|
Court Of Common Pleas (Ireland)
The Court of Common Pleas was one of the principal courts of common law in Ireland. It was a mirror image of the equivalent court in England. Common Pleas was one of the four courts of justice which gave the Four Courts in Dublin, which is still in use as a courthouse, its name. History According to Elrington Ball the Irish Court of Common Pleas, which was known in its early years as ''the Common Bench'' or simply ''the Bench'', was fully operational by 1276. It was headed by its Chief Justice (the Chief Justice of the Irish Common Pleas, as distinct from the Lord Chief Justice of Ireland, who was the head of the Irish Court of King's Bench). He had two (occasionally three) justices to assist him. The first Chief Justice was Sir Robert Bagod, former High Sheriff of County Limerick, a member of an old Dublin family which gave its name to Baggot Street. In the early centuries, he was often referred to as "Chief Justice of the Bench", or "the Dublin Bench". Traditionally its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courts Of Common Law
A court is any person or institution, often as a government institution, with the authority to adjudicate legal disputes between parties and carry out the administration of justice in civil, criminal, and administrative matters in accordance with the rule of law. In both common law and civil law legal systems, courts are the central means for dispute resolution, and it is generally understood that all people have an ability to bring their claims before a court. Similarly, the rights of those accused of a crime include the right to present a defense before a court. The system of courts that interprets and applies the law is collectively known as the judiciary. The place where a court sits is known as a venue. The room where court proceedings occur is known as a courtroom, and the building as a courthouse; court facilities range from simple and very small facilities in rural communities to large complex facilities in urban communities. The practical authority given to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Language
Irish ( Standard Irish: ), also known as Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Insular Celtic branch of the Celtic language family, which is a part of the Indo-European language family. Irish is indigenous to the island of Ireland and was the population's first language until the 19th century, when English gradually became dominant, particularly in the last decades of the century. Irish is still spoken as a first language in a small number of areas of certain counties such as Cork, Donegal, Galway, and Kerry, as well as smaller areas of counties Mayo, Meath, and Waterford. It is also spoken by a larger group of habitual but non-traditional speakers, mostly in urban areas where the majority are second-language speakers. Daily users in Ireland outside the education system number around 73,000 (1.5%), and the total number of persons (aged 3 and over) who claimed they could speak Irish in April 2016 was 1,761,420, representing 39.8% of respondents. For most of recorded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
13th-century Establishments In Ireland
The 13th century was the century which lasted from January 1, 1201 ( MCCI) through December 31, 1300 ( MCCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Mongol Empire was founded by Genghis Khan, which stretched from Eastern Asia to Eastern Europe. The conquests of Hulagu Khan and other Mongol invasions changed the course of the Muslim world, most notably the Siege of Baghdad (1258), the destruction of the House of Wisdom and the weakening of the Mamluks and Rums which, according to historians, caused the decline of the Islamic Golden Age. Other Muslim powers such as the Mali Empire and Delhi Sultanate conquered large parts of West Africa and the Indian subcontinent, while Buddhism witnessed a decline through the conquest led by Bakhtiyar Khilji. The Southern Song dynasty would begin the century as a prosperous kingdom but would eventually be invaded and annexed into the Yuan dynasty of the Mongols. The Kamakura Shogunate of Japan would be invaded by the Mongols. Goryeo resiste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courts And Tribunals Established In The 13th Century
A court is any person or institution, often as a government institution, with the authority to adjudicate legal disputes between parties and carry out the administration of justice in civil, criminal, and administrative matters in accordance with the rule of law. In both common law and civil law legal systems, courts are the central means for dispute resolution, and it is generally understood that all people have an ability to bring their claims before a court. Similarly, the rights of those accused of a crime include the right to present a defense before a court. The system of courts that interprets and applies the law is collectively known as the judiciary. The place where a court sits is known as a venue. The room where court proceedings occur is known as a courtroom, and the building as a courthouse; court facilities range from simple and very small facilities in rural communities to large complex facilities in urban communities. The practical authority given to the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courts Of Ireland Before 1922
A court is any person or institution, often as a government institution, with the authority to adjudicate legal disputes between parties and carry out the administration of justice in civil, criminal, and administrative matters in accordance with the rule of law. In both common law and civil law legal systems, courts are the central means for dispute resolution, and it is generally understood that all people have an ability to bring their claims before a court. Similarly, the rights of those accused of a crime include the right to present a defense before a court. The system of courts that interprets and applies the law is collectively known as the judiciary. The place where a court sits is known as a venue. The room where court proceedings occur is known as a courtroom, and the building as a courthouse; court facilities range from simple and very small facilities in rural communities to large complex facilities in urban communities. The practical authority given to the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Court Of Justice In Ireland
The High Court of Justice in Ireland was the court created by the Supreme Court of Judicature Act (Ireland) 1877 to replace the existing court structure in Ireland. Its creation mirrored the reform of the courts of England and Wales five years earlier under the Judicature Acts. The Act created a Supreme Court of Judicature, consisting of a High Court of Justice and a Court of Appeal. Establishment The High Court was created by the Supreme Court of Judicature (Ireland) Act 1877, through the amalgamation of a number of courts. Most importantly, the three superior common-law courts (the Court of King's Bench, the Court of Common Pleas, and the Court of Exchequer) and the Court of Chancery were merged into the new court. Also merged into it were the courts of Landed Estates, Probate, Matrimonial Causes, Admiralty, and Bankruptcy.Delaney, V.T.H. ''Christopher Palles'' Alan Figgis and Co. 1960, p. 94-5 However, the right of appeal from Ireland to the House of Lords in Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supreme Court Of Judicature Act (Ireland) 1877
The Supreme Court of Judicature Act (Ireland) 1877 was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that brought about a major reorganisation of the superior courts in Ireland. It created a Supreme Court of Judicature, comprising the High Court of Justice in Ireland and the Court of Appeal in Ireland. It mirrored in Ireland the changes which the Supreme Court of Judicature Act 1873 had made in the courts of England and Wales. Provisions The Act marked the fusion of the administration of common law and equity in Ireland, although not a merger of the jurisdictions themselves. Prior to the Act coming into force a litigant had to sue in equity in the Court of Chancery and at common law in the common law courts of the Common Pleas, the Exchequer, and the Queen's Bench. Mirroring earlier legislation applying to England and Wales, the Act merged these four courts to become a single High Court of Justice in Ireland; the old courts continued as divisions of the new court. Amending leg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Tirel
John Tirel, or Tyrell (died 1395) was a prominent judge and statesman in fourteenth-century Ireland who held office as Serjeant-at-law and Chief Justice of the Irish Common Pleas.Ball, F. Elrington ''The Judges in Ireland 1221-1921'' London John Murray 1926 Vol. 1 p.88 He was the son of Warin Tirel. The Tirels or Tyrells of Powerstown were a junior branch of the leading Anglo-Irish family of Tyrell. The senior branch of the family, which died out in the male line in 1370, held the Irish feudal barony of Castleknock. He was a substantial landowner in County Dublin, with his principal residence at Powerstown Avas. The district is now called Tyrellstown.Ball, F. Elrington ''A History of the County Dublin'' Vol.6 Dublin University Press 1920 p.39 He is known to have been in England, presumably studying law, in 1354; he then returned to Ireland, where he held office as King's Serjeant, or King's Pleader, from 1372 to 1376. The position of Serjeant then was an onerous one, and on occasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leinster
Leinster ( ; ga, Laighin or ) is one of the provinces of Ireland, situated in the southeast and east of Ireland. The province comprises the ancient Kingdoms of Meath, Leinster and Osraige. Following the 12th-century Norman invasion of Ireland The Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland took place during the late 12th century, when Anglo-Normans gradually conquered and acquired large swathes of land from the Irish, over which the kings of England then claimed sovereignty, all allegedly sanc ..., the historic provinces of Ireland, "fifths" of Leinster and Meath gradually merged, mainly due to the impact of the Pale, which straddled both, thereby forming the present-day province of Leinster. The ancient kingdoms were shired into a number of counties of Ireland#2.1 Pre-Norman sub-divisions, counties for administrative and judicial purposes. In later centuries, local government legislation has prompted further sub-division of the historic counties. Leinster has no official funct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
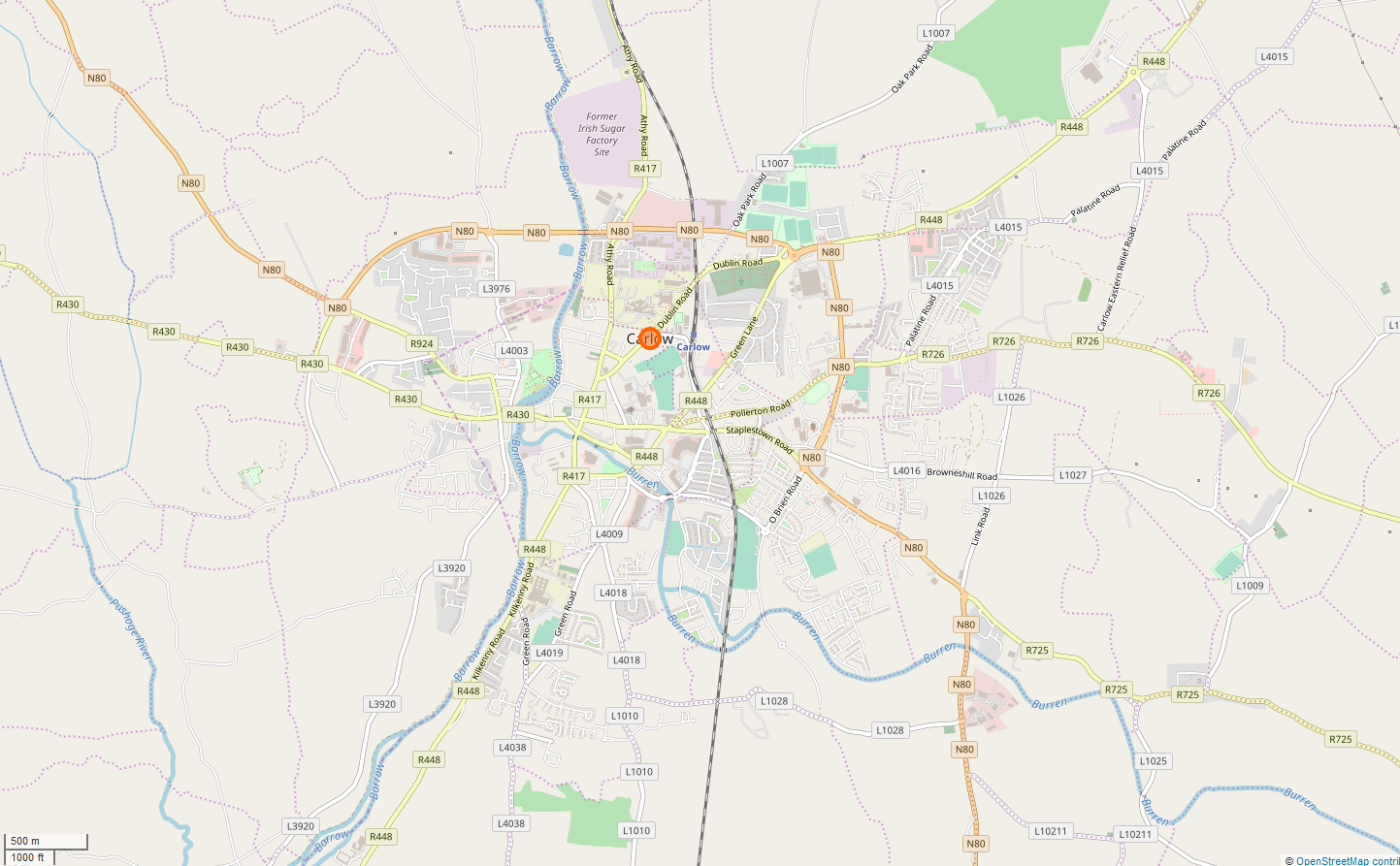
Carlow
Carlow ( ; ) is the county town of County Carlow, in the south-east of Ireland, from Dublin. At the 2016 census, it had a combined urban and rural population of 24,272. The River Barrow flows through the town and forms the historic boundary between counties Laois and Carlow. However, the Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898 included the town entirely in County Carlow. The settlement of Carlow is thousands of years old and pre-dates written Irish history. The town has played a major role in Irish history, serving as the capital of the country in the 14th century. Etymology The name is an anglicisation of the Irish ''Ceatharlach''. Historically, it was anglicised as ''Caherlagh'', ''Caterlagh'' and ''Catherlagh'', which are closer to the Irish spelling. According to logainm.ie, the first part of the name derives from the Old Irish word ''cethrae'' ("animals, cattle, herds, flocks"), which is related to ''ceathar'' ("four") and therefore signified "four-legged". The second p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court Of Exchequer (Ireland)
The Court of Exchequer (Ireland) or the Irish Exchequer of Pleas, was one of the senior courts of common law in Ireland. It was the mirror image of the equivalent court in England. The Court of Exchequer was one of the four royal courts of justice which gave their name to the building in which they were located, which is still called the Four Courts, and in use as a Courthouse, in Dublin. History According to Elrington BallBall, F. Elrington. ''The Judges in Ireland 1221–1921''. London: John Murray, 1926 the Irish Court of Exchequer was established by 1295, and by 1310 it was headed by the Chief Baron of the Irish Exchequer, assisted by at least one associate Baron of the Exchequer. The Court seems to have functioned for some years without a Chief Baron. Sir David de Offington, former Sheriff of County Dublin, was appointed the first Baron in 1294, followed by Richard de Soham the following year, and William de Meones in 1299. The first Chief Baron was Walter de Islip, an E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Fauvel
William Fauvel, or Flauvel (died 1339) was an English-born judge and Crown official of the fourteenth century, part of whose career was spent in Ireland. Despite his eminence, he died in prison in England while awaiting sentence for murder. Background He was a Yorkshire man with strong links to the town of Skipton. He was the son of Constantine Fauvel or Flauvel of Skipton:Ball p.69 Constantine was a close relative, probably a younger son, of Everard Fauvel (died 1308) who held, as tenant-in-chief from the English Crown, substantial lands at Skipton and Broughton. William had at least one brother: he was married but had no children. Career Apart from his time serving as a judge in Ireland, William lived mainly in York, where he was residing in 1327. He served as a justice of the Court of Common Pleas (Ireland) from 1329 to about 1332, and then returned to England. He served there as a tax collector, and in 1332 he was employed by the Crown to levy a tax in Westmorland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |