|
Costas Soukoulis
Costas M. Soukoulis ( el, Κώστας Μ. Σούκουλης) is a Senior Scientist in the Ames Laboratory and Distinguished Professor of Physics Emeritusat Iowa State University. He received his B.Sc. from University of Athens in 1974. He obtained his Ph.D. in Physics from the University of Chicago in 1978, under the supervision of Kathryn Liebermann Levin. From 1978 to 1981 he was at the Physics Department at University of Virginia. He spent 3 years (1981–84) at Exxon Research and Engineering Co. and since 1984 has been at Iowa State University (ISU) and Ames Laboratory. He has been part-time Professor at the Department of Materials Science and Technology of the University of Crete (2001-2011) and an associated member of IESL-FORTH at Heraklion, Crete, Greece since 1984. Research Soukoulis and his collaborators at Ames Lab/ISU in 1990 and 1994, suggested photonic crystal designs (lattice diamond and the woodpile structure, respectively), which gave the largest omnidirection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corinth
Corinth ( ; el, Κόρινθος, Kórinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part of the municipality of Corinth, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. It is the capital of Corinthia. It was founded as Nea Korinthos (), or New Corinth, in 1858 after an earthquake destroyed the existing settlement of Corinth, which had developed in and around the site of ancient Corinth. Geography Located about west of Athens, Corinth is surrounded by the coastal townlets of (clockwise) Lechaio, Isthmia, Kechries, and the inland townlets of Examilia and the archaeological site and village of ancient Corinth. Natural features around the city include the narrow coastal plain of Vocha, the Corinthian Gulf, the Isthmus of Corinth cut by its canal, the Saronic Gulf, the Oneia Mountains, and the monolithic rock of Acrocorinth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OSA Fellow
The Optica Fellow is a membership designation of Optica (formerly known as The Optical Society (OSA)) that denotes distinguished scientific accomplishment. The bylaws of this society only allow 10% of its membership to be designated as an Optica Fellow. The Optica Fellow requires peer group nomination. The nominee An Optica member can only become an Optica Fellow when nominated by a peer group of other current Optica Fellows. Review of the nomination is then passed to the Optica Fellow Members Committee. This committee then nominates the candidate to the Board of Directors on an annual basis. Finally, the purpose of this award is to designate a member as one who has "made significant contributions to the advancement of optics". The process The process includes actively identifying possible candidates who might qualify for this award. Contributing factors for qualification are diverse within the optics community. These factors include significant or distinguishing scientific a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
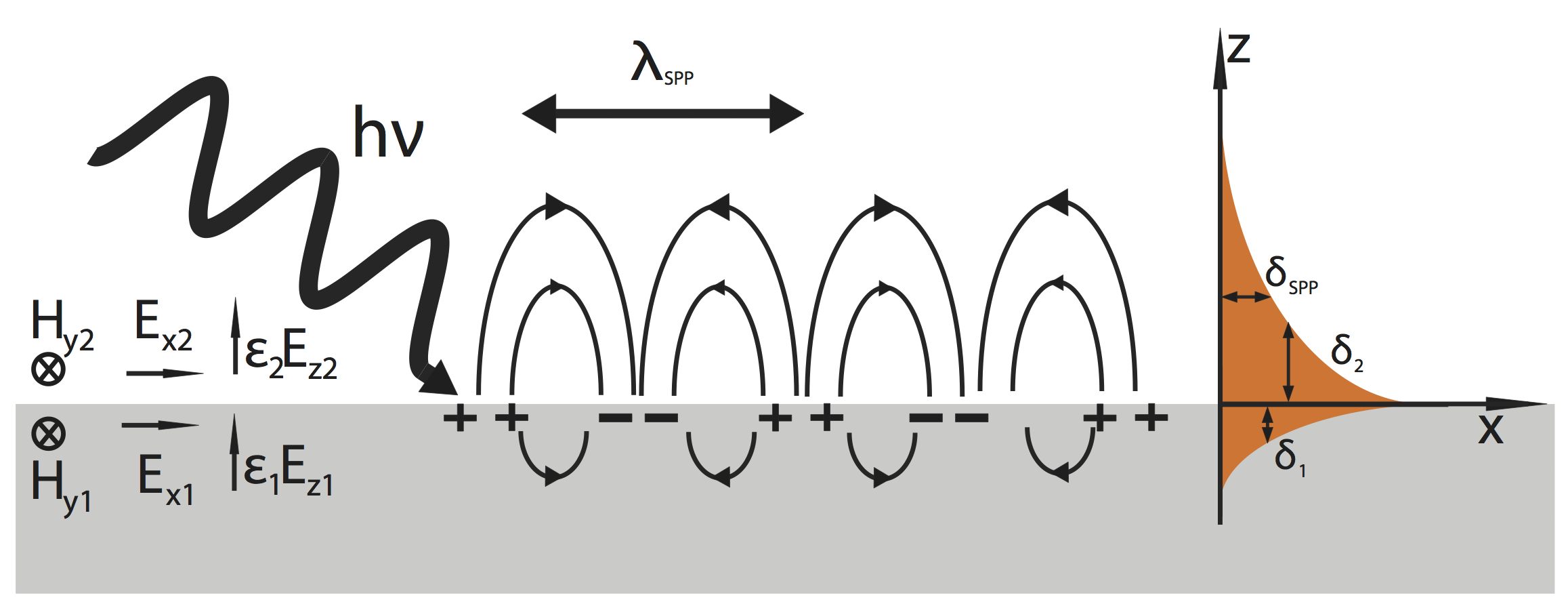
Surface Plasmon
Surface plasmons (SPs) are coherent delocalized electron oscillations that exist at the interface between any two materials where the real part of the dielectric function changes sign across the interface (e.g. a metal-dielectric interface, such as a metal sheet in air). SPs have lower energy than bulk (or volume) plasmons which quantise the longitudinal electron oscillations about positive ion cores within the bulk of an electron gas (or plasma). The charge motion in a surface plasmon always creates electromagnetic fields outside (as well as inside) the metal. The ''total'' excitation, including both the charge motion and associated electromagnetic field, is called either a surface plasmon polariton at a planar interface, or a localized surface plasmon for the closed surface of a small particle. The existence of surface plasmons was first predicted in 1957 by Rufus Ritchie. In the following two decades, surface plasmons were extensively studied by many scientists, the foremost o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphene
Graphene () is an allotrope of carbon consisting of a single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice nanostructure. "Carbon nanostructures for electromagnetic shielding applications", Mohammed Arif Poothanari, Sabu Thomas, et al., ''Industrial Applications of Nanomaterials'', 2019. "Carbon nanostructures include various low-dimensional allotropes of carbon including carbon black (CB), carbon fiber, carbon nanotubes (CNTs), fullerene, and graphene." The name is derived from "graphite" and the suffix -ene, reflecting the fact that the allotrope of carbon contains numerous double bonds. Each atom in a graphene sheet is connecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Laser
A random laser (RL) is a laser in which optical feedback is provided by scattering particles. As in conventional lasers, a gain medium is required for optical amplification. However, in contrast to Fabry–Pérot interferometer, Fabry–Pérot cavities and distributed feedback laser, distributed feedback lasers, neither reflective surfaces nor distributed periodic structures are used in RLs, as light is confined in an active region by diffusive elements that either may or may not be spatially distributed inside the gain medium. The main principle behind a random laser is to increase the light path with disordered media; this can be done by diffusive disordered media or by using strong localization in a disordered media, with laser active background. Random lasing has been reported from a large variety of materials, e.g. colloidal solutions of dye and scattering particles, semiconductor powders, optical fibers and polymers. Due to the output emission with low spatial coherence an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anderson Localization
In condensed matter physics, Anderson localization (also known as strong localization) is the absence of diffusion of waves in a ''disordered'' medium. This phenomenon is named after the American physicist P. W. Anderson, who was the first to suggest that electron localization is possible in a lattice potential, provided that the degree of randomness (disorder) in the lattice is sufficiently large, as can be realized for example in a semiconductor with impurities or defects. Anderson localization is a general wave phenomenon that applies to the transport of electromagnetic waves, acoustic waves, quantum waves, spin waves, etc. This phenomenon is to be distinguished from weak localization, which is the precursor effect of Anderson localization (see below), and from Mott localization, named after Sir Nevill Mott, where the transition from metallic to insulating behaviour is ''not'' due to disorder, but to a strong mutual Coulomb repulsion of electrons. Introduction In the or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamaterials
A metamaterial (from the Ancient Greek, Greek word Meta, μετά ''meta'', meaning "beyond" or "after", and the Latin word ''materia'', meaning "matter" or "material") is any material engineered to have a property that is not found in naturally occurring materials. They are made from assemblies of multiple elements fashioned from composite materials such as metals and plastics. The materials are usually arranged in Periodic function, repeating patterns, at scales that are smaller than the wavelengths of the phenomena they influence. Metamaterials derive their properties not from the properties of the base materials, but from their newly designed structures. Their precise shape, geometry, dimensions, size, orientation (geometry), orientation and arrangement gives them their smart properties capable of manipulating Electromagnetism, electromagnetic waves: by blocking, absorbing, enhancing, or bending waves, to achieve benefits that go beyond what is possible with conventional materi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative Index Metamaterials
Negative-index metamaterial or negative-index material (NIM) is a metamaterial whose refractive index for an electromagnetic wave has a negative value over some frequency range. NIMs are constructed of periodic basic parts called unit cells, which are usually significantly smaller than the wavelength of the externally applied electromagnetic radiation. The unit cells of the first experimentally investigated NIMs were constructed from circuit board material, or in other words, wires and dielectrics. In general, these artificially constructed cells are stacked or planar and configured in a particular repeated pattern to compose the individual NIM. For instance, the unit cells of the first NIMs were stacked horizontally and vertically, resulting in a pattern that was repeated and intended (see below images). Specifications for the response of each unit cell are predetermined prior to construction and are based on the intended response of the entire, newly constructed, material. In o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photonic Crystal
A photonic crystal is an optical nanostructure in which the refractive index changes periodically. This affects the propagation of light in the same way that the structure of Crystal structure, natural crystals gives rise to X-ray crystallography, X-ray diffraction and that the atomic lattices (crystal structure) of semiconductors affect their conductivity of electrons. Photonic crystals occur in nature in the form of structural coloration and animal reflectors, and, as artificially produced, promise to be useful in a range of applications. Photonic crystals can be fabricated for one, two, or three dimensions. One-dimensional photonic crystals can be made of thin film layers deposited on each other. Two-dimensional ones can be made by photolithography, or by drilling holes in a suitable substrate. Fabrication methods for three-dimensional ones include drilling under different angles, stacking multiple 2-D layers on top of each other, direct laser writing, or, for example, instig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heraklion, Crete
Heraklion or Iraklion ( ; el, Ηράκλειο, , ) is the largest city and the administrative capital of the island of Crete and capital of Heraklion regional unit. It is the fourth largest city in Greece with a population of 211,370 (Urban Area) according to the 2011 census. The population of the municipality was 177,064. The Bronze Age palace of Knossos, also known as the Palace of Minos, is located 5.5 km (3.1m) southeast of the city. Heraklion was Europe's fastest growing tourism destination for 2017, according to Euromonitor, with an 11.2% growth in international arrivals. According to the ranking, Heraklion was ranked as the 20th most visited region in Europe, as the 66th area on the planet and as the 2nd in Greece for the year 2017, with 3.2 million visitors and the 19th in Europe for 2018, with 3.4 million visitors. Etymology The Arab traders from al-Andalus (Iberia) who founded the Emirate of Crete moved the island's capital from Gortyna to a new castle they called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Crete
The University of Crete (UoC; Greek: Πανεπιστήμιο Κρήτης) is a multi-disciplinary, research-oriented institution in Crete, Greece, located in the cities of Rethymno (official seat) and Heraklion, and one of the country's most academically acclaimed and reputable universities."''Overall, the external evaluation committee was impressed by the commitment to excellence permeating all levels of the institution. For a relatively new university, UoC has made remarkable achievements in the Greek academic world and beyond.''" There are 16 main undergraduate degree programmes corresponding to the university's departments and more than 30 master's programmes. As of 2017, there is a student population of 16.000 registered undergraduates and 2.500 registered postgraduates, more than 500 Faculty members as well as approximately 420 administrative staff. The university ranked 62nd in The Times Higher Education (THE) 2018 list of the top universities aged 50 years or under. Ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamaterials
A metamaterial (from the Ancient Greek, Greek word Meta, μετά ''meta'', meaning "beyond" or "after", and the Latin word ''materia'', meaning "matter" or "material") is any material engineered to have a property that is not found in naturally occurring materials. They are made from assemblies of multiple elements fashioned from composite materials such as metals and plastics. The materials are usually arranged in Periodic function, repeating patterns, at scales that are smaller than the wavelengths of the phenomena they influence. Metamaterials derive their properties not from the properties of the base materials, but from their newly designed structures. Their precise shape, geometry, dimensions, size, orientation (geometry), orientation and arrangement gives them their smart properties capable of manipulating Electromagnetism, electromagnetic waves: by blocking, absorbing, enhancing, or bending waves, to achieve benefits that go beyond what is possible with conventional materi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |