|
Craig AFB
Craig Air Force Base near Selma, Alabama, was a U.S. Air Force undergraduate pilot training (UPT) installation that closed in 1977. Today the facility is a civilian airport known as Craig Field Airport and Industrial Complex (ICAO: KSEM; FAA: SEM). History World War II Originally built by the U.S. Army Air Force in 1940 to accommodate the growing number of flight trainees before World War II, Craig Field was one of the first training fields to offer single-engine training. Its first graduating class of 1941, the 39 cadets of Class 41D, completed the training course seven months before the United States' entry into World War II. The naming of the base was important to the nearby city of Selma, and several names were considered. The name finally chosen was to honor 1st Lt Bruce Kilpatrick Craig, who was killed when his B-24 crashed in June 1941. He was born in Selma and was initially commissioned as an officer in the Infantry Reserve prior to transferring to the Army Air Force an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Craig Field Alabama 1942 Photo Pictorial
__NOTOC__ Craig may refer to: Geology *Craig (landform), a rocky hill or mountain often having large casims or sharp intentations. People (and fictional characters) * Craig (surname) * Craig (given name) Places Scotland *Craig, Angus, aka Barony of Craigie United States *Craig, Alaska, a city *Craig, Colorado, a city * Craig, Indiana, an unincorporated place * Craig, Iowa, a city *Craig, Missouri, a city * Craig, Montana, an unincorporated place *Craig, Nebraska, a village *Craig, Ohio, an unincorporated community *Craig County, Virginia *Craig County, Oklahoma *Craig Township (other) (two places) Other uses *Craig (song) *Craig Electronics, a consumer electronics company * Craig Broadcast Systems, later Craig Media and finally Craig Wireless, a defunct Canadian media and communication company *Clan Craig, a Scottish clan *Craig tube, a piece of scientific apparatus See also *'' Craig v. Boren'', a U.S. Supreme Court case * Justice Craig (other) *Craic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing B-52 Stratofortress
The Boeing B-52 Stratofortress is an American long-range, subsonic, jet-powered strategic bomber. The B-52 was designed and built by Boeing, which has continued to provide support and upgrades. It has been operated by the United States Air Force (USAF) since the 1950s. The bomber is capable of carrying up to 70,000 pounds (32,000 kg) of weapons,"Fact Sheet: B-52 Superfortress." ''Minot Air Force Base'', United States Air Force, October 2005. Retrieved: 12 January 2009. and has a typical combat range of around 8,800 miles (14,080 km) without aerial refueling. Beginning with the successful contract bid in June 1946, the B-52 design evolved from a [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
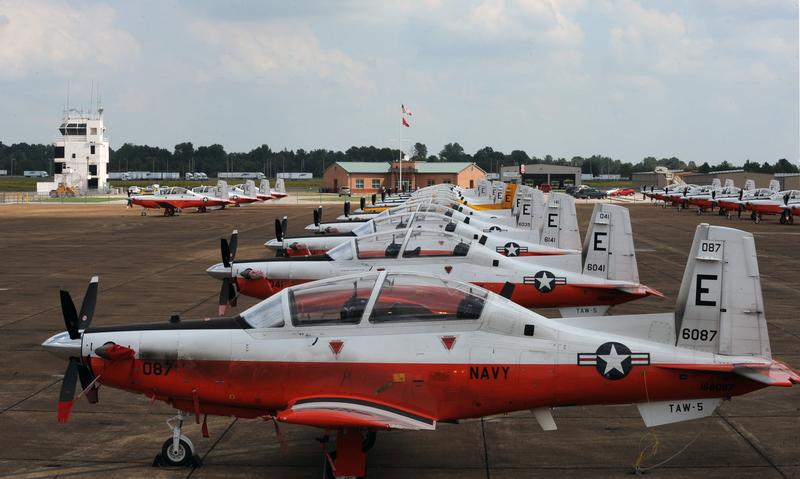
T-6A
The Beechcraft T-6 Texan II is a single-engine turboprop aircraft built by the Raytheon Aircraft Company (Textron Aviation since 2014). A trainer aircraft based on the Pilatus PC-9, the T-6 has replaced the United States Air Force's Cessna T-37B Tweet and the United States Navy's T-34C Turbo Mentor. The T-6A is used by the United States Air Force for basic pilot training and Combat Systems Officer (CSO) training, the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps for primary Naval Aviator training and primary and intermediate Naval Flight Officer (NFO) training, and by the Royal Canadian Air Force (CT-156 Harvard II designation), Greek Air Force, Israeli Air Force (with the "Efroni" nickname), and Iraqi Air Force for basic flight training. The T-6B is the primary trainer for U.S. student naval aviators (SNAs). The T-6C is used for training by the Mexican Air Force, Royal Air Force, Royal Moroccan Air Force, and the Royal New Zealand Air Force. Design and development Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
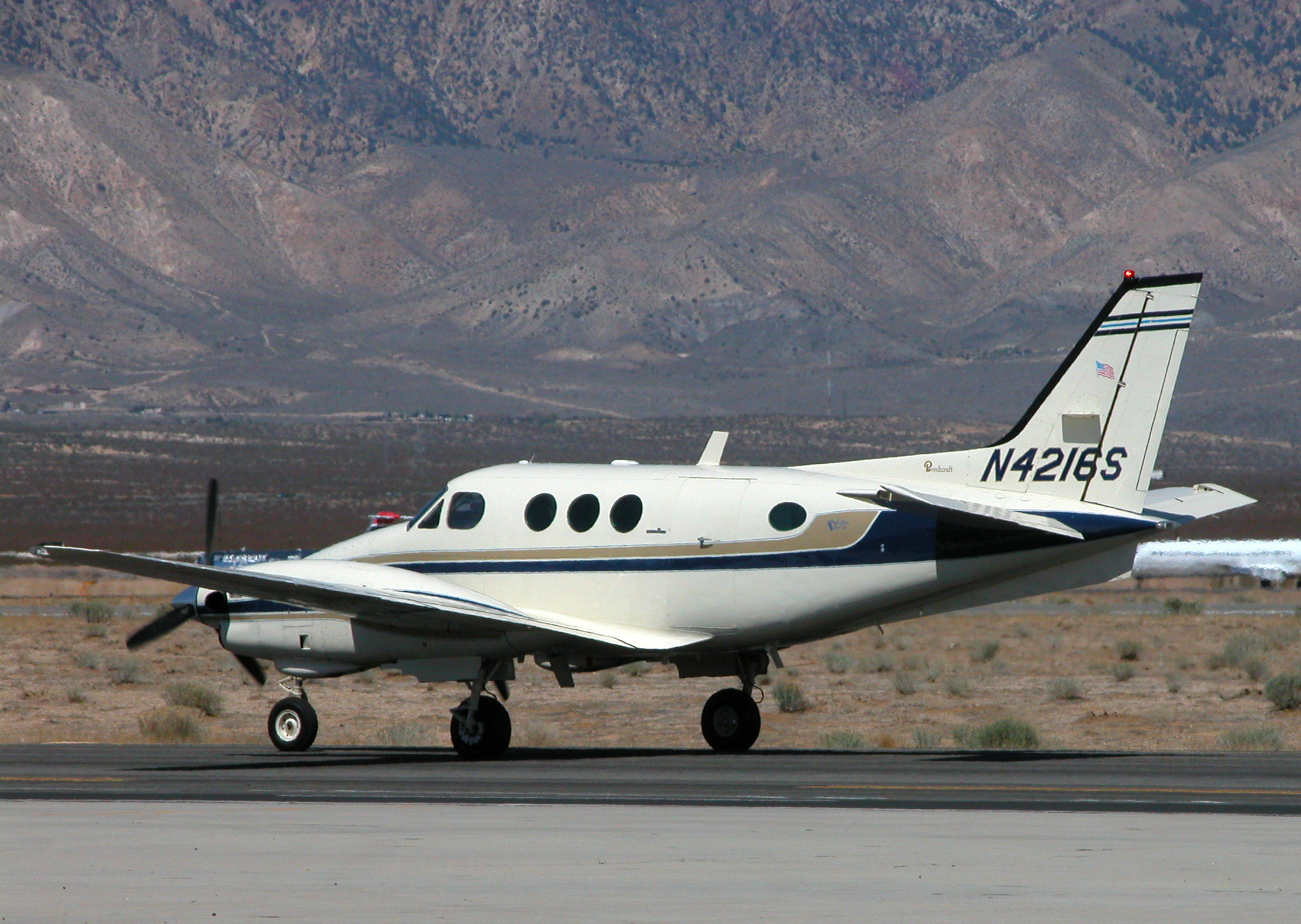
Beechcraft C-12 Huron
The Beechcraft C-12 Huron is the military designation for a series of twin-engine turboprop aircraft based on the Beechcraft Super King Air and Beechcraft 1900. C-12 variants are used by the United States Air Force, United States Army, United States Navy and United States Marine Corps. These aircraft are used for various duties, including embassy support, medical evacuation, as well as passenger and light cargo transport. Some aircraft are modified with surveillance systems for various missions, including the Cefly Lancer, Beechcraft RC-12 Guardrail and Project Liberty programs. Design and development The first C-12A models entered service with the U.S. Army in 1974 and were used as a liaison and general personnel transport. The aircraft was essentially an "off-the-shelf" Super King Air 200, powered by the type's standard Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6A-41 engines. The U.S. Navy followed suit in 1979, ordering a version of the Super King Air A200C (modified with a 1.32 m by 1.32 m; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beechcraft King Air
The Beechcraft King Air is a line of American utility aircraft produced by Beechcraft. The King Air line comprises a number of twin-turboprop models that have been divided into two families. The Model 90 and 100 series developed in the 1960s are known as King Airs, while the later T-tail Model 200 and 300 series were originally marketed as Super King Airs, with the name "Super" being dropped by Beechcraft in 1996 (although it is still often used to differentiate the 200 and 300 series King Airs from their smaller stablemates). The King Air was the first aircraft in its class and was produced continuously from 1964 to 2021. It outsold all of its turboprop competitors combined. It has recently faced competition from jet aircraft such as the Embraer Phenom 100, Honda HA-420 HondaJet and Cessna Citation Mustang; as well as from newer turboprop aircraft including the Piaggio P180 Avanti, and single-engine Piper Malibu Meridian, Pilatus PC-12, and Socata TBM. Development Mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
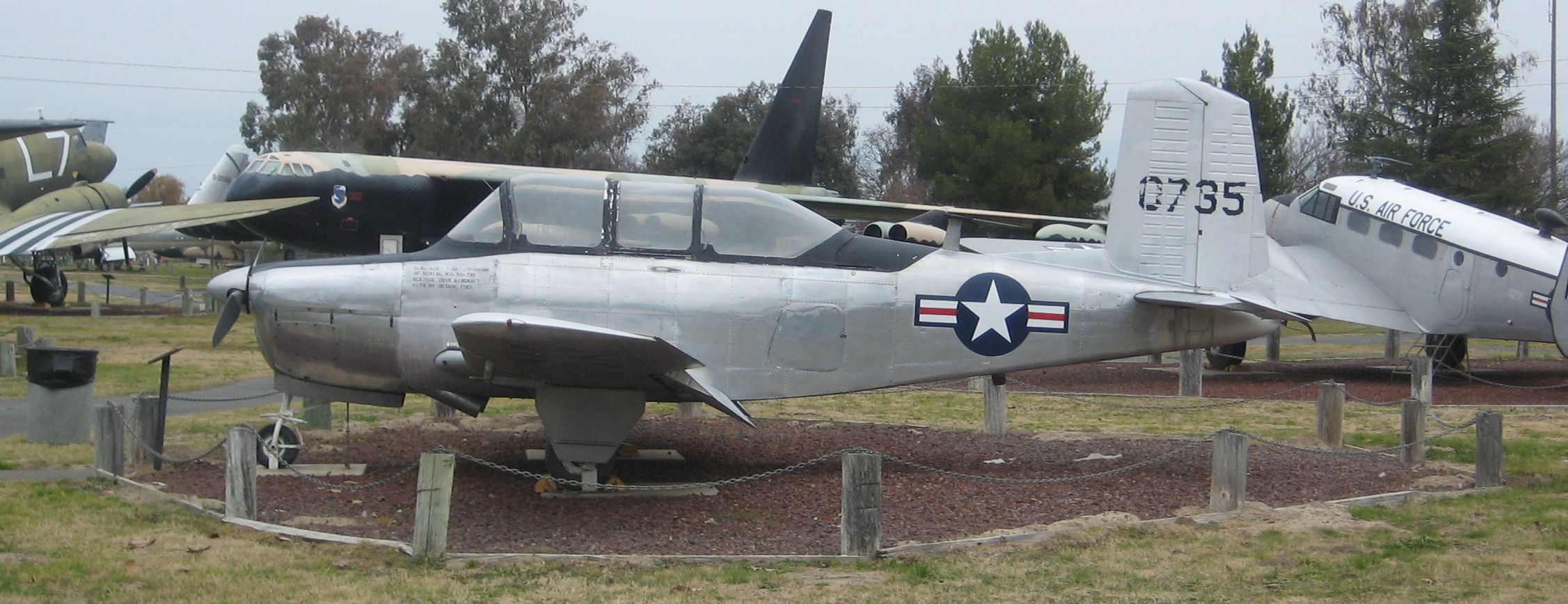
Beechcraft T-34 Mentor
The Beechcraft T-34 Mentor is an American propeller-driven, single-engined, military trainer aircraft derived from the Beechcraft Model 35 Bonanza. The earlier versions of the T-34, dating from around the late 1940s to the 1950s, were piston-engined. These were eventually succeeded by the upgraded T-34C Turbo-Mentor, powered by a turboprop engine. The T-34 remains in service more than seven decades after it was first designed. Design and development The T-34 was the brainchild of Walter Beech, who developed it as the Beechcraft Model 45 private venture at a time when there was no defense budget for a new trainer model. Beech hoped to sell it as an economical alternative to the North American T-6/SNJ Texan, then in use by all services of the U.S. military. Three initial design concepts were developed for the Model 45, including one with the Bonanza's signature V-tail, but the final design that emerged in 1948 incorporated conventional tail control surfaces for the benefit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L3 Technologies
L3 Technologies, formerly L-3 Communications Holdings, was an American company that supplied command and control, communications, Intelligence (information gathering), intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance (C3ISR) systems and products, avionics, ocean products, training devices and services, instrumentation, aerospace, and navigation products. Its customers included the United States Department of Defense, Department of Defense, Department of Homeland Security, United States Intelligence Community, NASA, aerospace contractors, and commercial telecommunications and wireless customers. In 2019, it merged with Harris Corporation and was renamed to L3Harris Technologies. L3 was headquartered in Murray Hill, Manhattan, New York City. History L3 was formed as L-3 Communications in 1997 to acquire certain business units from Lockheed Martin that had previously been part of Loral Corporation. These units had belonged to Lockheed Corporation and Martin Marietta, which had merge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
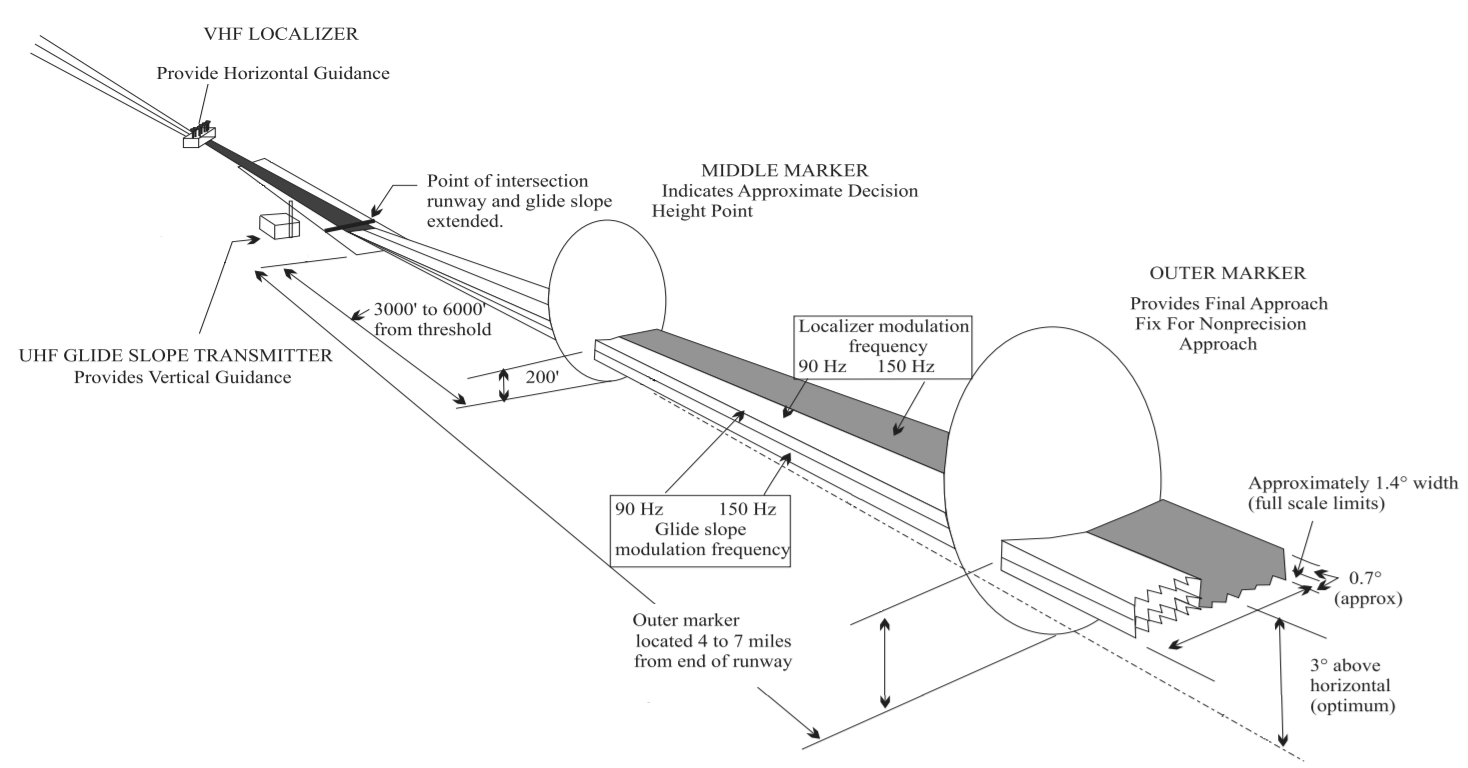
Instrument Landing System
In aviation, the instrument landing system (ILS) is a precision radio navigation system that provides short-range guidance to aircraft to allow them to approach a runway at night or in bad weather. In its original form, it allows an aircraft to approach until it is over the ground, within a of the runway. At that point the runway should be visible to the pilot; if it is not, they perform a missed approach. Bringing the aircraft this close to the runway dramatically increases the range of weather conditions in which a safe landing can be made. Other versions of the system, or "categories", have further reduced the minimum altitudes, runway visual ranges (RVRs), and transmitter and monitoring configurations designed depending on the normal expected weather patterns and airport safety requirements. ILS uses two directional radio signals, the ''localizer'' (108 to 112 MHz frequency), which provides horizontal guidance, and the ''glideslope'' (329.15 to 335 MHz frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VORTAC
Very high frequency omnirange station (VOR) is a type of short-range radio navigation system for aircraft, enabling aircraft with a receiving unit to determine its position and stay on course by receiving radio signals transmitted by a network of fixed ground radio beacons. It uses frequencies in the very high frequency (VHF) band from 108.00 to 117.95 MHz. Developed in the United States beginning in 1937 and deployed by 1946, VOR became the standard air navigational system in the world,VOR VHF omnidirectional Range , Aviation Tutorial – Radio Navaids, kispo.net used by both commercial and general aviation, until supplanted by satellite navigation systems such as in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNICOM
A UNICOM (universal communications) station is an air-ground communication facility operated by a non-air traffic control private agency to provide advisory service at uncontrolled aerodromes and airports and to provide various non-flight services, such as requesting a taxi, even at towered airports. It is also known as an ''aeronautical advisory station''. The equivalent European/ICAO service is known as ''(aerodrome) flight information service'', abbreviated as AFIS or FIS. Description UNICOM is employed at airports with a low volume of general aviation traffic and where no control tower is active. UNICOM stations typically use a single communications frequency. Some airfields always offer UNICOM service while others revert to UNICOM procedures only during hours when the control tower is closed. Under this protocol, aircraft may call a non-government ground station to make announcements of their intentions. Pilots who join the frequency later can request field advisories, which m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Webb Air Force Base
Webb Air Force Base , previously named Big Spring Air Force Base, was a United States Air Force facility of the Air Training Command that operated from 1951 to 1977 in West Texas within the current city limits of Big Spring. Webb AFB was a major undergraduate pilot training (UPT) facility for the Air Force, and by 1969, almost 9,000 pilots had been trained at Webb. The last operational wing at Webb AFB was the 78th Flying Training Wing. History World War II The facility first was used by the United States Army Air Forces as Big Spring Army Air Field, opening on 28 April 1942 as part of the Central Flying Training Command. Activated on 26 June 1942, the mission of Big Spring AAF was to train aviation cadets in high-altitude precision bombing as bombardiers. It was one of the "West Texas Bombardier Quadrangle" schools of the Army Air Forces Training Command. The other bases in the quad were Midland Army Airfield, San Angelo Army Airfield, and Childress Army Airfield. Const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Iranian Air Force
The history of the Iranian Air Force, currently known as the Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force, can be divided into two phases—before the Islamic Revolution, and after it. Imperial era The Imperial Iranian Air Force (IIAF) was a branch of the Imperial Iranian Armed Forces and was established by Reza Shah, the Shah of Iran, in 1920. It became operational with its first fully trained pilots on February 25, 1925. Iran's first attempt to procure aircraft from the United States in the 1920s failed due to Washington's refusal to supply equipment because of a World War I treaty. Until World War II, the IIAF's aircraft inventory consisted entirely of European aircraft, mainly British and German. However, following a coordinated United Kingdom, British and Soviet Union, Soviet Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran, invasion of Iran during World War II in response to Reza Shah's declaration of neutrality, the IIAF's bases were occupied by the Allies and all existing IIAF aircraft were eit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


%2C_USA_-_Army_AN2087007.jpg)