|
Crimes Involving Radioactive Substances
This is a list of criminal (or arguably, allegedly, or potentially criminal) acts intentionally involving radioactive substances. Inclusion in this list does not necessarily imply that anyone involved was guilty of a crime. For accidents or crimes that involved radioactive substances unbeknownst to those involved, see the Nuclear and radiation accidents and incidents. Murder and attempted murder The Karlsruhe plutonium affair Johannes M. was convicted of attempting to poison his ex-wife in 2001 with plutonium stolen from WAK (Wiederaufbereitungsanlage Karlsruhe), a small scale reprocessing plant where he worked. He did not steal a large amount of plutonium, only rags used for wiping surfaces and a small amount of liquid waste. At least two people (besides the criminal) were contaminated by the plutonium. Two flats in Landau in the Rhineland-Palatinate were contaminated, and had to be cleaned at a cost of two million euro. Photographs of the case and details of other nuclear cri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Warning Symbol
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium. This includes: * ''electromagnetic radiation'', such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, and gamma radiation (γ) * ''particle radiation'', such as alpha radiation (α), beta radiation (β), proton radiation and neutron radiation (particles of non-zero rest energy) * '' acoustic radiation'', such as ultrasound, sound, and seismic waves (dependent on a physical transmission medium) * ''gravitational wave, gravitational radiation'', that takes the form of gravitational waves, or ripples in the curvature of spacetime Radiation is often categorized as either ''ionizing radiation, ionizing'' or ''non-ionizing radiation, non-ionizing'' depending on the energy of the radiated particles. Ionizing radiation carries more than 10 electron volt, eV, which is enough to ionize atoms and molecules and break ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Sunday Times (UK)
''The Sunday Times'' is a British newspaper whose circulation makes it the largest in Britain's quality press market category. It was founded in 1821 as ''The New Observer''. It is published by Times Newspapers Ltd, a subsidiary of News UK, which is owned by News Corp. Times Newspapers also publishes ''The Times''. The two papers were founded independently and have been under common ownership since 1966. They were bought by News International in 1981. ''The Sunday Times'' has a circulation of just over 650,000, which exceeds that of its main rivals, including The Sunday Telegraph, ''The'' ''Sunday Telegraph'' and The Observer, ''The'' ''Observer'', combined. While some other national newspapers moved to a Tabloid (newspaper format), tabloid format in the early 2000s, ''The Sunday Times'' has retained the larger broadsheet format and has said that it would continue to do so. As of December 2019, it sells 75% more copies than its sister paper, ''The Times'', which is published fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East German
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state was a part of the Eastern Bloc in the Cold War. Commonly described as a communist state, it described itself as a socialist "workers' and peasants' state".Patrick Major, Jonathan Osmond, ''The Workers' and Peasants' State: Communism and Society in East Germany Under Ulbricht 1945–71'', Manchester University Press, 2002, Its territory was administered and occupied by Soviet forces following the end of World War II—the Soviet occupation zone of the Potsdam Agreement, bounded on the east by the Oder–Neisse line. The Soviet zone surrounded West Berlin but did not include it and West Berlin remained outside the jurisdiction of the GDR. Most scholars and academics describe the GDR as a totalitarian dictatorship. The GDR was established i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grozny
Grozny ( rus, Грозный, p=ˈgroznɨj; ce, Соьлжа-ГӀала, translit=Sölƶa-Ġala), also spelled Groznyy, is the capital city of Chechnya, Russia. The city lies on the Sunzha River. According to the 2010 census, it had a population of 271,573 — up from 210,720 recorded in the 2002 census, but still only about two-thirds of 399,688 recorded in the 1989 census. It was previously known as (until 1870). Names In Russian, "Grozny" means "fearsome", "menacing", or "redoubtable", the same word as in Ivan Grozny ( Ivan the Terrible). While the official name in Chechen is the same, informally the city is known as "" (""), which literally means "the city () on the Sunzha River ()". In 1996, during the First Chechen War, the Chechen separatists renamed the city Dzhokhar-Ghala ( ce, Джовхар-ГӀала, Dƶovxar-Ġala), literally Dzhokhar City, or Dzhokhar/Djohar for short, after Dzhokhar Dudayev, the first president of the Chechen Republic of Ichker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
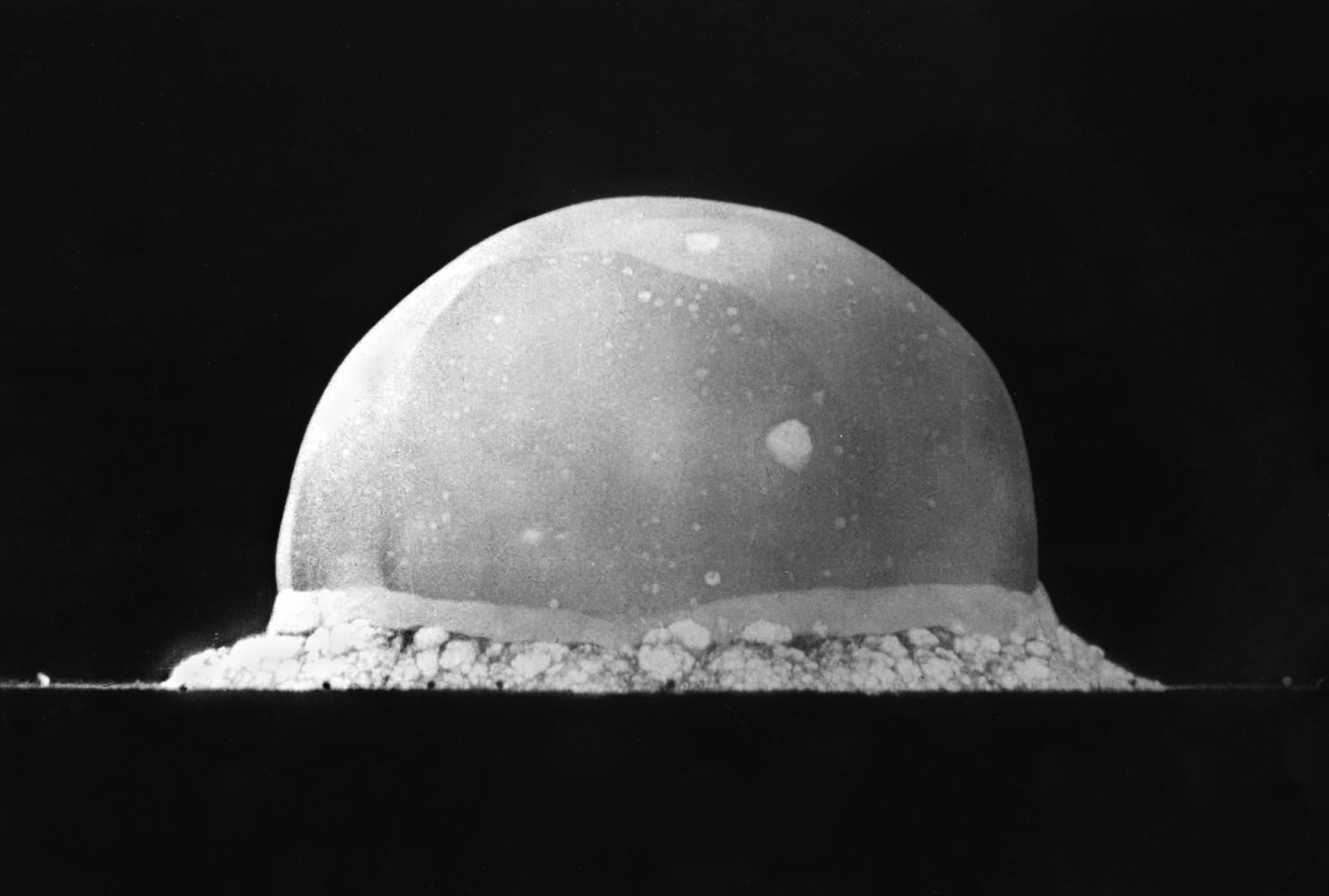
Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory (often shortened as Los Alamos and LANL) is one of the sixteen research and development laboratories of the United States Department of Energy (DOE), located a short distance northwest of Santa Fe, New Mexico, in the American southwest. Best known for its central role in helping develop the first atomic bomb, LANL is one of the world's largest and most advanced scientific institutions. Los Alamos was established in 1943 as Project Y, a top-secret site for designing nuclear weapons under the Manhattan Project during World War II.The site was variously called Los Alamos Laboratory and Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory. Chosen for its remote yet relatively accessible location, it served as the main hub for conducting and coordinating nuclear research, bringing together some of the world's most famous scientists, among them numerous Nobel Prize winners. The town of Los Alamos, directly north of the lab, grew extensively through this period. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive Contamination
Radioactive contamination, also called radiological pollution, is the deposition of, or presence of radioactive substances on surfaces or within solids, liquids, or gases (including the human body), where their presence is unintended or undesirable (from the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) definition). Such contamination presents a hazard because the radioactive decay of the contaminants, produces ionizing radiation (namely alpha, beta, gamma rays and free neutrons). The degree of hazard is determined by the concentration of the contaminants, the energy of the radiation being emitted, the type of radiation, and the proximity of the contamination to organs of the body. It is important to be clear that the contamination gives rise to the radiation hazard, and the terms "radiation" and "contamination" are not interchangeable. The sources of radioactive pollution can be classified into two groups: natural and man-made. Following an atmospheric nuclear weapon discharge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the north, Missouri on the northeast, Arkansas on the east, New Mexico on the west, and Colorado on the northwest. Partially in the western extreme of the Upland South, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 20th-most extensive and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 28th-most populous of the 50 United States. Its residents are known as Oklahomans and its capital and largest city is Oklahoma City. The state's name is derived from the Choctaw language, Choctaw words , 'people' and , which translates as 'red'. Oklahoma is also known informally by its List of U.S. state and territory nicknames, nickname, "Sooners, The Sooner State", in reference to the settlers who staked their claims on land before the official op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
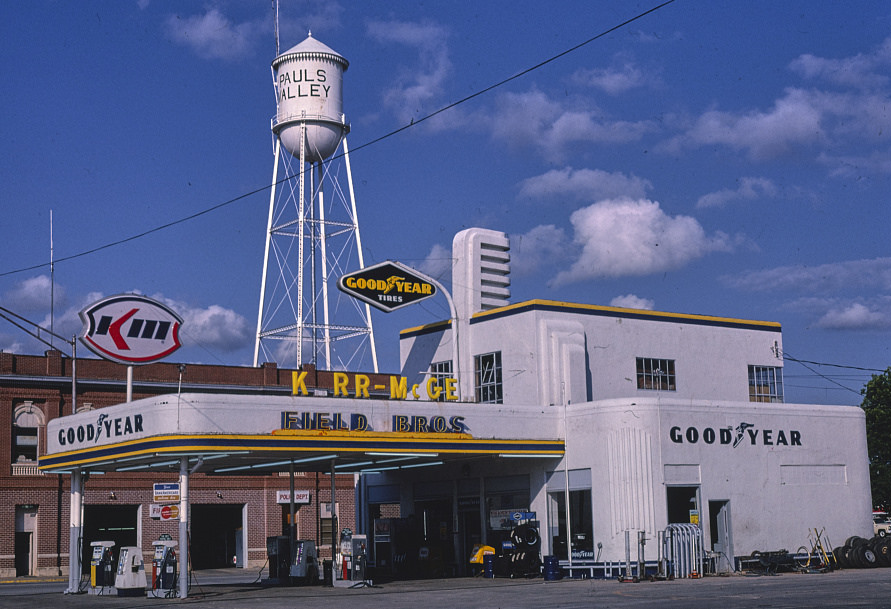
Cimarron Fuel Fabrication Site
The Cimarron Fuel Fabrication Site was a nuclear fuel production facility located by the Cimarron River near Cimarron City, Oklahoma. It was operated by Kerr-McGee Corporation (KMC) from 1965 to 1975.anadarko.com 2006 aug 10 press release Kerr-McGee Completes Separation of Tronox 2006 Mar 31 Jan 13, 2009 The Oklahoman via COMTEX History < ...
|
Plutonium-239
Plutonium-239 (239Pu or Pu-239) is an isotope of plutonium. Plutonium-239 is the primary fissile isotope used for the production of nuclear weapons, although uranium-235 is also used for that purpose. Plutonium-239 is also one of the three main isotopes demonstrated usable as fuel in thermal spectrum nuclear reactors, along with uranium-235 and uranium-233. Plutonium-239 has a half-life of 24,110 years. Nuclear properties The nuclear properties of plutonium-239, as well as the ability to produce large amounts of nearly pure 239Pu more cheaply than highly enriched weapons-grade uranium-235, led to its use in nuclear weapons and nuclear power plants. The fissioning of an atom of uranium-235 in the reactor of a nuclear power plant produces two to three neutrons, and these neutrons can be absorbed by uranium-238 to produce plutonium-239 and other isotopes. Plutonium-239 can also absorb neutrons and fission along with the uranium-235 in a reactor. Of all the common nuclear fuels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karen Silkwood
Karen Gay Silkwood (February 19, 1946 – November 13, 1974) was an American chemical technician and labor union activist known for raising concerns about corporate practices related to health and safety in a nuclear facility. She worked at the Kerr-McGee Cimarron Fuel Fabrication Site in Oklahoma, making plutonium pellets, and became the first woman on the union's negotiating team. After testifying to the Atomic Energy Commission about her concerns, she was found to have plutonium contamination on her person and in her home. While driving to meet with a ''New York Times'' journalist and an official of her union's national office, she died in a car crash under unclear circumstances. Her family sued Kerr-McGee for the plutonium contamination. The company settled out of court for US $1.38 million, while not admitting liability. Her story was chronicled in Mike Nichols's 1983 Academy Award nominated film '' Silkwood'' in which she was portrayed by Meryl Streep. Fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labor Union
A trade union (labor union in American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers intent on "maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment", ch. I such as attaining better wages and benefits (such as holiday, health care, and retirement), improving working conditions, improving safety standards, establishing complaint procedures, developing rules governing status of employees (rules governing promotions, just-cause conditions for termination) and protecting the integrity of their trade through the increased bargaining power wielded by solidarity among workers. Trade unions typically fund their head office and legal team functions through regularly imposed fees called ''union dues''. The delegate staff of the trade union representation in the workforce are usually made up of workplace volunteers who are often appointed by members in democratic elections. The trade union, through an elected leadership and bargaining committee, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerr-McGee
The Kerr-McGee Corporation, founded in 1929, was an American energy company involved in oil exploration, production of crude oil, natural gas, perchlorate and uranium mining and milling in various countries. On June 23, 2006, Anadarko Petroleum acquired Kerr-McGee in an all-cash transaction totaling $16.5 billion plus $2.6 billion in debt and all operations moved from their base in Oklahoma, United States. History The company later known as Kerr-McGee was founded in 1929 as Anderson & Kerr Drilling Company by Oklahoma businessman-politician Robert S. Kerr (1896-1963) and oil driller James L. Anderson. When Dean A. McGee (1904-1989), a former chief geologist for Phillips Petroleum, joined the firm in 1946, it changed its name to Kerr-McGee Oil Industries, Incorporated. The company initially focused mostly on off-shore oil exploration and production, being one of the first companies to use drillships in the Gulf of Mexico, and later one of the first companies to use a Spar type pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |