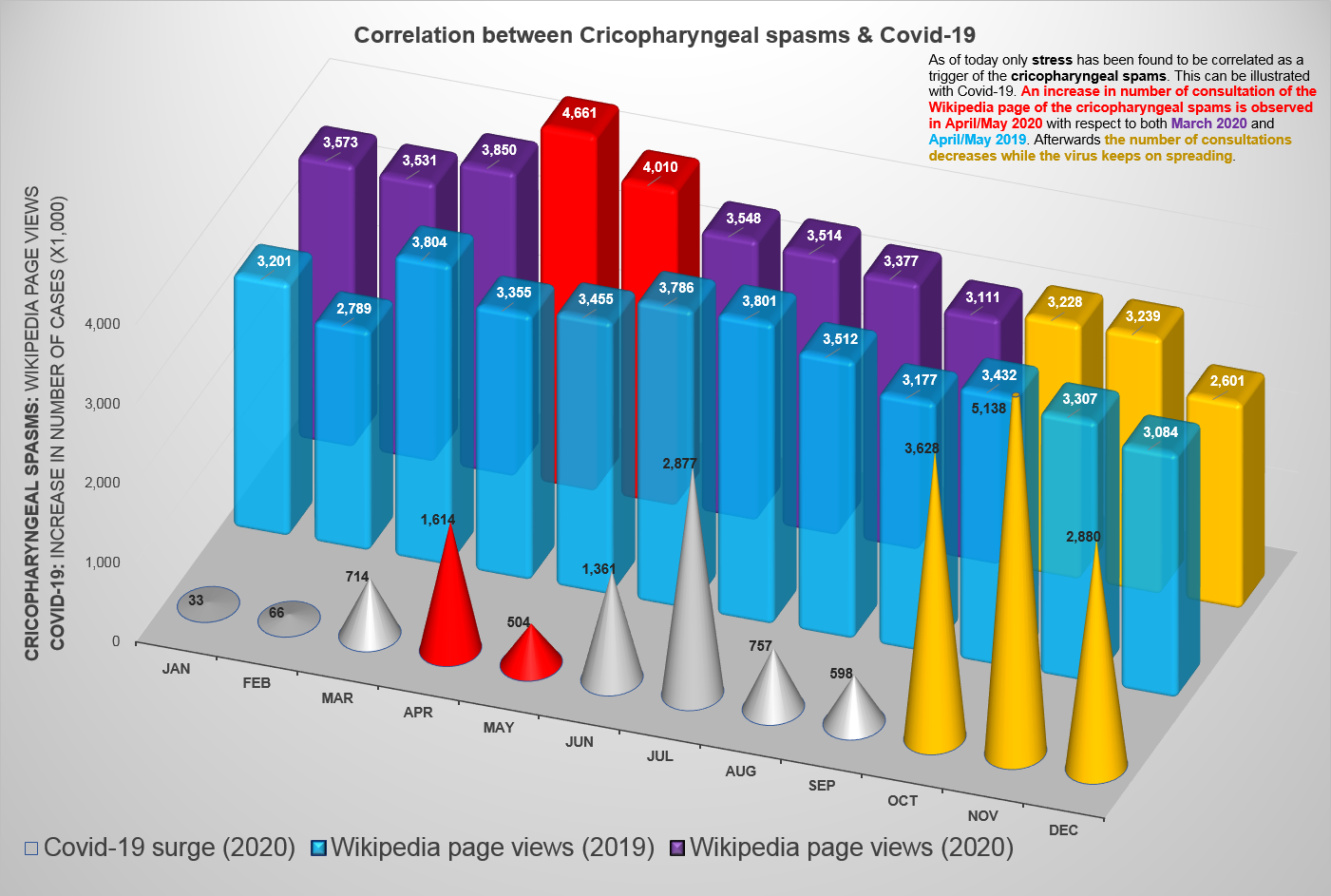
|
Cricopharyngeus
The inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle is a skeletal muscle of the neck. It is the thickest of the three outer pharyngeal muscles. It arises from the sides of the cricoid cartilage and the thyroid cartilage. It is supplied by the vagus nerve (CN X). It is active during swallowing, and partially during breathing and speech. It may be affected by Zenker's diverticulum. Structure The inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle is composed of two parts. The first part (and more superior) arises from the thyroid cartilage (thyropharyngeal part), and the second part arises from the cricoid cartilage (cricopharyngeal part). * On the ''thyroid cartilage'', it arises from the oblique line on the side of the lamina, from the surface behind this nearly as far as the posterior border and from the inferior horn of the thyroid cartilage. * From the ''cricoid cartilage'', it arises in the interval between the cricothyroid muscle in front, and the articular facet for the inferior horn of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zenker's Diverticulum
A Zenker's diverticulum, also pharyngeal pouch, is a diverticulum of the mucosa of the human pharynx, just above the cricopharyngeal muscle (i.e. above the upper sphincter of the esophagus). It is a pseudo diverticulum (not involving all layers of the esophageal wall). It was named in 1877 after German pathologist Friedrich Albert von Zenker. Signs and symptoms In simple words, when there is excessive pressure within the lower pharynx, the weakest portion of the pharyngeal wall balloons out, forming a diverticulum which may reach several centimetres in diameter. More precisely, while traction and pulsion mechanisms have long been deemed the main factors promoting development of a Zenker's diverticulum, current consensus considers occlusive mechanisms to be most important: uncoordinated swallowing, impaired relaxation and spasm of the cricopharyngeus muscle lead to an increase in pressure within the distal pharynx, so that its wall herniates through the point of least resistan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Killian's Dehiscence
Killian's dehiscence (also known as Killian's triangle) is a triangular area in the wall of the pharynx between the cricopharyngeus and thyropharyngeus which are the two parts of the inferior constrictors(also see Pharyngeal pouch). It can be seen as a locus minoris resistentiae. Similar triangular area between circular fibres of cricopharyngeus and longitudinal fibres of esophagus is Lamier's triangle or Lamier-hackermann's area. Clinical significance It represents a potentially weak spot where a pharyngoesophageal diverticulum (Zenker's diverticulum) is more likely to occur. Eponym It is named after the German ENT surgeon Gustav Killian Gustav Killian (2 June 1860 – 24 February 1921) was a German laryngologist and founder of the bronchoscopy. Life and death His father Johann Baptist Caesar Killian (1820–1889), the son of a ''städtischen Wegeaufsehers'' an urban way overseer, .... References Human head and neck Otorhinolaryngology {{anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cricopharyngeal Spasm
Cricopharyngeal spasms occur in the cricopharyngeus muscle of the pharynx. Cricopharyngeal spasm is an uncomfortable but harmless and temporary disorder. Signs and symptoms * Sensation of a 'lump' in the back of the throat * Throat feels swollen * Discomfort - Lump can often feel quite big and pain is occasional * Symptoms normally worse in the evening * Stress aggravates the symptoms * Saliva is difficult to swallow, yet food is easy to swallow - eating, in fact, often makes the tightness go away for a time * 'Lump' sensation comes and goes from day to day * Symptoms can persist for very long periods, often several months. * The symptoms can be mimicked by pushing on the cartilage in the neck, just below the Adam's apple Physiology There are two sphincters in the oesophagus. They are normally contracted and they relax when one swallows so that food can pass through them going to the stomach. They then squeeze closed again to prevent regurgitation of the stomach contents and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swallowing
Swallowing, sometimes called deglutition in scientific contexts, is the process in the human or animal body that allows for a substance to pass from the mouth, to the pharynx, and into the esophagus, while shutting the epiglottis. Swallowing is an important part of eating and drinking. If the process fails and the material (such as food, drink, or medicine) goes through the trachea, then choking or pulmonary aspiration can occur. In the human body the automatic temporary closing of the epiglottis is controlled by the swallowing reflex. The portion of food, drink, or other material that will move through the neck in one swallow is called a bolus. In colloquial English, the term "swallowing" is also used to describe the action of taking in a large mouthful of food without any biting, where the word gulping is more adequate. In humans Swallowing comes so easily to most people that the process rarely prompts much thought. However, from the viewpoints of physiology, of spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Pharyngeal Constrictor Muscle
The middle pharyngeal constrictor is a fan-shaped muscle located in the neck. It is one of three pharyngeal constrictors. Similarly to the superior and inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscles, the middle pharyngeal constrictor is innervated by a branch of the vagus nerve through the pharyngeal plexus. The middle pharyngeal constrictor is smaller than the inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle. Structure The middle pharyngeal constrictor arises from the whole length of the upper border of the greater cornu of the hyoid bone, from the lesser cornu, and from the stylohyoid ligament. The fibers diverge from their origin: the lower ones descend beneath the constrictor inferior, the middle fibers pass transversely, and the upper fibers ascend and overlap the constrictor superior. It is inserted into the posterior median fibrous raphe, blending in the middle line with the muscle of the opposite side. Function As soon as the bolus of food is received in the pharynx, the elevato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Neurology
''Experimental Neurology'' is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal that focuses on research in neuroscience concerning mechanisms underlying neurological disorders. The journal focuses on neural development, neuroregeneration, neuroplasticity, and transplantation,. It was established in 1959 and is published by Elsevier. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 5.33. In 1997, ''Experimental Neurology'' absorbed the quarterly journal ''Neurodegeneration'', which had been established in 1992. Past editors-in-chief * 1959–1975: William F. Windle * 1973–1988: Carmine D. Clemente References External links * Elsevier academic journals Monthly journals Neurology journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sleep
Sleep is a sedentary state of mind and body. It is characterized by altered consciousness, relatively inhibited sensory activity, reduced muscle activity and reduced interactions with surroundings. It is distinguished from wakefulness by a decreased ability to react to stimuli, but more reactive than a coma or disorders of consciousness, with sleep displaying different, active brain patterns. Sleep occurs in repeating periods, in which the body alternates between two distinct modes: REM sleep and non-REM sleep. Although REM stands for "rapid eye movement", this mode of sleep has many other aspects, including virtual paralysis of the body. Dreams are a succession of images, ideas, emotions, and sensations that usually occur involuntarily in the mind during certain stages of sleep. During sleep, most of the body's systems are in an anabolic state, helping to restore the immune, nervous, skeletal, and muscular systems; these are vital processes that maintain mood, memory, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
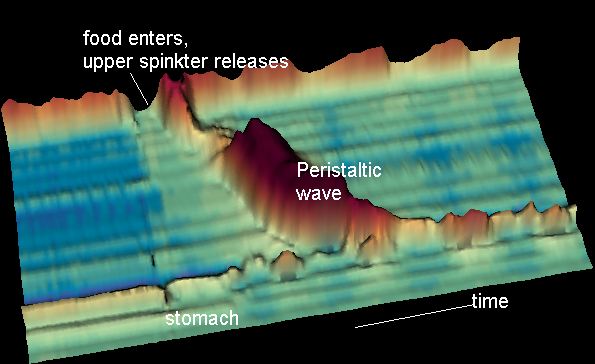
Peristalsis
Peristalsis ( , ) is a radially symmetrical contraction and relaxation of muscles that propagate in a wave down a tube, in an anterograde direction. Peristalsis is progression of coordinated contraction of involuntary circular muscles, which is preceded by a simultaneous contraction of the longitudinal muscle and relaxation of the circular muscle in the lining of the gut. In much of a digestive tract such as the human gastrointestinal tract, smooth muscle tissue contracts in sequence to produce a peristaltic wave, which propels a ball of food (called a bolus before being transformed into chyme in the stomach) along the tract. The peristaltic movement comprises relaxation of circular smooth muscles, then their contraction behind the chewed material to keep it from moving backward, then longitudinal contraction to push it forward. Earthworms use a similar mechanism to drive their locomotion, and some modern machinery imitate this design. The word comes from New Latin and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolus (digestion)
In digestion, a bolus (from Latin ''bolus'', "ball") is a ball-like mixture of food and saliva that forms in the mouth during the process of chewing (which is largely an adaptation for plant-eating mammals). It has the same color as the food being eaten, and the saliva gives it an alkaline pH. Under normal circumstances, the bolus is swallowed, and travels down the esophagus to the stomach The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ... for digestion. See also * Chyme * Chyle References Digestive system {{Digestive-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food and air to the esophagus and larynx respectively. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx. In humans, the pharynx is part of the digestive system and the conducting zone of the respiratory system. (The conducting zone—which also includes the nostrils of the nose, the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles—filters, warms and moistens air and conducts it into the lungs). The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx. It is also important in vocalization. In humans, two sets of pharyngeal muscles form the pharynx and determine the shape of its lumen. They are arranged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharyngobasilar Fascia
As it descends it diminishes in thickness, and is gradually lost. It is strengthened posteriorly by a strong fibrous band, which is attached above to the pharyngeal spine on the under surface of the basilar portion of the occipital bone, and passes downward, forming a median raphé, which gives attachment to the Constrictores pharyngis The pharyngeal muscles are a group of muscles that form the pharynx, which is posterior to the oral cavity, determining the shape of its lumen, and affecting its sound properties as the primary resonating cavity. The pharyngeal muscles (involunta .... Additional images File:Slide1kuku.JPG, Larynx, pharynx and tongue.Deep dissection, posterior view. File:Slide2kuku.JPG, Larynx, pharynx and tongue.Deep dissection, posterior view. File:Slide3kuku.JPG, Larynx, pharynx and tongue.Deep dissection, Posterior view. References External links * * http://ect.downstate.edu/courseware/haonline/labs/l31/100101.htm * http://www.instantanatomy.net/headne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Pharyngeal Constrictor Muscle
The superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle is a muscle in the pharynx. It is the highest located muscle of the three pharyngeal constrictors. The muscle is a quadrilateral muscle, thinner and paler than the inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle and middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle. The muscle is divided into four parts: A pterygopharyngeal, buccopharyngeal, mylopharyngeal and a glossopharyngeal part. Origin and insertion The four parts of this muscle arise from: - the lower third of the posterior margin of the medial pterygoid plate and its hamulus (Pterygopharyngeal part) - from the pterygomandibular raphe (Buccopharyngeal part) - from the alveolar process of the mandible above the posterior end of the mylohyoid line (Mylopharyngeal part) - and by a few fibers from the side of the tongue (Glossopharyngeal part) The fibers curve backward to be inserted into the median raphe, being also prolonged by means of an aponeurosis to the pharyngeal spine on the basilar part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |