|
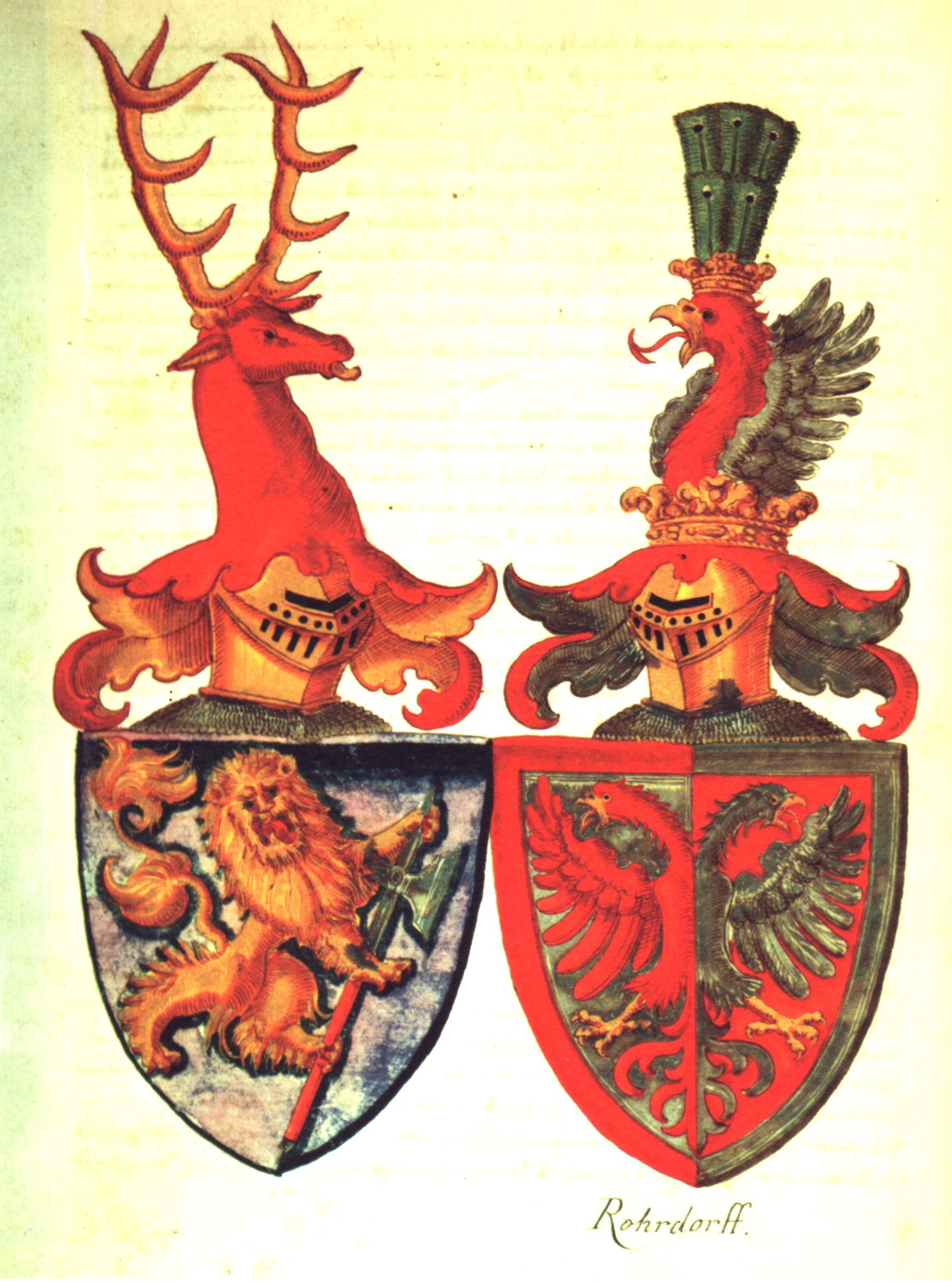
Courtoisie
Heraldic courtesy or courtoisie (French) is a practice typical of the heraldry of German heraldry, Germany (or more generally the former Holy Roman Empire), in which coats of arms are mirrored if necessary so that animate charge (heraldry), charges, such as lion (heraldry), lions, face the center of a composition. This may be done in arms of alliance (displaying the two shields of a married couple), as in the first illustration here; or within a single shield, such as that of the dukes of Guelders and Duchy of Jülich, Jülich in which the gold lion of Guelders turns to face the black lion of Jülich. See also *Arms of alliance References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heraldry
Heraldry is a discipline relating to the design, display and study of armorial bearings (known as armory), as well as related disciplines, such as vexillology, together with the study of ceremony, rank and pedigree. Armory, the best-known branch of heraldry, concerns the design and transmission of the heraldic achievement. The achievement, or armorial bearings usually includes a coat of arms on a shield, helmet and crest, together with any accompanying devices, such as supporters, badges, heraldic banners and mottoes. Although the use of various devices to signify individuals and groups goes back to antiquity, both the form and use of such devices varied widely, as the concept of regular, hereditary designs, constituting the distinguishing feature of heraldry, did not develop until the High Middle Ages. It is often claimed that the use of helmets with face guards during this period made it difficult to recognize one's commanders in the field when large armies gathered together ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Heraldry
German heraldry is the tradition and style of heraldic achievements in Germany and the Holy Roman Empire, including national and civic arms, noble and burgher arms, ecclesiastical heraldry, heraldic displays and heraldic descriptions. German heraldic style is one of the four major broad traditions within European heraldry and stands in contrast to Gallo-British, Latin and Eastern heraldry, and strongly influenced the styles and customs of heraldry in the Nordic countries, which developed comparatively late. Together, German and Nordic heraldry are often referred to as German-Nordic heraldry. p.129. The German heraldic tradition is noted for its scant use of heraldic furs, multiple crests, inseparability of the crest, and repetition of charges in the shield and the crest. Mullets have six points (rather than five as in Gallo-British heraldry), and beasts may be colored with patterns, (barry, bendy, paly, chequy, ''etc.''). As in other European heraldic traditions, the most p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. From the accession of Otto I in 962 until the twelfth century, the Empire was the most powerful monarchy in Europe. Andrew Holt characterizes it as "perhaps the most powerful European state of the Middle Ages". The functioning of government depended on the harmonic cooperation (dubbed ''consensual rulership'' by Bernd Schneidmüller) between monarch and vassals but this harmony was disturbed during the Salian Dynasty, Salian period. The empire reached the apex of territorial expansion and power under the House of Hohenstaufen in the mid-thirteenth century, but overextending led to partial collapse. On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned the List of Frankish kings, Frankish king Charlemagne as Carolingi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge (heraldry)
In heraldry, a charge is any emblem or device occupying the field of an '' escutcheon'' (shield). That may be a geometric design (sometimes called an '' ordinary'') or a symbolic representation of a person, animal, plant, object, building, or other device. In French blazon, the ordinaries are called ''pièces'', and other charges are called ''meubles'' (" hemobile nes). The term ''charge'' can also be used as a verb; for example, if an escutcheon depicts three lions, it is said to be ''charged with three lions''; similarly, a crest or even a charge itself may be "charged", such as a pair of eagle wings ''charged with trefoils'' (as on the coat of arms of Brandenburg). It is important to distinguish between the ordinaries and divisions of the field, as that typically follow similar patterns, such as a shield ''divided'' "per chevron", as distinct from being ''charged with'' a chevron. While thousands of objects found in religion, nature, mythology, or technology have appeared in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lion (heraldry)
The lion is a common charge in heraldry. It traditionally symbolises courage, nobility, royalty, strength, stateliness and valour, because historically the lion has been regarded as the "king of beasts". The lion also carries Judeo-Christian symbolism. The Lion of Judah stands in the coat of arms of Jerusalem. Similar-looking lions can be found elsewhere, such as in the coat of arms of the Swedish royal House of Bjelbo, from there in turn derived into the coat of arms of Finland, formerly belonging to Sweden. History The animal designs in the heraldry of the high medieval period are a continuation of the animal style of the Viking Age, ultimately derived from the style of Scythian art as it developed from c. the 7th century BC. Symmetrically paired animals in particular find continuation from Migration Period art via Insular art to Romanesque art and heraldry. The animals of the "barbarian" (Eurasian) predecessors of heraldic designs are likely to have been used as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guelders
The Duchy of Guelders ( nl, Gelre, french: Gueldre, german: Geldern) is a historical duchy, previously county, of the Holy Roman Empire, located in the Low Countries. Geography The duchy was named after the town of Geldern (''Gelder'') in present-day Germany. Though the present province of Gelderland (English also ''Guelders'') in the Netherlands occupies most of the area, the former duchy also comprised parts of the present Dutch province of Limburg (Netherlands), Limburg as well as those territories in the present-day German States of Germany, state of North Rhine-Westphalia that were acquired by Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia in 1713. Four parts of the duchy had their own centres, as they were separated by rivers: * the quarter of Roermond, also called Upper Quarter or Upper Guelders – upstream on both sides of the Meuse (river), Maas, comprising the town of Geldern as well as Erkelenz, Goch, Nieuwstadt, Venlo and Straelen; spatially separated from the Lower Quarters (Gelde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Jülich
The Duchy of Jülich (german: Herzogtum Jülich; nl, Hertogdom Gulik; french: Duché de Juliers) comprised a state within the Holy Roman Empire from the 11th to the 18th centuries. The duchy lay west of the Rhine river and was bordered by the Electorate of Cologne to the east and the Duchy of Limburg to the west. It had territories on both sides of the river Rur, around its capital Jülich – the former Roman ''Iuliacum'' – in the lower Rhineland. The duchy amalgamated with the County of Berg beyond the Rhine in 1423, and from then on also became known as ''Jülich-Berg''. Later it became part of the United Duchies of Jülich-Cleves-Berg. Its territory lies in present-day Germany (part of North Rhine-Westphalia) and in the present-day Netherlands (part of the Limburg province), its population sharing the same Limburgish dialect. History In the 9th century a certain Matfried was count of Jülich (pagus Juliacensis). The first count in the gau of Jülich in Lower Lorrai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arms Of Alliance
Arms of alliance are those coat of arms that families or private persons take up and join to their own to denote the alliance An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...s they have contracted by marriage. In England arms of alliance are used exclusively by royalty, with non-royal / commoner armigers impaling the arms of both parties within a single shield. See also * Heraldic courtesy References ;Attribution * Heraldry {{Heraldry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |