|
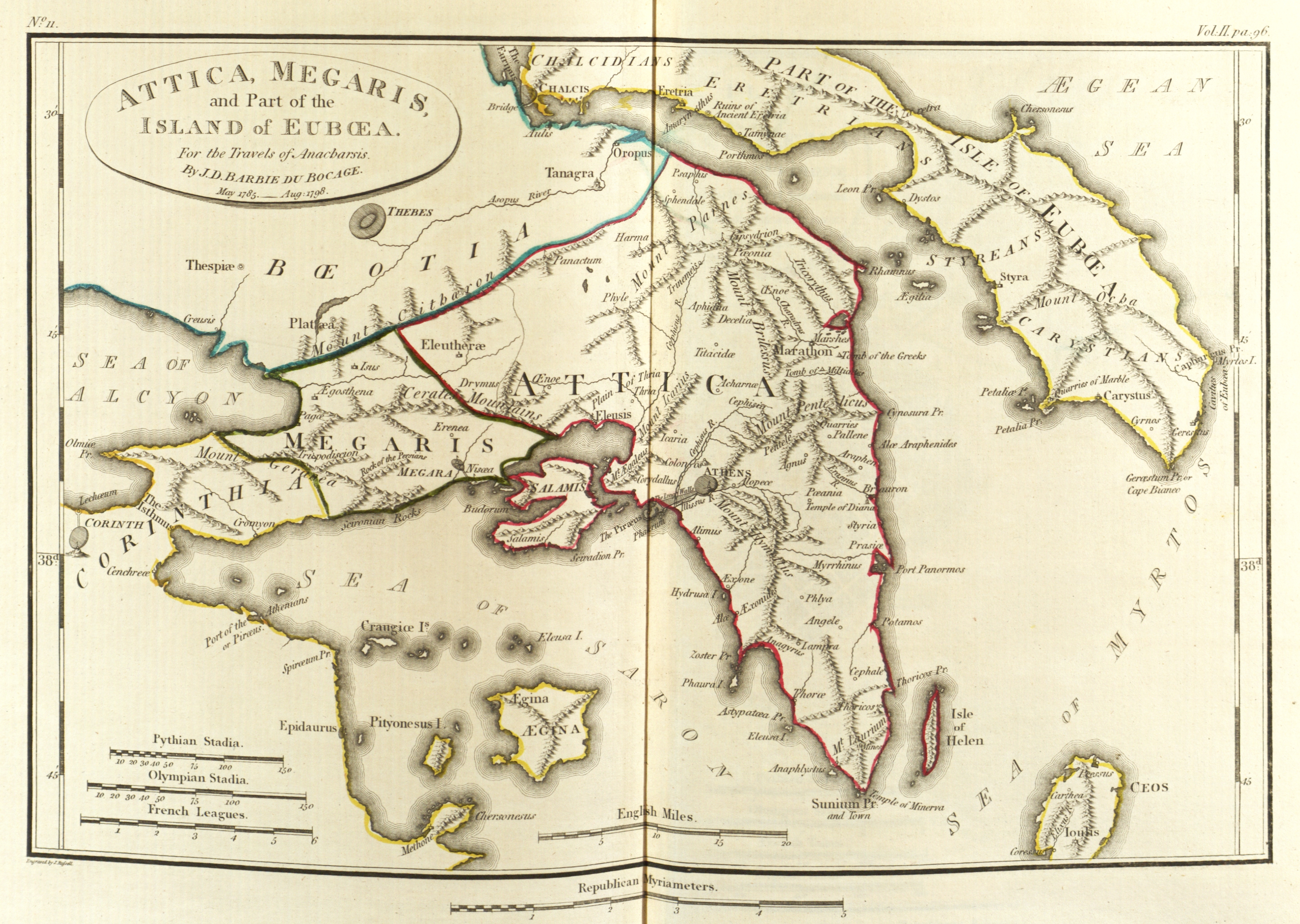
Creusis
Creusis or Kreusis ( grc, Κρεῦσις), or Creusa or Kreousa (Κρέουσα), also Creusia or Kreousia (Κρεουσία), was a town of ancient Boeotia, at the head of a small bay in the Corinthian Gulf, described by ancient writers as the port of Thespiae. The navigation from Peloponnesus to Creusis is described by Pausanias as insecure, on account of the many headlands which it was necessary to double, and of the violent gusts of wind rushing down from the mountains. Creusis was on the borders of Megaris. One of the highest points of Mount Cithaeron projects into the sea between Creusis and Aegosthena, the frontier town in Megaris, leaving no passage along the shore except a narrow path on the side of the mountain. In confirmation of Pausanias, William Martin Leake, who visited the site in the 19th century, remarks that this termination of Mt. Cithaeron, as well as all the adjoining part of the Alcyonic Sea, is subject to sudden gusts of wind, by which the passage of such a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Leuctra
The Battle of Leuctra ( grc-gre, Λεῦκτρα, ) was a battle fought on 6 July 371 BC between the Boeotians led by the Thebans, and the Spartans along with their allies amidst the post-Corinthian War conflict. The battle took place in the vicinity of Leuctra, a village in Boeotia in the territory of Thespiae. The Theban victory shattered Sparta's immense influence over the Greek peninsula, which Sparta had gained with its victory in the Peloponnesian War a generation earlier. Prelude In 371 BC, the newly established democracy of Thebes had elected four Boeotarchs, the traditional title of the generals of the Boeotian League, and so proclaimed their intention of reconstituting the aforementioned league that Sparta had disbanded.Tritle 1987, p. 80 During this period, Thebes had an ally in Athens, but Athens was far from happy with the treatment Plataea had received. When it came to swearing an oath to respect the treaty, Sparta swore on behalf of itself and its allies. When Ep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thespiae
Thespiae ( ; grc, Θεσπιαί, Thespiaí) was an ancient Greece, ancient Greek city (''polis'') in Boeotia. It stood on level ground commanded by the low range of hills which run eastward from the foot of Mount Helicon to Thebes, Greece, Thebes, near modern Thespies. History In the ancient Greece#History, history of ancient Greece, Thespiae was one of the cities of the federal league known as Boeotia, the Boeotian League. Several traditions agree that the Boeotians were a people expelled from Ancient Thessaly, Thessaly some time after the mythical Trojan War, and who colonised the Boeotian plain over a series of generations, of which the occupation of Thespiae formed a later stage. Other traditions suggest that they were of Mycenaeans, Mycenean origin. Archaic period In the Archaic period the Thespian nobility was heavily dependent on Thebes. This possibly reflected that land ownership was concentrated in the hands of a small number of nobles, and therefore there was difficul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Boeotia
Boeotia ( ), sometimes Latinized as Boiotia or Beotia ( el, Βοιωτία; modern: ; ancient: ), formerly known as Cadmeis, is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Central Greece. Its capital is Livadeia, and its largest city is Thebes. Boeotia was also a region of ancient Greece, from before the 6th century BC. Geography Boeotia lies to the north of the eastern part of the Gulf of Corinth. It also has a short coastline on the Gulf of Euboea. It bordered on Megaris (now West Attica) in the south, Attica in the southeast, Euboea in the northeast, Opuntian Locris (now part of Phthiotis) in the north and Phocis in the west. The main mountain ranges of Boeotia are Mount Parnassus in the west, Mount Helicon in the southwest, Cithaeron in the south and Parnitha in the east. Its longest river, the Cephissus, flows in the central part, where most of the low-lying areas of Boeotia are found. Lake Copais was a large lake in the center of Boeotia. It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corinthian Gulf
The Gulf of Corinth or the Corinthian Gulf ( el, Κορινθιακός Kόλπος, ''Korinthiakόs Kόlpos'', ) is a deep inlet of the Ionian Sea, separating the Peloponnese from western mainland Greece. It is bounded in the east by the Isthmus of Corinth which includes the shipping-designed Corinth Canal and in the west by the Strait of Rion which widens into the shorter Gulf of Patras (part of the Ionian Sea) and of which the narrowest point is crossed since 2004 by the Rio–Antirrio bridge. The gulf is bordered by the large administrative divisions (regional units): Aetolia-Acarnania and Phocis in the north, Boeotia in the northeast, Attica in the east, Corinthia in the southeast and south and Achaea in the southwest. The gulf is in tectonic movement comparable to movement in parts of Iceland and Turkey, growing by per year. In the Middle Ages, the gulf was known as the Gulf of Lepanto (the Italian form of Naupactus). Shipping routes between the Greek commercial port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peloponnesus
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, Πελοπόννησος, Pelopónnēsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridge which separates the Gulf of Corinth from the Saronic Gulf. From the late Middle Ages until the 19th century the peninsula was known as the Morea ( grc-x-byzant, Μωρέας), (Morèas) a name still in colloquial use in its demotic form ( el, Μωριάς, links=no), (Moriàs). The peninsula is divided among three administrative regions: most belongs to the Peloponnese region, with smaller parts belonging to the West Greece and Attica regions. Geography The Peloponnese is a peninsula located at the southern tip of the mainland, in area, and constitutes the southernmost part of mainland Greece. It is connected to the mainland by the Isthmus of Corinth, where the Corinth Canal was constructed in 1893. However, it is also connected to the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pausanias (geographer)
Pausanias ( /pɔːˈseɪniəs/; grc-gre, Παυσανίας; c. 110 – c. 180) was a Greek traveler and geographer of the second century AD. He is famous for his ''Description of Greece'' (, ), a lengthy work that describes ancient Greece from his firsthand observations. ''Description of Greece'' provides crucial information for making links between classical literature and modern archaeology. Biography Not much is known about Pausanias apart from what historians can piece together from his own writing. However, it is mostly certain that he was born c. 110 AD into a Greek family and was probably a native of Lydia in Asia Minor. From c. 150 until his death in 180, Pausanias travelled through the mainland of Greece, writing about various monuments, sacred spaces, and significant geographical sites along the way. In writing ''Description of Greece'', Pausanias sought to put together a lasting written account of "all things Greek", or ''panta ta hellenika''. Living in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megaris
:''This is also the ancient Greek name of a small island off Naples, site of the Castel dell'Ovo.'' Megaris ( grc, Μεγαρίς) was a small but populous state of ancient Greece, west of Attica and north of Corinthia, whose inhabitants were adventurous seafarers, credited with deceitful propensities. The capital, Megara, was famous for white marble and fine clay. Mount Geraneia dominates the center of the region. The island of Salamis was originally under the control of Megara, before it was lost to Athens in the late 7th century BCE. Province The province of Megaris or Megarida ( el, Επαρχία Μεγαρίδας or ) was one of the provinces of the East Attica Prefecture. Its territory corresponded with that of the current municipalities Aspropyrgos, Eleusis, Mandra-Eidyllia Mandra-Eidyllia ( el, Μάνδρα-Ειδύλλια) is a municipality in the West Attica regional unit, Attica, Greece. The seat of the municipality is the town Mandra. The municipality has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Cithaeron
Cithaeron or Kithairon (Κιθαιρών, -ῶνος) is a mountain and mountain range about sixteen kilometres (ten miles) long in Central Greece. The range is the physical boundary between Boeotia in the north and Attica in the south. It is mainly composed of limestone and rises to . The north-east side of the range is formed by the mountain Pastra. The range was the scene of many events in Greek mythology and was especially sacred to Dionysus. In Euripides' ''Bacchae'', Dionysus carries out his dances and rites with his bacchants, his priestesses, on Cithaeron. Oedipus was exposed on the mountain, while Actaeon and Pentheus were both dismembered on its slopes. It was also the place where Heracles or Alcathous hunted and killed the Lion of Cithaeron. In historic times, the mountain acted as a backdrop to the Battle of Plataea of 479 BC and was the scene of much skirmishing before the battle itself. In later times, fortifications were built both at Plataea and Erythrai as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aegosthena
Aigosthena ( grc, Αἰγόσθενα) was an ancient Greek fortified port city of Megaris, northwest of the ancient city of Megara to which it belonged. It is also the name of the coastal settlement at the foot of the ancient city walls, also known as Porto Germeno. The ancient citadel which stands at the foot of Mt Cithaeron and extends down to the sea at the inlet of Aigosthena, on the east side of the Gulf of Corinth, is famous for retaining several of the tallest surviving towers of ancient Greece. Geography Aigosthena is situated on the Alkyonides Gulf, a bay of the Gulf of Corinth. It is surrounded by forested mountains: the Cithaeron to the north and the Pateras to the south. Aigosthena was historically the northernmost city of the Megaris (Megarida). It is 10 km west of Vilia, 20 km southwest of Thebes northwest of Athens. Ancient Aigosthena The ancient site of Aigosthena consisted of a fortified citadel connected to the sea by two fortification walls; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Martin Leake
William Martin Leake (14 January 17776 January 1860) was an English military man, topographer, diplomat, antiquarian, writer, and Fellow of the Royal Society. He served in the British military, spending much of his career in the Mediterranean seaports. He developed an interest in geography and culture of the regions visited, and authored a number of works, mainly about Greece. Life He was born in London to John Martin Leake and Mary Calvert Leake. After completing his education at the Royal Military Academy, Woolwich, he was commissioned a 2nd Lieutenant in the Royal Regiment of Artillery in 1794. Having spent four years in the West Indies as lieutenant of marine artillery, he was promoted to captain, and was sent in 1799 by the government to Constantinople to train the forces of the Ottoman Empire in the use of artillery. The British Empire had decided to support the Ottoman in its defence against Napoleonic France. A journey through Asia Minor in 1800 to join the British ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement on the banks of the Eurotas River in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Given its military pre-eminence, Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city nevertheless ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |