM released a new methodology called '' Analytics Solutions Unified Method for Data Mining/Predictive Analytics'' (also known as ASUM-DM) which refines and extends CRISP-DM. History CRISP-DM was conceived in 1996 and became a European Union project under the ESPRIT funding initiative in 1997. The project was led by five companies: Integral Solutions Ltd (ISL), Teradata, Daimler AG, NCR Corporation and OHRA, an insurance company. This core consortium brought different experiences to the project: ISL, later acquired and merged into SPSS. The computer giant NCR Corporation produced the Teradata data warehouse and its own data mining software. Daimler-Benz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Registry Information Service Protocol
WHOIS (pronounced as the phrase "who is") is a query and response protocol that is widely used for querying databases that store the registered users or assignees of an Internet resource, such as a domain name, an IP address block or an autonomous system, but is also used for a wider range of other information. The protocol stores and delivers database content in a human-readable format.RFC 3912, ''WHOIS Protocol Specification'', L. Daigle (September 2004) The current iteration of the WHOIS protocol was drafted by the Internet Society, and is documented in . Whois is also the name of the command-line utility on most UNIX systems used to make WHOIS protocol queries. In addition WHOIS has a sister protocol called ''Referral Whois'' (RWhois). History Elizabeth Feinler and her team (who had created the Resource Directory for ARPANET) were responsible for creating the first WHOIS directory in the early 1970s. Feinler set up a server in Stanford's Network Information Center (NIC) wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine-rich Secretory Protein
Cysteine-rich secretory proteins, often abbreviated as CRISPs, are a group of glycoproteins. They are a subgroup of the CRISP, antigen 5 and Pr-1 (CAP) protein superfamily and also contain a domain related to the ShK toxins. They are substantially implicated in the functioning of the mammalian reproductive system. CRISPs are also found in a variety of snake venoms where they inhibit both smooth muscle contraction and cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channels. Structure CRISPs contain two domains joined by a hinge region. The larger domain is a CAP-like 'Pathogenesis-related 1' domain (PR-1), followed by the smaller ShK-like 'Cysteine-Rich Domain' (CRD). CRISPs are glycoproteins, with a number of carbohydrate glycans covalently attached to amino acid side-chains on their surface via glycosylation. The primary structure is also rich in cysteine that form disulfide bonds, particularly in the hinge region and CRD. Mammalian reproduction CRISPs are found in the testes and epidid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)