|
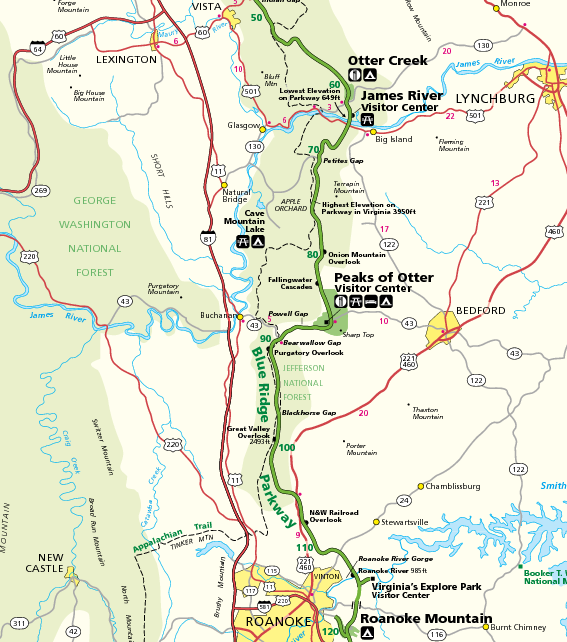
Cove Mountain, Virginia
Cove Mountain is a wildland in the George Washington and Jefferson National Forests of western Virginia that has been recognized by the Wilderness Society as a special place worthy of protection from logging and road construction.Virginia's Mountain Treasures, report issued by The Wilderness Society, May, 1999 The wild area includes a seven-mile section of the Appalachian Trail with four miles following along Cove Mountain ridge. There are excellent winter views of Flat Top Mountain, Sharp Top and Peaks of Otter to the east. The area contains the headwaters of prime trout fisheries. The area is part of the Glenwood Cluster. Location and access The area is located in the Appalachian Mountains of Southwestern Virginia about 4 miles east of Buchanan, Virginia, between the James River on the north, Va 43 on the west, the Blue Ridge Parkway on the south and McFalls Creek Rd (Va 618) on the east. The Forest Service 2015 Motor Vehicle Use Map shows roads and trails in the forest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Washington And Jefferson National Forests
The George Washington and Jefferson National Forests is an administrative entity combining two U.S. National Forests into one of the largest areas of public land in the Eastern United States. The forests cover of land in the Appalachian Mountains of Virginia, West Virginia, and Kentucky. Approximately of the forest are remote and undeveloped and have been designated as wilderness areas, which prohibits future development. History George Washington National Forest was established on May 16, 1918, as the Shenandoah National Forest. The forest was renamed after the first President on June 28, 1932. Natural Bridge National Forest was added on July 22, 1933. Jefferson National Forest was formed on April 21, 1936, by combining portions of the Unaka and George Washington National Forests with other land. In 1995, the George Washington and Jefferson National Forests were administratively combined. The border between the two forests roughly follows the James River. The combine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inventoried Roadless Area
Inventoried Roadless Areas are a group of United States Forest Service lands that have been identified by government reviews as lands without existing roads that could be suitable for roadless area conservation as wilderness or other non-standard protections. The Inventoried Roadless areas include approximately of land in 40 states and Puerto Rico. Most of these lands are in the western portion of the lower 48 states and Alaska.Maps of inventoried roadless areasUS Forest Service Maps Idaho alone contains over of inventoried roadless areas. The inventoried roadless areas range from large areas with wilderness characteristics to small tracts of land that are immediately adjacent to wilderness areas, parks and other protected lands. Roadless Area Review and Evaluations (RARE) The first review of Forest Service roadless lands was started in 1967 after the creation of the Wilderness Act by Congress in 1964. This effort was called the “Roadless Area Review and Evaluation” or “ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Creek (conservation Area)
North Creek (conservation area) is a wildland in the George Washington and Jefferson National Forests of western Virginia that has been recognized by the Wilderness Society as a special place worthy of protection from logging and road construction. Tall evergreen and hardwood trees in the area around Apple Orchard Falls tower above ferns and wildflowers.Virginia's Mountain Treasures, report issued by The Wilderness Society, May, 1999 The area includes a valley which extends from Sunset Fields in the east to its western border near the North Creek Camping Area. The area is part of the Glenwood Cluster. Location and access The area, located in the Appalachian Mountains of Southwestern Virginia about 7 miles northeast of Buchanan, Virginia, is between the Blue Ridge Parkway on the east, Middle Creek Road (Rt. 3101) on the west and Parkers Gap Road (Va 612) on the north. The Forest Service 2015 Motor Vehicle Use Map shows roads and trails in the forest and gives the type of vehic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Oak Ridge-Terrapin Mountain
White Oak Ridge-Terrapin Mountain is a wildland in the George Washington and Jefferson National Forests of western Virginia that has been recognized by the Wilderness Society as a special place worthy of protection from logging and road construction. With over 1200 acres of possible old growth forest, this is a rugged area with a rich diversity of geology and plant life.Virginia's Mountain Treasures, report issued by The Wilderness Society, May, 1999 The area is part of the ''Glenwood Cluster''. Location and access The area is located in the Appalachian Mountains of Southwestern Virginia about 10 miles south of Glasgow, Virginia. The area is bounded by the Blue Ridge Parkway on the northwest and Va 602 (Hunting Camp Creek Road) on the east. Good access is gained from Va 602. The Forest Service has issued a document entitled "Motor Vehicle Use Map" dated January 1, 2015. The document is a set of 56 maps covering the George Washington and Jefferson National Forest. The maps sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James River Face Wilderness Addition
James River Face Wilderness Addition is a wildland in the George Washington and Jefferson National Forests of western Virginia that has been recognized by the Wilderness Society as a special place worthy of protection from logging and road construction. Adjacent to the James River Face Wilderness, it extends the wildland opportunities of the wilderness on the east to the Jefferson National Forest boundary.Virginia's Mountain Treasures, report issued by The Wilderness Society, May, 1999 The area, managed for bear, has hardwood forests with ages between 60 and almost 100 years. The area is part of the Glenwood Cluster. Location and access The area is located in the Appalachian Mountains of Southwestern Virginia about 6 miles south of Glasgow, Virginia, between the James River Wilderness on the west, the Blue Ridge Parkway on the east, and Hunt Club Road (FS 54) on the southwest. The Forest Service 2015 Motor Vehicle Use Map shows roads and trails in the forest and gives the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thunder Ridge Wilderness
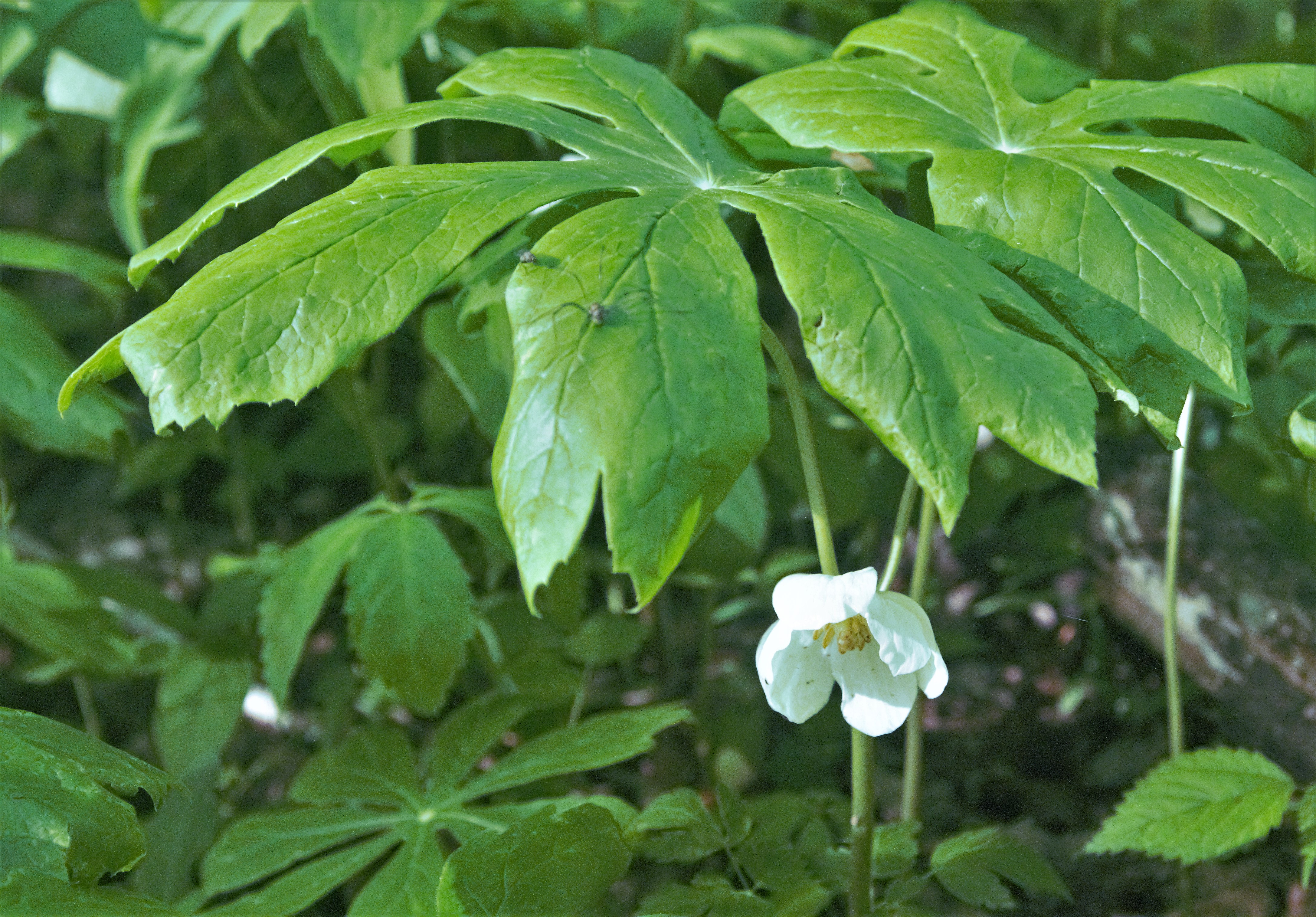
The Thunder Ridge Wilderness is a area located near Natural Bridge, Virginia, which is protected by the Eastern Wilderness Act of Congress to maintain its present, natural condition. As part of the National Wilderness Preservation System, it helps to preserve a variety of natural life forms and contributes to a diversity of plant and animal gene pools. Over half of the ecosystems in the United States exist within designated wilderness. Dominated by Thunder Ridge with steep slopes towering above Arnold Valley, the interior is incredibly rugged, remote and rarely visited. The top of the ridge contains flowers blooming late into summer, long past blooms in the hot valley below. Trillium, may apple, pink lady slipper, Indian cucumber root and columbine flourish in the shade of black cherry trees, northern red oak and hickories. The area is part of the ''Glenwood Cluster''. Location and access Thunder Ridge Wilderness is located in the Jefferson National Forest several miles from Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James River Face Wilderness
The James River Face Wilderness is an 8,907-acre area located near Natural Bridge, Virginia that is protected by the Eastern Wilderness Act of Congress to maintain its present, natural condition. As part of the National Wilderness Preservation System, it helps to preserve a variety of natural life forms and contributes to a diversity of plant and animal gene pools. Over half of the ecosystems in the United States exist within designated wilderness. The wilderness contains many contrasting features. A short distance separates scorched hillsides, stark rockpiles and dry forest on one side and exceedingly rich vegetation on the crest of the Blue Ridge on the other. The area is part of the '' Glenwood Cluster''. Location and access James River Face Wilderness is located in the Jefferson National Forest several miles from Natural Bridge Station, Virginia. It is bounded on the northeast by the James River, on the west by Forest Service Road 35, and on the south by the Blue Rid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruffed Grouse
The ruffed grouse (''Bonasa umbellus'') is a medium-sized grouse occurring in forests from the Appalachian Mountains across Canada to Alaska. It is the most widely distributed game bird in North America. It is non-migratory. It is the only species in the genus ''Bonasa''. The ruffed grouse is sometimes incorrectly referred to as a "partridge", an unrelated phasianid, and occasionally confused with the grey partridge, a bird of open areas rather than woodlands. The ruffed grouse is the state game bird of Pennsylvania, United States. Taxonomy ''Bonasa umbellus'' was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1766 12th edition of ''Systema Naturae''. He classified it as ''Tetrao umbellus'', placing it in a subfamily with Eurasian grouse. The genus ''Bonasa'' was applied by British naturalist John Francis Stephens in 1819. Ruffed grouse is the preferred common name because it applies only to this species. Misleading vernacular names abound, however, and it is often called partridge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roadless Area Conservation
Roadless area conservation is a conservation policy limiting road construction and the resulting environmental impact on designated areas of public land. In the United States, roadless area conservation has centered on U.S. Forest Service areas known as inventoried roadless areas. The most significant effort to support the conservation of these efforts was the Forest Service 2001 Roadless Area Conservation Rule (Roadless Rule). Concept Access roads provide convenient access for industry as well as for a variety of recreational activities, such as sightseeing, fishing, hunting, and off-roading. However, these activities can cause erosion, pollution, species loss, and loss of aesthetic appeal. In addition, the building of roads can lead to further development of "splinter roads" that take off from them, and the encroachment of human settlement and development in sensitive areas. In the United States, about 30%, of National Forest lands in 38 states and Puerto Rico are roadless a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elaeagnus Umbellata
''Elaeagnus umbellata'' is known as Japanese silverberry, umbellata oleaster, autumn olive, autumn elaeagnus, or spreading oleaster. The species is indigenous to eastern Asia and ranges from the Himalayas eastwards to Japan. It is a hardy, aggressive invasive species able to readily colonize barren land, becoming a troublesome plant in the central and northeastern United States and Europe. Description ''Elaeagnus umbellata'' grows as a deciduous shrub or small tree, typically up to tall, with a dense crown.Parmar, C. and M.K. Kaushal. 1982. ''Elaeagnus umbellata''. p. 23–25. In: ''Wild Fruits''. Kalyani Publishers, New Delhi, IndiaNewCROP, New Crop Resource Online Program, Purdue University/ref> It commonly bears sharp thorns in the form of spur branches. Flowers are fragrant and occur in clusters of white to yellow, 8–9 mm in length and 7 mm in diameter, and have four lobes. The leaves are alternate, 4–10 cm long and 2–4 cm wide with wavy margins. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenwood Cluster
The Glenwood Cluster is a region in the George Washington and Jefferson National Forests recognized by The Wilderness Society for its rich biodiversity, scenery, wildflower displays, cold-water trout streams and horse trails. It offers a unique habitat for rare plants, salamanders and other rare species. The Blue Ridge Parkway and the Appalachian Trail traverse the area, giving ready access with views to the east of the Piedmont region and to the west of the Valley of Virginia.Virginia's Mountain Treasures, report issued by The Wilderness Society, May, 1999 Description The region includes wilderness areas protected by Congressional action, inventoried wilderness, and uninventoried areas recognized by the Wilderness Society as worthy of protection from timbering and roads. A corridor along the Blue Ridge Parkway, managed by the National Park Service, and forest service land in the Glenwood Ranger District act as a buffer for the protected areas. The following areas are in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paulownia
''Paulownia'' ( ) is a genus of seven to 17 species of hardwood tree (depending on taxonomic authority) in the family Paulowniaceae, the order Lamiales. They are present in much of China, south to northern Laos and Vietnam and are long cultivated elsewhere in eastern Asia, notably in Japan and Korea. It was introduced to North America in 1844 from Europe and Asia where it was originally sought after as an exotic ornamental tree. Its fruits (botanically capsules) were also used as packaging material for goods shipped from East Asia to North America, leading to ''Paulownia'' groves where they were dumped near major ports. The tree has not persisted prominently in US gardens, in part due to its overwintering brown fruits that some consider ugly. In some areas it has escaped cultivation and is found in disturbed plots. Some US authorities consider the genus an invasive species, but in Europe, where it is also grown in gardens, it is not regarded as invasive. The genus, originall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |