|
Cresol Red
Cresol red (full name: ''o''-cresolsulfonephthalein) is a triarylmethane dye frequently used for monitoring the pH in aquaria. Molecular biology Cresol red can be used in many common molecular biology reactions in place of other loading dyes. Cresol Red does not inhibit ''Taq'' polymerase to the same degree as other common loading dyes. Color marker Cresol red can also be used as an electrophoretic color marker to monitor the process of agarose gel electrophoresis and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. In a 1% agarose gel, it runs approximately at the size of a 125 base pair (bp) DNA molecule (it depends on the concentration of buffer and other component). Bromophenol blue and xylene cyanol Xylene cyanol can be used as an electrophoretic color marker, or tracking dye, to monitor the process of agarose gel electrophoresis and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Bromophenol blue and orange G Orange G also called C.I. 16230, Acid ... can also be used for this purpose. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triarylmethane Dye
Triarylmethane dyes are synthetic organic compounds containing triphenylmethane backbones. As dyes, these compounds are intensely colored. They are produced industrially as dyes. Families Triarylmethane dyes can be grouped into families according to the nature of the substituents on the aryl groups. In some cases, the anions associated with the cationic dyes (say crystal violet) vary even though the name of the dye does not. Often it is shown as chloride. Methyl violet dyes Methyl violet dyes have dimethylamino groups at the ''p''-positions of two aryl groups. Image:Methyl Violet 2B.png, Methyl violet 2B Image:Methyl Violet 6B.png, Methyl violet 6B Image:Methyl Violet 10B.png, Methyl violet 10B Fuchsine dyes Fuchsine dyes have primary or secondary amines (NH2 or NHMe) functional groups at the ''p''-positions of each aryl group. File:Pararosaniline.png, Pararosaniline File:Rosaniline hydrochloride.svg, Fuchsine (hydrochloride salt) Neofuchsin.svg, New fuchsine (As chlorid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquarium
An aquarium (plural: ''aquariums'' or ''aquaria'') is a vivarium of any size having at least one transparent side in which aquatic plants or animals are kept and displayed. Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, aquatic reptiles, such as turtles, and aquatic plants. The term ''aquarium'', coined by English naturalist Philip Henry Gosse, combines the Latin root , meaning 'water', with the suffix , meaning 'a place for relating to'. The aquarium principle was fully developed in 1850 by the chemist Robert Warington, who explained that plants added to water in a container would give off enough oxygen to support animals, so long as the numbers of animals did not grow too large. The aquarium craze was launched in early Victorian England by Gosse, who created and stocked the first public aquarium at the London Zoo in 1853, and published the first manual, ''The Aquarium: An Unveiling of the Wonders of the Deep Sea'' in 1854.Katherine C. Grier (2008) "Pet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
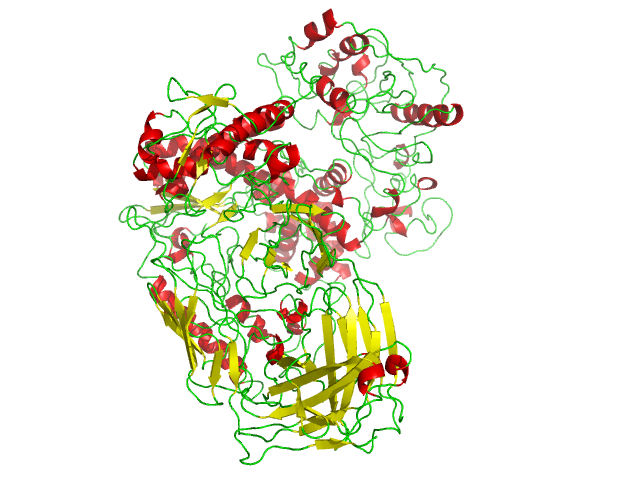
Taq Polymerase
''Taq'' polymerase is a thermostable DNA polymerase I named after the thermophilic eubacterial microorganism ''Thermus aquaticus,'' from which it was originally isolated by Chien et al. in 1976. Its name is often abbreviated to ''Taq'' or ''Taq'' pol. It is frequently used in the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), a method for greatly amplifying the quantity of short segments of DNA. ''T. aquaticus'' is a bacterium that lives in hot springs and hydrothermal vents, and ''Taq'' polymerase was identified as an enzyme able to withstand the protein-denaturing conditions (high temperature) required during PCR. Therefore, it replaced the DNA polymerase from '' E. coli'' originally used in PCR. Enzymatic properties ''Taqs optimum temperature for activity is 75–80 °C, with a half-life of greater than 2 hours at 92.5 °C, 40 minutes at 95 °C and 9 minutes at 97.5 °C, and can replicate a 1000 base pair strand of DNA in less than 10 seconds at 72 °C. At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrophoretic Color Marker
An electrophoretic color marker is used to monitor the progress of agarose gel electrophoresis and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) since DNA, RNA, and most proteins are colourless. They are also referred to as tracking dyes, and are frequently present in loading dyes as well as molecular weight ladders. Examples Commonly used color markers include Bromophenol blue, Cresol Red, Orange G and Xylene cyanol. Generally speaking, Orange G migrates faster than bromophenol blue, which migrates faster than xylene cyanol, but the apparent "sizes" of these dyes (compared to DNA molecules) varies with the concentration of agarose and the buffer system used. For instance, in a 1% agarose gel made in TAE buffer (Tris-acetate-EDTA), xylene cyanol migrates at the speed of a 3000 base pair (bp) molecule of DNA and bromophenol blue migrates at 400 bp. However, in a 1% gel made in TBE buffer (Tris-borate A borate is any of several boron oxyanions, negative ions consisting of boron and oxy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
Agarose gel electrophoresis is a method of gel electrophoresis used in biochemistry, molecular biology, genetics, and clinical chemistry to separate a mixed population of macromolecules such as DNA or proteins in a matrix of agarose, one of the two main components of agar. The proteins may be separated by charge and/or size (isoelectric focusing agarose electrophoresis is essentially size independent), and the DNA and RNA fragments by length. Biomolecules are separated by applying an electric field to move the charged molecules through an agarose matrix, and the biomolecules are separated by size in the agarose gel matrix. Agarose gel is easy to cast, has relatively fewer charged groups, and is particularly suitable for separating DNA of size range most often encountered in laboratories, which accounts for the popularity of its use. The separated DNA may be viewed with stain, most commonly under UV light, and the DNA fragments can be extracted from the gel with relative ease. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) is a technique widely used in biochemistry, forensic chemistry, genetics, molecular biology and biotechnology to separate biological macromolecules, usually proteins or nucleic acids, according to their electrophoretic mobility. Electrophoretic mobility is a function of the length, conformation, and charge of the molecule. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is a powerful tool used to analyze RNA samples. When polyacrylamide gel is denatured after electrophoresis, it provides information on the sample composition of the RNA species. Hydration of acrylonitrile results in formation of acrylamide molecules () by nitrile hydratase. Acrylamide monomer is in a powder state before addition of water. Acrylamide is toxic to the human nervous system, therefore all safety measures must be followed when working with it. Acrylamide is soluble in water and upon addition of free-radical initiators it polymerizes resulting in formation of polyacrylamide. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromophenol Blue
Bromophenol blue (3′,3″,5′,5″-tetrabromophenolsulfonphthalein, BPB), albutest is used as a pH indicator, an electrophoretic color marker, and a dye. It can be prepared by slowly adding excess bromine to a hot solution of phenolsulfonphthalein in glacial acetic acid. Acid–base indicator As an acid–base indicator, its useful range lies between pH 3.0 and 4.6. It changes from yellow at pH 3.0 to blue at pH 4.6; this reaction is reversible. Bromophenol blue is structurally related to phenolphthalein (a popular indicator). Color marker Bromophenol is also used as a colour marker to monitor the process of agarose gel electrophoresis and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Since bromophenol blue carries a slight negative charge at moderate pH, it will migrate in the same direction as DNA or protein in a gel; the rate at which it migrates varies according to gel density and buffer composition, but in a typical 1% agarose gel in a 1X TAE buffer or TBE buff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xylene Cyanol
Xylene cyanol can be used as an electrophoretic color marker, or tracking dye, to monitor the process of agarose gel electrophoresis and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Bromophenol blue and orange G Orange G also called C.I. 16230, Acid Orange 10, or orange gelb is a synthetic azo dye used in histology in many staining formulations. It usually comes as a disodium salt. It has the appearance of orange crystals or powder. Staining Orange G ... can also be used for this purpose. Once mixed with the sample, the concentration of xylene cyanol is typically about 0.005% to 0.03%. Migration speed In 1% agarose gels, xylene cyanol migrates at about the same rate as a 4 to 5 kilobase pair DNA fragment,{{cite book , author = Lela Buckingham and Maribeth L. Flaws , title = Molecular Diagnostics: Fundamentals, Methods, & Clinical Applications , url = https://archive.org/details/moleculardiagnos00lela , url-access = limited , publisher = F.A. Davis Company , date = 2007 , pag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenol Dyes
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns. Phenol was first extracted from coal tar, but today is produced on a large scale (about 7 billion kg/year) from petroleum-derived feedstocks. It is an important industrial commodity as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds. It is primarily used to synthesize plastics and related materials. Phenol and its chemical derivatives are essential for production of polycarbonates, epoxies, Bakelite, nylon, detergents, herbicides such as phenoxy herbicides, and numerous pharmaceutical drugs. Properties Phenol is an organic compound appreciably soluble in water, with about 84.2 g dissolving in 1000 mL (0.895 M). Homogeneous mixtures of phenol and water at phenol to wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |