|
Coutumes De Beauvaisis
The ''Coutumes of Beauvaisis'' is a book on medieval French law composed by Philippe de Beaumanoir at the end of the 13th century in Old French prose. The text covers a wide range of topics both on procedural and substantive law and is quite voluminous, which explains its attractiveness to scholars. The bibliography of the ''Coutumes'' is large, although it contains mostly articles and only few subject-specific books. The latest edition has been prepared by Amédée Salmon and was published back in 1899–1900, respecting the original old French syntax. It has not been put into modern French, but translations exist in English and Japanese. Authorship During a long period of time the author of the text had been falsely identified as poet Philippe de Rémi, bailli of the Gâtinais, who was renowned for his 20,000 verses of poems including ''La Manekine'', ''Jehan et Blonde'' and ''Salut d’amour''. As a result, in the 19th and at the beginning of 20th century Philippe de Rémi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the Post-classical, post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern history, modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early Middle Ages, Early, High Middle Ages, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bailli
A bailiff (french: bailli, ) was the king's administrative representative during the ''ancien régime'' in northern France, where the bailiff was responsible for the application of justice and control of the administration and local finances in his bailiwick ('). Name ''Bailli'' (12th-century French ''bailif'', "administrative official, deputy") was derived from a Vulgar Latin term ''*bajulivus'' meaning "official in charge of a castle", i.e. a royal castellan. History In the late 12th and early 13th century, King Philip II, an able and ingenious administrator who founded the central institutions on which the French monarchy's system of power would be based, prepared the expansion of the royal demesne through his appointment of bailiffs in the king's northern lands (the '' domaine royal''), based on medieval fiscal and tax divisions (the "") which had been used by earlier sovereign princes such as the Duke of Normandy. In Flanders Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Customary Legal Systems
Custom, customary, or consuetudinary may refer to: Traditions, laws, and religion * Convention (norm), a set of agreed, stipulated or generally accepted rules, norms, standards or criteria, often taking the form of a custom * Norm (social), a rule that is socially enforced * Customary law or consuetudinary, laws and regulations established by common practice * Customary (liturgy) or consuetudinary, a Christian liturgical book describing the adaptation of rites and rules for a particular context * Custom (Catholic canon law), an unwritten law established by repeated practice * Customary international law, an aspect of international law involving the principle of custom * Mores * Tradition * Minhag (pl. minhagim), Jewish customs * ʿUrf (Arabic: العرف), the customs of a given society or culture Import-export * Customs, a tariff on imported or exported goods * Custom house Modification * Modding * Bespoke, anything commissioned to a particular specification * Custom car * Cus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Law
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—most recently part of the Eastern Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edwin Mellen Press
The Edwin Mellen Press or Mellen Press is an international Independent business, independent company and Academic publisher, academic publishing house with editorial offices in Lewiston (town), New York, Lewiston, New York, and Lampeter, Lampeter, Wales. It was founded, in 1972, by the religious studies scholar Professor Herbert Richardson (publisher), Herbert W. Richardson. The press is a "non-subsidy academic publisher of books in the humanities and social sciences" releasing "Monographs, Textual criticism, critical editions, collections, translations, revisionist studies, constructive essays, bibliographies, dictionaries, reference guides and Thesis, dissertations". Most Mellen books are in English but many are also in a variety of other languages, including French, German, Spanish, and Russian. History When it was founded in 1972, the press's initial purpose was to publish specialized scholarship produced in Herbert Richardson (publisher), Richardson's department at the Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American digital library with the stated mission of "universal access to all knowledge". It provides free public access to collections of digitized materials, including websites, software applications/games, music, movies/videos, moving images, and millions of books. In addition to its archiving function, the Archive is an activist organization, advocating a free and open Internet. , the Internet Archive holds over 35 million books and texts, 8.5 million movies, videos and TV shows, 894 thousand software programs, 14 million audio files, 4.4 million images, 2.4 million TV clips, 241 thousand concerts, and over 734 billion web pages in the Wayback Machine. The Internet Archive allows the public to upload and download digital material to its data cluster, but the bulk of its data is collected automatically by its web crawlers, which work to preserve as much of the public web as possible. Its web archiving, web archive, the Wayback Machine, contains hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auguste-Arthur Beugnot
Count Auguste-Arthur Beugnot (25 March 1797, Bar-sur-Aube – 15 March 1865, Paris) was a French historian and statesman. He was a son of Jacques-Claude Beugnot. Originally he adopted the profession of advocate, but soon abandoned it in order to devote himself entirely to the study of history and especially the history of the Crusades. Politics Beugnot entered politics in 1841 as a Peer of France, was Deputy for Haute-Marne in the Chamber of 1849, and, under the Second Empire, went into a retirement that lasted until his death. The Villemain educational plan of 1844 to subject the heads of independent institutions to the jurisdiction of the university to impose upon their pupils the obligation of making their studies in rhetoric and philosophy in certain prescribed establishments was opposed by Beugnot on liberal principles, whilst others opposed it on religious grounds. This project was withdrawn in January 1845, its author having become demented. Beugnot, who had destroyed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gâtinais
Gâtinais () or Gâtine () was a province of France, containing the area around the valley of the Loing, corresponding roughly to the northeastern part of the département of Loiret, and the south of the present department of Seine-et-Marne. Under the Bourbons, the Gâtinais had already been divided between the provinces of Île-de-France and Orléans. In the words of the modern tourist slogan for the "two Gâtinais", it lies between the Seine and the Loire. Under the Franks, Gâtinais was the ''pagus'' Wastinensis (eventually to become Wasteney in the 20th Century), (or Vastinensis) one of five belonging to the Archbishop of Sens. The west part of Puisaye and the archbishop's other fiefs in the northwest of the modern department of Yonne, west of that river, are also often considered part of Gâtinais; as is the area around Étampes in the present department of Essonne. Around the 10th century, the main town of this province was Château-Landon, and a twenty-five mile circle aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippe De Rémi (poet)
Philippe de Rémi may refer to: *Philippe de Rémi (died 1265) (1210–1265), poet and bailli, also Sire de Beaumanoir *Philippe de Rémi (died 1296) (1247–1296), his son, jurist and royal official {{hndis, Remi, Philippe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
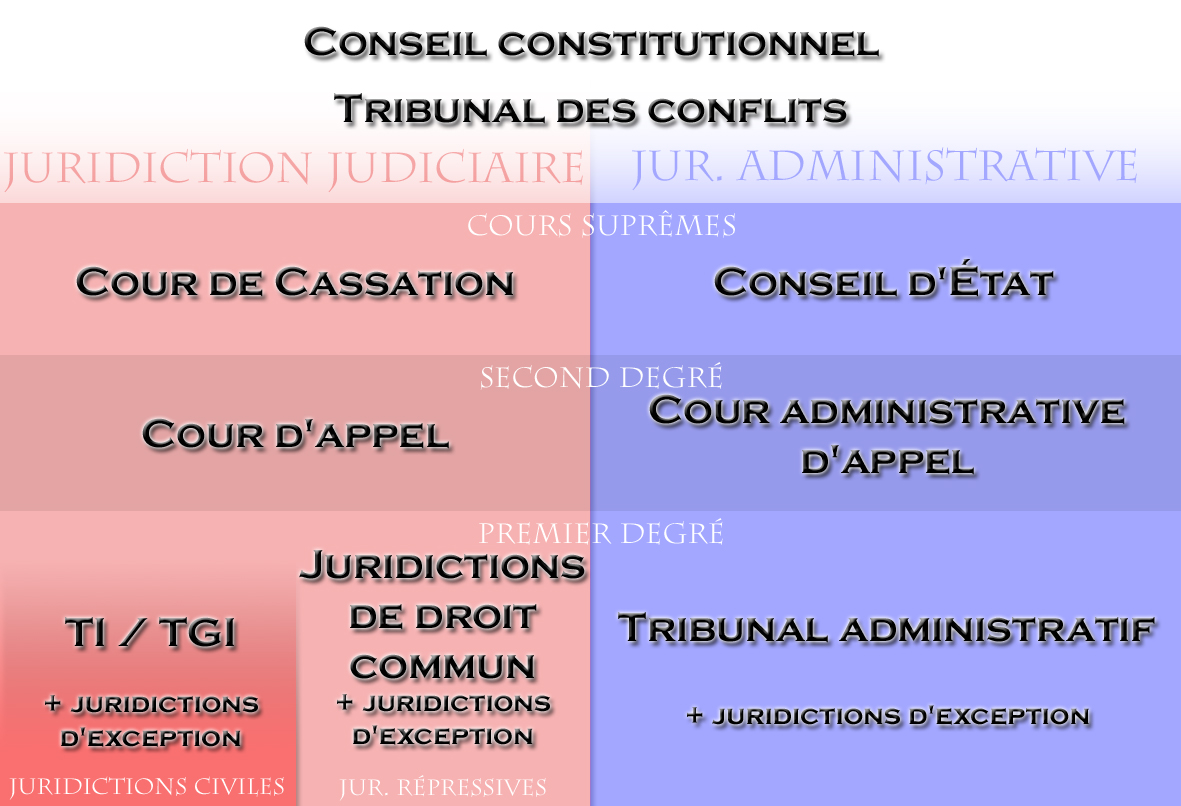
French Law
The Law of France refers to the legal system in the French Republic, which is a civil law legal system primarily based on legal codes and statutes, with case law also playing an important role. The most influential of the French legal codes is the Napoleonic Civil Code, which inspired the civil codes of Europe and later across the world. The Constitution of France adopted in 1958 is the supreme law in France. European Union law is becoming increasingly important in France, as in other EU member states. In academic terms, French law can be divided into two main categories: private law (''Droit privé'') and public law (''droit public''). This differs from the traditional common law concepts in which the main distinction is between criminal law and civil law. Private law governs relationships between individuals. It includes, in particular: * Civil law ('). This branch refers to the field of private law in common law systems. This branch encompasses the fields of inheritance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amédée Salmon
Amédée is a French masculine forename. Notable people with the forename include: Persons * Amédée, stage name of Philippe de Chérisey (1923-1985), French writer, radio humorist, surrealist and actor * Amédée Artus (1815-1892), French conductor and composer *Amédée Baillot de Guerville (1869–1913), French war correspondent *Amédée de Béjarry (1840-1916), French politician * Amédée Bollée (1844-1917), French bellfounder and inventor * Amédée Borrel (1867-1936), French biologist * Amédée Courbet (1827-1885), French army admiral * Amédée Dechambre (1812-1886), French physician *Amédée Despans-Cubières (1786-1853), French army general *Amédée Domenech (1933-2003), French rugby union player and politician *Amédée Dumontpallier (1826-1899), French gynecologist *Amédée Dunois (1878-1945), French lawyer, journalist, politician *Amédée Faure (1801-1878), French painter * Amédée Fengarol (1905-1951), French politician * Amédée E. Forget (1847-1923), Cana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substantive Law
Substantive law is the set of laws that governs how members of a society are to behave.Substantive Law vs. Procedural Law: Definitions and Differences, Study.com/ref> It is contrasted with procedural law, which is the set of procedures for making, administering, and enforcing substantive law. Substantive law defines rights and responsibilities in civil law, and crimes and punishments in criminal law. It may be codified in statutes or exist through precedent in common law. Henry Sumner Maine Sir Henry James Sumner Maine, (15 August 1822 – 3 February 1888), was a British Whig comparative jurist and historian. He is famous for the thesis outlined in his book '' Ancient Law'' that law and society developed "from status to contract. ... said of early law, "So great is the ascendency of the Law of Actions in the infancy of Courts of Justice, that substantive law has at first the look of being gradually secreted in the interstices of procedure; and the early lawyer can only s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)