|
Cowboy Halls Of Fame
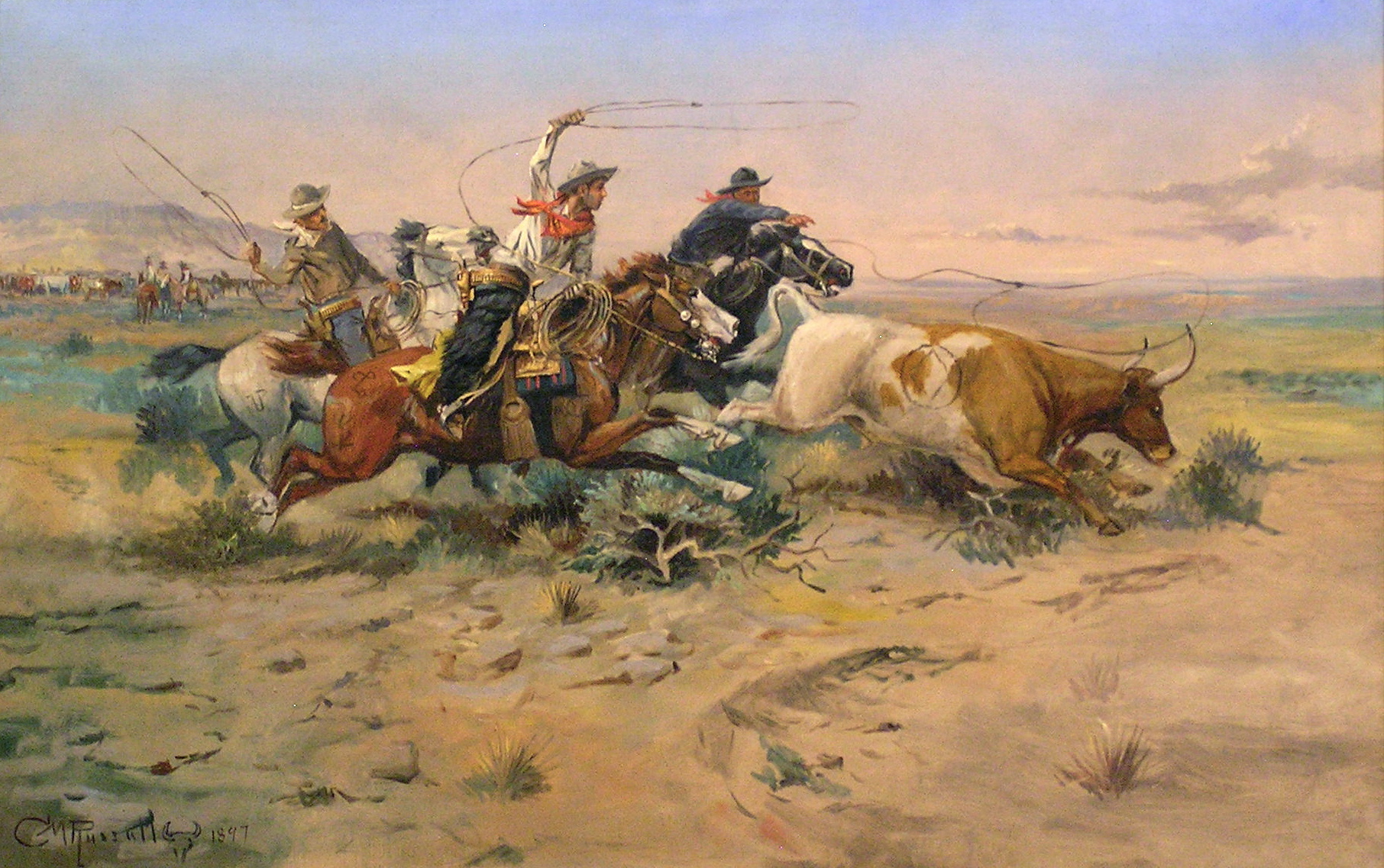
A cowboy is an animal herder who tends cattle on ranches in North America, traditionally on horseback, and often performs a multitude of other ranch-related tasks. The historic American cowboy of the late 19th century arose from the ''vaquero'' traditions of northern Mexico and became a figure of special significance and legend.Malone, J., p. 1. A subtype, called a Wrangler (profession), wrangler, specifically tends the horses used to work cattle. In addition to ranch work, some cowboys work for or participate in rodeos. Cowgirls, first defined as such in the late 19th century, had a less-well documented historical role, but in the modern world work at identical tasks and have obtained considerable respect for their achievements. Cattle handlers in many other parts of the world, particularly South America and Australia, perform work similar to the cowboy. The cowboy has deep historic roots tracing back to Spain and the earliest European Settlement of the Americas, settlers of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jonathan Swift
Jonathan Swift (30 November 1667 – 19 October 1745) was an Anglo-Irish Satire, satirist, author, essayist, political pamphleteer (first for the Whig (British political party), Whigs, then for the Tories (British political party), Tories), poet, and Anglican cleric who became Dean (Christianity), Dean of St Patrick's Cathedral, Dublin, hence his common sobriquet, "Dean Swift". Swift is remembered for works such as ''A Tale of a Tub'' (1704), ''An Argument Against Abolishing Christianity'' (1712), ''Gulliver's Travels'' (1726), and ''A Modest Proposal'' (1729). He is regarded by the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' as the foremost prose satirist in the English language, and is less well known for his poetry. He originally published all of his works under pseudonyms—such as Lemuel Gulliver, Isaac Bickerstaff, M. B. Drapier—or anonymously. He was a master of two styles of satire, the Satire#Classifications, Horatian and Juvenalian styles. His deadpan, ironic writing style, partic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), gaining independence from the British Crown and establishing the United States of America as the first nation-state founded on Enlightenment principles of liberal democracy. American colonists objected to being taxed by the Parliament of Great Britain, a body in which they had no direct representation. Before the 1760s, Britain's American colonies had enjoyed a high level of autonomy in their internal affairs, which were locally governed by colonial legislatures. During the 1760s, however, the British Parliament passed a number of acts that were intended to bring the American colonies under more direct rule from the British metropole and increasingly intertwine the economies of the colonies with those of Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developing Country
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreement on which countries fit this category. The term low and middle-income country (LMIC) is often used interchangeably but refers only to the economy of the countries. The World Bank classifies the world's economies into four groups, based on gross national income per capita: high, upper-middle, lower-middle, and low income countries. Least developed countries, landlocked developing countries and small island developing states are all sub-groupings of developing countries. Countries on the other end of the spectrum are usually referred to as high-income countries or developed countries. There are controversies over this term's use, which some feel it perpetuates an outdated concept of "us" and "them". In 2015, the World Bank declared that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient History
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population stood at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donkey
The domestic donkey is a hoofed mammal in the family Equidae, the same family as the horse. It derives from the African wild ass, ''Equus africanus'', and may be classified either as a subspecies thereof, ''Equus africanus asinus'', or as a separate species, ''Equus asinus''. It was domesticated in Africa some years ago, and has been used mainly as a working animal since that time. There are more than 40 million donkeys in the world, mostly in underdeveloped countries, where they are used principally as draught or pack animals. While working donkeys are often associated with those living at or below subsistence, small numbers of donkeys or asses are kept for breeding or as pets in developed countries. A male donkey is known as a ''jack'' or ''jackass'', a female is a ''jenny'' or ''jennet'', and an immature donkey of either sex is a '' foal''. Jacks are often mated with female horses (mares) to produce '' mules''; the less common hybrid of a male horse (stallion) and j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equestrianism
Equestrianism (from Latin , , , 'horseman', 'horse'), commonly known as horse riding (Commonwealth English) or horseback riding (American English), includes the disciplines of riding, Driving (horse), driving, and Equestrian vaulting, vaulting. This broad description includes the use of horses for practical working animal, working purposes, transportation, recreational activities, artistic or cultural exercises, and animals in sport, competitive sport. Overview of equestrian activities Horses are horse training, trained and ridden for practical working purposes, such as in Mounted police, police work or for controlling herd animals on a ranch. They are also used in Horse#Sport, competitive sports including dressage, endurance riding, eventing, reining, show jumping, tent pegging, equestrian vaulting, vaulting, polo, horse racing, driving (horse), driving, and rodeo (see additional equestrian sports listed later in this article for more examples). Some popular forms of competi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by both List of U.S. states and territories by area, area (after Alaska) and List of U.S. states and territories by population, population (after California). Texas shares borders with the states of Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the west, and the Mexico, Mexican States of Mexico, states of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León, and Tamaulipas to the south and southwest; and has a coastline with the Gulf of Mexico to the southeast. Houston is the List of cities in Texas by population, most populous city in Texas and the List of United States cities by population, fourth-largest in the U.S., while San Antonio is the second most pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territories of the United States by population, most populous U.S. state and the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 3rd largest by area. It is also the most populated Administrative division, subnational entity in North America and the 34th most populous in the world. The Greater Los Angeles area and the San Francisco Bay Area are the nation's second and fifth most populous Statistical area (United States), urban regions respectively, with the former having more than 18.7million residents and the latter having over 9.6million. Sacramento, California, Sacramento is the state's capital, while Los Angeles is the List of largest California cities by population, most populous city in the state and the List of United States cities by population, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
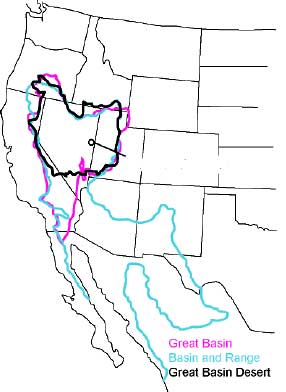
Great Basin
The Great Basin is the largest area of contiguous endorheic basin, endorheic watersheds, those with no outlets, in North America. It spans nearly all of Nevada, much of Utah, and portions of California, Idaho, Oregon, Wyoming, and Baja California. It is noted for both its arid climate and the basin and range topography that varies from the North American low point at Badwater Basin in Death Valley to the highest point of the contiguous United States, less than away at the summit of Mount Whitney. The region spans several physical geography, physiographic divisions, biomes, ecoregions, and deserts. Definition The term "Great Basin" is applied to hydrography, hydrographic, ecology, biological, floristic province, floristic, physiographic, topography, topographic, and Ethnography, ethnographic geographic areas. The name was originally coined by John C. Frémont, who, based on information gleaned from Joseph R. Walker as well as his own travels, recognized the hydrographic nature o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in the southwestern United States. Depending on differing definitions between Canada and the U.S., its northern terminus is located either in northern British Columbia's Terminal Range south of the Liard River and east of the Trench, or in the northeastern foothills of the Brooks Range/ British Mountains that face the Beaufort Sea coasts between the Canning River and the Firth River across the Alaska-Yukon border. Its southernmost point is near the Albuquerque area adjacent to the Rio Grande rift and north of the Sandia–Manzano Mountain Range. Being the easternmost portion of the North American Cordillera, the Rockies are distinct from the tectonically younger Cascade Range and Sierra Nevada, which both lie farther to its west. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, and grassland. It is the southern and main part of the Interior Plains, which also include the tallgrass prairie between the Great Lakes and Appalachian Plateau, and the Taiga Plains and Boreal Plains ecozones in Northern Canada. The term Western Plains is used to describe the ecoregion of the Great Plains, or alternatively the western portion of the Great Plains. The Great Plains lies across both Central United States and Western Canada, encompassing: * The entirety of the U.S. states of Kansas, Nebraska, North Dakota and South Dakota; * Parts of the U.S. states of Colorado, Iowa, Minnesota, Missouri, Montana, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Texas and Wyoming; * The southern portions of the Canadian provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)