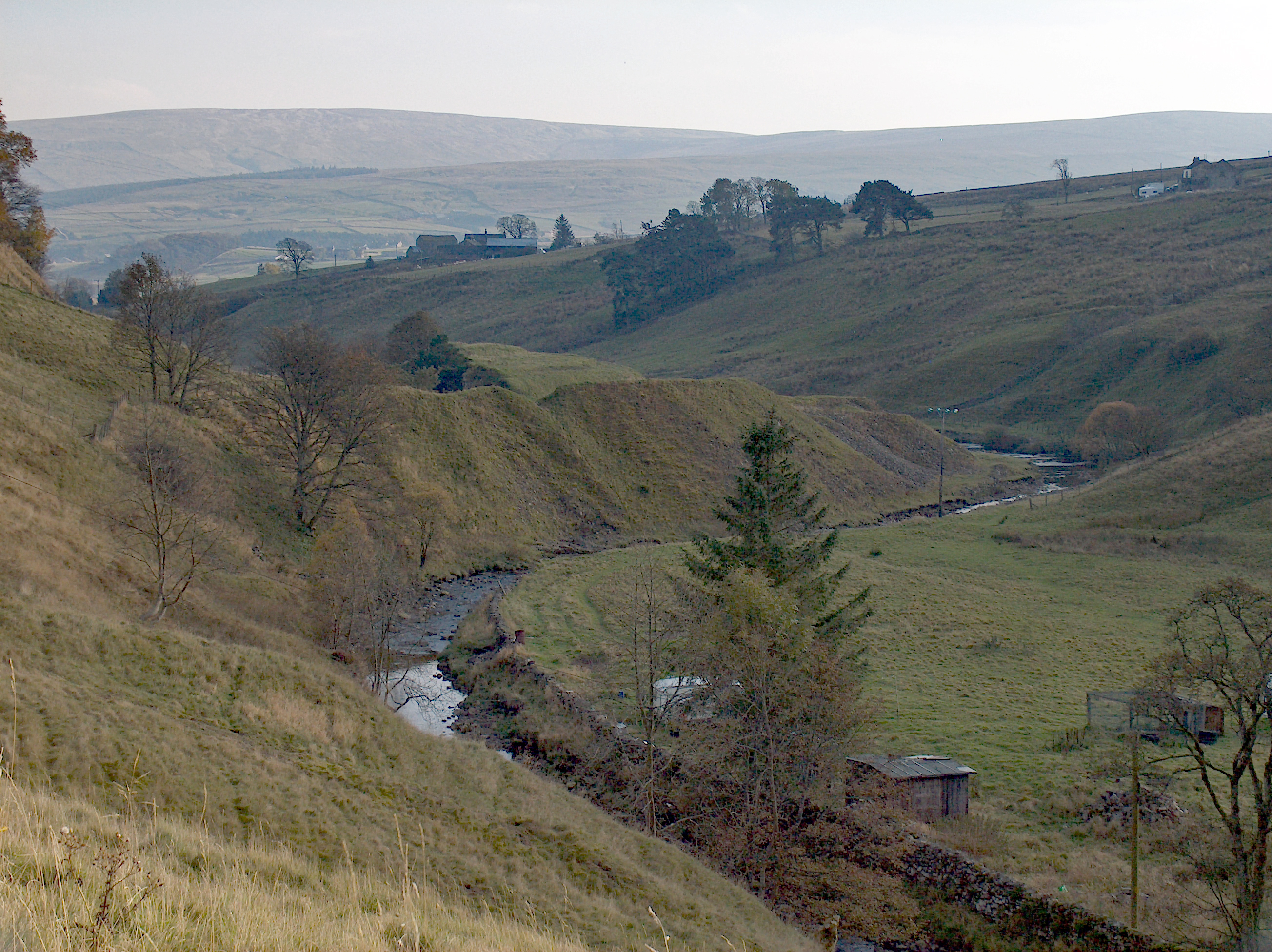
|
Crawley Edge Cairns
The Crawley Edge Cairns are a series of forty-two Bronze Age round barrows, cairns and clearance cairns located in a field in Crawleyside, near Stanhope, County Durham, England. The Cairnfield The cairnfield site lies on a gentle south-facing slope of a hill-spur in Weardale and remains in open moorland. Two of the cairns were excavated in 1977 and surveys undertaken in 1984 and 1991. The inclusion of clearance cairns at the site is usually taken as an indication of clearance in advance of arable farming, but the Crawley Edge field unusually includes a barrow cremation mound among the cairns. See also * History of County Durham * Bronze Age Britain Bronze Age Britain is an era of British history that spanned from until . Lasting for approximately 1,700 years, it was preceded by the era of Neolithic Britain and was in turn followed by the period of Iron Age Britain. Being categorised as t ... * Heathery Burn Cave References External linksYoung, R. 1984. PhD Thesis – ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Durham
County Durham ( ), officially simply Durham,UK General Acts 1997 c. 23Lieutenancies Act 1997 Schedule 1(3). From legislation.gov.uk, retrieved 6 April 2022. is a ceremonial county in North East England.North East Assembly �About North East England. Retrieved 30 November 2007. The ceremonial county spawned from the historic County Palatine of Durham in 1853. In 1996, the county gained part of the abolished ceremonial county of Cleveland.Lieutenancies Act 1997 . Retrieved 27 October 2014. The county town is the of |
Stanhope, County Durham
Stanhope is a market town and civil parish in the County Durham district, in the ceremonial county of Durham, England. It lies on the River Wear between Eastgate and Frosterley, in the north-east of Weardale. The main A689 road over the Pennines is crossed by the B6278 between Barnard Castle and Shotley Bridge. In 2001 Stanhope had a population of 1,633, in 2019 an estimate of 1,627, and a figure of 1,602 in the 2011 census for the ONS built-up-area which includes Crawleyside. In 2011 the parish population was 4,581. Civil parish The civil parish includes the settlements of Cornriggs, Cowshill, Daddry Shield, Eastgate, Frosterley, Ireshopeburn, Lanehead, St John's Chapel, Wearhead and Westgate, all on the A689 road, and also Bollihope, Bridge End, Brotherlee, Copthill, Crawleyside, East Blackdene, Hill End, Lintzgarth, New House, Rookhope and West Blackdene. Other places it includes are Killhope, Shittlehope, Unthank and White Kirkley. This gives it the lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Bronze Age
Bronze Age Britain is an era of British history that spanned from until . Lasting for approximately 1,700 years, it was preceded by the era of Neolithic Britain and was in turn followed by the period of Iron Age Britain. Being categorised as the Bronze Age, it was marked by the use of copper and then bronze by the prehistoric Britons, who used such metals to fashion tools. Great Britain in the Bronze Age also saw the widespread adoption of agriculture. During the British Bronze Age, large megalithic monuments similar to those from the Late Neolithic continued to be constructed or modified, including such sites as Avebury, Stonehenge, Silbury Hill and Must Farm. That has been described as a time "when elaborate ceremonial practices emerged among some communities of subsistence agriculturalists of western Europe". History Early Bronze Age (EBA), c. 2500–1500 BC There is no clear consensus on the date for the beginning of the Bronze Age in Great Britain and Ireland. Some sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Round Barrow
A round barrow is a type of tumulus and is one of the most common types of archaeological monuments. Although concentrated in Europe, they are found in many parts of the world, probably because of their simple construction and universal purpose. In Britain, most of them were built between 2200BC and 1100BC. This was the Late Neolithic period to the Late Bronze Age. Later Iron Age barrows were mostly different, and sometimes square. Description At its simplest, a round barrow is a hemispherical mound of earth and/or stone raised over a burial placed in the middle. Beyond this there are numerous variations which may employ surrounding ditches, stone kerbs or flat berms between ditch and mound. Construction methods range from a single creation process of heaped material to a complex depositional sequence involving alternating layers of stone, soil and turf with timbers or wattle used to help hold the structure together. The center may be placed a stone chamber or cist or in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cairn
A cairn is a man-made pile (or stack) of stones raised for a purpose, usually as a marker or as a burial mound. The word ''cairn'' comes from the gd, càrn (plural ). Cairns have been and are used for a broad variety of purposes. In prehistoric times, they were raised as markers, as memorials and as burial monuments (some of which contained chambers). In modern times, cairns are often raised as landmarks, especially to mark the summits of mountains. Cairns are also used as trail markers. They vary in size from small stone markers to entire artificial hills, and in complexity from loose conical rock piles to elaborate megalithic structures. Cairns may be painted or otherwise decorated, whether for increased visibility or for religious reasons. A variant is the inuksuk (plural inuksuit), used by the Inuit and other peoples of the Arctic region of North America. History Europe The building of cairns for various purposes goes back into prehistory in Eurasia, ranging in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clearance Cairn
A clearance cairn is an irregular and unstructured collection of fieldstones which have been removed from arable land or pasture to allow for more effective agriculture and collected into a usually low mound or cairn. Commonly of Bronze Age origins, these cairns may be part of a cairnfield (a collection of closely spaced cairns) where some cairns might be funerary. Clearance cairns are a worldwide phenomenon wherever organised agriculture has been practised. Purpose of clearance By removing large and moderate size stones from the surface and sub-surface, ploughing can take place with much less potential damage taking place to the plough blade. Stones also prevent the growth of plants where they physically block access to the soil and their removal allows for a greater surface area for crops to grow and to allow for plants to grow to their full potential; Stones also increase drainage and may therefore deprive plants of moisture. Stones were removed from fields to allow for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crawleyside
Crawleyside is a village in County Durham, in England. It is situated to the north of Stanhope, in Weardale. In the 2001 census Crawleyside had a population of 170. The Crawley Edge Cairns, in a field to the west of the village are a series of forty-two Bronze Age cairn A cairn is a man-made pile (or stack) of stones raised for a purpose, usually as a marker or as a burial mound. The word ''cairn'' comes from the gd, càrn (plural ). Cairns have been and are used for a broad variety of purposes. In prehis ...s. References External links Villages in County Durham Stanhope, County Durham {{Durham-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weardale
Weardale is a dale, or valley, on the east side of the Pennines in County Durham, England. Large parts of Weardale fall within the North Pennines Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB) – the second-largest AONB in England and Wales. The upper dale is surrounded by high fells (up to O.D. at Burnhope Seat) and heather grouse moors. The River Wear flows through Weardale before reaching Bishop Auckland and then Durham, meeting the sea at Sunderland. The Wear Valley local government district covered the upper part of the dale, including Weardale, between 1974 and 2009, when it was abolished on County Durham's becoming a unitary authority. (From 1894 to 1974 there was a Weardale Rural District.) Upper Weardale is in the parliamentary constituency of North West Durham. The dale's principal settlements include St John's Chapel and the towns of Crook, Stanhope and Wolsingham. Local climate Weardale's winters are typically harsh and prolonged with regular snow, nowadays ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Round Barrow
A round barrow is a type of tumulus and is one of the most common types of archaeological monuments. Although concentrated in Europe, they are found in many parts of the world, probably because of their simple construction and universal purpose. In Britain, most of them were built between 2200BC and 1100BC. This was the Late Neolithic period to the Late Bronze Age. Later Iron Age barrows were mostly different, and sometimes square. Description At its simplest, a round barrow is a hemispherical mound of earth and/or stone raised over a burial placed in the middle. Beyond this there are numerous variations which may employ surrounding ditches, stone kerbs or flat berms between ditch and mound. Construction methods range from a single creation process of heaped material to a complex depositional sequence involving alternating layers of stone, soil and turf with timbers or wattle used to help hold the structure together. The center may be placed a stone chamber or cist or in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of County Durham
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age Britain
Bronze Age Britain is an era of British history that spanned from until . Lasting for approximately 1,700 years, it was preceded by the era of Neolithic Britain and was in turn followed by the period of Iron Age Britain. Being categorised as the Bronze Age, it was marked by the use of copper and then bronze by the prehistoric Britons, who used such metals to fashion tools. Great Britain in the Bronze Age also saw the widespread adoption of agriculture. During the British Bronze Age, large megalithic monuments similar to those from the Late Neolithic continued to be constructed or modified, including such sites as Avebury, Stonehenge, Silbury Hill and Must Farm. That has been described as a time "when elaborate ceremonial practices emerged among some communities of subsistence agriculturalists of western Europe". History Early Bronze Age (EBA), c. 2500–1500 BC There is no clear consensus on the date for the beginning of the Bronze Age in Great Britain and Ireland. Some sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heathery Burn Cave
Heathery Burn Cave is a cave near Stanhope, County Durham, England, in which a large collection of Late Bronze Age weapons and tools was discovered and excavated between 1859 and 1872. Location The cave was in a ravine formed by Stanhope Burn, a small tributary of the River Wear.Greenwell, W. 1894. "Antiquities of the Bronze Age found in the Heathery Burn Cave, County Durham", ''Archaeologia'' (2nd Series, 4), 87–114. The cave itself was about a mile north of the confluence of the burn and the river, on the left bank. The floor of the cave was above the level of the burn, and was a tourist destination before the quarrying of the limestone for smelting purposes. The cave has subsequently been destroyed.Britton, D. 1971. "The Heathery Burn Cave Revisited: Towards the Reconstruction of a Well-Known Archaeological Discovery", ''The British Museum Quarterly'' 35 (1/4), 20–38. Geology The geology of the area forms part of the Yoredale Group of limestone with subordinate sandsto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)