|
Cotys IV
Cotys IV (Ancient Greek: Κότυς, Kotys) was a king of the Odrysians in Thrace from before 171 until after 166 BC. He was the son of Seuthes V and succeeded either his father or another king, Amadocus III, who was captured by the Macedonians in 184 BC (it is unclear whether Amadocus III and Cotys IV ruled the same political formation and whether kingship was unitary). While the survival of a specifically Odrysian state past the mid-3rd century has been doubted, Cotys IV is described as an Odrysian by Polybius and Livy, although the term may have been used in a less than specific sense. During the Third Macedonian War (171-168 BC), Cotys IV was initially an ally of the Macedonian king Perseus, sending a force of a thousand cavalry and a thousand infantry to his ally, which contributed to the initial Macedonian victory over the Romans at Callinicus in 171 BC. However, following an attack on Cotys' kingdom by another Thracian ruler, Autlesbis (of the Caeni?), and the Attalid comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
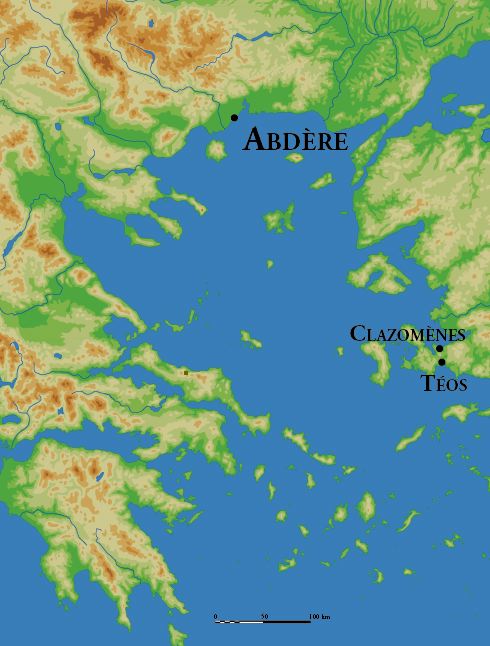
Abdera, Thrace
Abdera () is a municipality in the Xanthi regional unit of Thrace, Greece. In classical antiquity, it was a major Greek ''polis'' on the Thracian coast. The ancient polis is to be distinguished from the municipality, which was named in its honor. The polis lay 17 km east-northeast of the mouth of the Nestos River, almost directly opposite the island of Thasos. It was a colony placed in previously unsettled Thracian territory, not then a part of Hellas, during the age of Greek colonization. The city that developed from it became of major importance in ancient Greece. After the 4th centuryAD it declined, contracted to its acropolis, and was abandoned, never to be reoccupied except by archaeologists. Meanwhile, life went on as the changing population settled in other communities in the region. One named Polystylus changed its name to Abdera. In 2011 the municipality of Abdera was synoecized from three previous municipalities comprising a number of modern settlements. The anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rulers Of Thrace And Dacia
This article lists rulers of Thrace and Dacia, and includes Thracian, Paeonian, Celtic, Dacian, Scythian, Persian or Ancient Greek up to the point of its fall to the Roman Empire, with a few figures from Greek mythology. Mythological *Haemus, became a mountain Haemus Mons * Thrax, son of Ares * Tegyrios, mortal *Eumolpus, inherited a kingdom from Tegyrios *Tereus, the king that was turned into a hoopoe *Phineus, Phoenician son of Agenor, blind king and seer *Poltys, son of Poseidon *Pyreneus, died trying to harm the Muses *Harpalykos, king of the Amymnaeans *Thoas, founder of Thoana *Mopsus, killed Myrine, an amazon queen *Peirous, a Thracian war leader killed by Thoas the Aetolian *Rhesus of Thrace, died in the Trojan war *Cisseus, father of Theano, the wife of Antenor *Diomedes of Thrace, Giant that ruled over the Bistones *Lycurgus, of the Edoni *Oeagrus, father of Orpheus and Linus *Orpheus of the Cicones *Polymestor of the Bistonians *Zalmoxis of the Getae * Charnabon of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Thracian Tribes
This is a list of ancient tribes in Thrace and Dacia ( grc, Θρᾴκη, Δακία) including possibly or partly Thracian or Dacian tribes, and non-Thracian or non-Dacian tribes that inhabited the lands known as Thrace and Dacia. A great number of Ancient Greek tribes lived in these regions as well, albeit in the Greek colonies. Tribes Thracian Certain tribes and subdivisions of tribes were named differently by ancient writers but modern research points out that these were in fact the same tribe. The name ''Thracians'' itself seems to be a Greek exonym and we have no way of knowing what the Thracians called themselves. Also certain tribes mentioned by Homer are not indeed historical. * Agrianes * Apsynthii * Astae,The Thracians 700 BC-AD 46 (Men-at-Arms) by Christopher Webber and Angus McBride, , 2001, page 11: "After the battle, 10,000 Thracians drawn from the Astii, Caeni, Maduateni and Coreli occupied each side of a narrow forested pass ..." they appear in the 2nd centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maedi
The Maedi (also ''Maidans'', ''Maedans'', or ''Medi''; grc, Μαῖδοι or Μαιδοί) were a Thracian tribe in antiquity. In historic times, they occupied the area between Paionia and Thrace, on the southwestern fringes of Thrace, along the middle course of the Strymon, between the Kresna Gorge and the Rupel Pass (present-day south-western Bulgaria). Strabo says that the Maedi bordered eastward on the Thunatae of Dardania, and that the Axius flowed through their territory. Their capital city was Iamphorynna, which lay somewhere in the southwest corner of what is now Bulgaria. Some archaeologists posit it in the area between the cities of Petrich and Sandanski, but its exact location remains unknown. They were an independent tribe through much of their history, and the Thracian king Sitalkes recognized their independence, along with several other warlike "border" tribes such as the Dardani, Agrianes, and Paeonians, whose lands formed a buffer zone between the pow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caeni
Kainoi ( el, Καινοί) or Caeni is the name of a Thracian tribe, mentioned by the Roman historian Livy. References See also *List of Thracian tribes This is a list of ancient tribes in Thrace and Dacia ( grc, Θρᾴκη, Δακία) including possibly or partly Thracian or Dacian tribes, and non-Thracian or non-Dacian tribes that inhabited the lands known as Thrace and Dacia. A great number o ... Ancient tribes in the Balkans Thracian tribes {{Ancient-Thrace-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotys I (Sapaean)
Cotys I (Ancient Greek: Κότυς; died 48 BC) was a Sapaean client king of the Odrysian kingdom of Thrace from c. 57 BC to c. 48 BC. He was the son of Rhoemetalces. Cotys was an ally of the Roman general Pompey, to whom he sent a body of auxiliaries under his son Rhescuporis I in 48 BC for use in the Roman civil war against Julius Caesar. On Cotys' death, Rhescuporis I became king under the regency of Rhoemetalces I Rhoemetalces I (Sapaean) ( grc, Ῥοιμητάλκης) was king of the Sapaean kingdom of Thrace from 15 BC to 12 AD. He was king of Odrysian kingdom of Thrace in succession to his nephew Rhescuporis II (Astaean). Rhoemetalces I was a loya ..., Cotys' younger brother. See also * List of rulers of Thrace and Dacia Notes Sources Smith, William, ed. ''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology''. Boston : Little, Brown, and Company, 1867, v. 3, p. 870 1st-century BC rulers in Europe Roman client rulers Year of birth unknown 48 BC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attalus III
Attalus III ( el, Ἄτταλος Γ΄) Philometor Euergetes ( – 133 BC) was the last Attalid king of Pergamon, ruling from 138 BC to 133 BC. Biography Attalus III was the son of king Eumenes II and his queen Stratonice of Pergamon, and he was the nephew of Attalus II, whom he succeeded. "Philometor Euergetes" means "Loving-his-Mother, Benefactor" in Greek; he was so-called because of his close relationship with his mother Stratonice. He is the likely addressee of a fragmentary hymn by the poet Nicander which celebrates his heritage. According to Livy, Attalus III had little interest in ruling Pergamon, devoting his time to studying medicine, botany, gardening, and other pursuits. He had no male children or heirs of his own, and in his will he left his kingdom to the Roman Republic, believing that if he did not then Rome would take the kingdom anyway and this way would avoid bloodshed.Asimov, I. and F. White, ''The March of the Millennia'' (1991), p. 74 Tiberius Gracchus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apama III
Prusias I Cholus (Greek: Προυσίας ὁ Χωλός "the Lame"; c. 243 – 182 BC) was a king of Bithynia, who reigned from c. 228 to 182 BC. Life and Reign Prusias was a vigorous and energetic leader; he fought a war against Byzantium (220 BC), seizing its Asiatic territory, a part of Mysia that had been in its possession for a long time. Then, he defeated the Galatians who Nicomedes I had invited across the Bosphorus to a territory called Arisba, putting to death all of their women and children and letting his men plunder their baggage. At some point during his reign, he formed a marriage alliance with Demetrius II of Macedon, receiving the latter's daughter, Apama, as his wife. He expanded the territories of Bithynia in a series of wars against Attalus I of Pergamum and Heraclea Pontica on the Black Sea, taking various cities formerly owned by the Heracleans, renaming one them, Prusias, after himself. While besieging the city of Heraclea Pontica, he dealt many cas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prusias II Of Bithynia
Prusias II Cynegus (Greek: Προυσίας ὁ Κυνηγός; "the Hunter", c. 220 BC – 149 BC, reigned c. 182 BC – 149 BC) was the Greek king of Bithynia. He was the son and successor of Prusias I and Apama III. Life Prusias was born to Prusias I and Apama III in 220 BC. His father died in 189 BC, at which point he became the king of Bithynia. Prusias II joined with the king of Pergamon, Eumenes II in a war against King Pharnaces I of Pontus (181–179 BC). He later invaded the territories of Pergamon (156–154 BC), only to be defeated, with Pergamon insisting on heavy reparations, including 500 talents and "twenty decked ships". Prusias II married his maternal cousin Apame IV, a sister of Perseus of Macedon and a princess from the Antigonid dynasty, by whom he had a son, Nicomedes II, and a daughter, Apama, who would marry Dyegilos, son of Cotys IV, King of Thrace, and his wife, Semestra. Prusias II was honoured by the Aetolian League The Aetolian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astae
Asti ( el, Αστοί) is the name of a Thracian tribe which is mentioned by Livy. It is believed that they lived around the old Thracian capital of Bizye. List of rulers A possible continuation of the earlier Odrysian monarchy under a line of kings reigning from Bizye (now Vize) in eastern Thrace. * Cotys V, son of ? Beithys (?-by 87 BC) * Sadalas I, son of Cotys V (by 87–after 79 BC) ** Amadocus, Odrysian royal sent to the aid of Sulla at Chaeronea in 86 BC * Cotys VI, son of Sadalas I (by 57–48 BC) * Sadalas II, son of Cotys VI (48–42 BC) * Sadalas III, kinsman of Sadalas II (42-31 BC) * Cotys VII, son of Sadalas II by Polemocratia (31–18 BC) * Rhescuporis II, son of Cotys VII by daughter of the Sapaean king Cotys II, killed by the Bessi (18–11 BC) ** 11 BC Astaean Thrace conferred on Rhescuporis II's maternal uncle, the Sapaean king Rhoemetalces I, by the Roman emperor Augustus, thereby uniting Thrace Family tree of Astaean kings in Thrace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sapaeans
Sapaeans, Sapaei or Sapaioi (Ancient Greek, "Σαπαίοι") were a Thracian tribe close to the Greek city of Abdera. One of their kings was named Abrupolis and had allied himself with the Romans. They ruled Thrace after the Odrysians until its incorporation by the Roman Empire as a province. Sapaean Kings of Thrace * Cotys I son of Rhoemetalces c.57 BC-48 BC * Rhescuporis I son of Cotys I 48 BC-41 BC * Cotys II son of Rhescuporis I 42 BC – 15 BC :*Thrace becomes a client state of Rome at 11 BC * Rhoemetalces I son of Cotys II 15 BC – 12 AD * Rhescuporis II son of Cotys II in western Thrace; 12–18 AD deposed * Cotys III son of Rhoemetalces I in eastern Thrace 12–18 murdered * Rhoemetalces II son of Cotys III and Tryphaena 18–26 :* Roman caretaker rules Rhoemetalces III part of Thrace 26-38 * Rhoemetalces III son of Rhescuporis II 38–46 :* 46 to the Roman Empire Family tree of Sapaean kings of Thrace References See also *List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |