|
Cosmos 772
Kosmos 772 (russian: Космос 772 meaning ''Cosmos 772'') was an uncrewed military Soyuz 7K-S test. It was an unsuccessful mission as only one transmitter worked. Only the 166 MHz frequency transmitter operated, all of the other normal Soyuz wavelengths transmitters failed. The experience from these flights were used in the development of the successor program Soyuz spacecraft the Soyuz 7K-ST. Mission parameters *Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-S *Mass: 6750 kg *Crew: None *Launched: September 29, 1975 *Landed: October 3, 1975 4:10 UTC *Perigee: 154 km *Apogee: 245 km *Inclination: 51.8 deg *Duration: 3.99 days Maneuver Summary *193 km X 270 km orbit to 195 km X 300 km orbit. Delta V: 8 m/s. *196 km X 300 km orbit to 196 km X 328 km orbit. Delta V: 8 m/s. Total Delta V: 16 m/s. See also *Soyuz 7K-OK *Soyuz TM-25 Soyuz TM-25 was a crewed Soyuz spaceflight, which launched on February 10, 1997.The mission report ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncrewed Spacecraft
Unmanned spacecraft or uncrewed spacecraft are spacecraft without people on board, used for robotic spaceflight. Uncrewed spacecraft may have varying levels of autonomy from human input; they may be Remotely operated vehicle, remote controlled, remote guided or even autonomous vehicle, autonomous, meaning they have a pre-programmed list of operations, which they will execute unless otherwise instructed. Many habitable spacecraft also have varying levels of robotic features. For example, the space stations Salyut 7 and Mir, and the International Space Station module Zarya (ISS module), Zarya, were capable of remote guided station-keeping and docking maneuvers with both resupply craft and new modules. The most common uncrewed spacecraft categories are robotic spacecraft, uncrewed resupply spacecraft, unmanned resupply spacecraft, space probed space observatory, space observatories. Not every uncrewed spacecraft is a robotic spacecraft; for example, a reflector ball is a non-ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
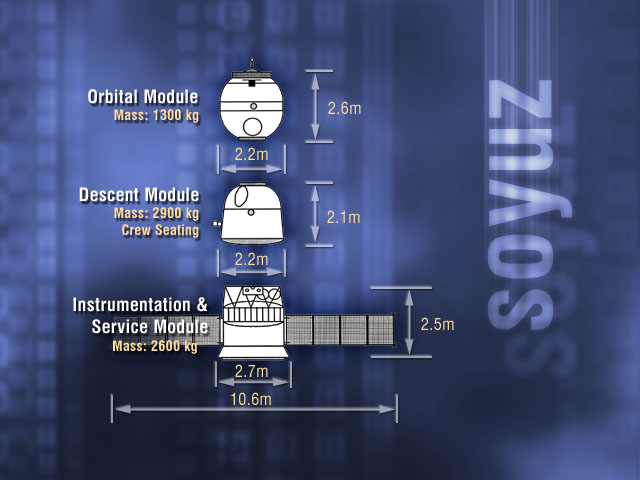
Soyuz Spacecraft
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraft and was originally built as part of the Soviet crewed lunar programs. It is launched on a Soyuz rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Between the 2011 retirement of the Space Shuttle and the 2020 demo flight of SpaceX Crew Dragon, the Soyuz served as the only means to ferry crew to or from the International Space Station, for which it remains heavily used. Although China did launch crewed Shenzhou flights during this time, none of them docked with the ISS. History The first Soyuz flight was uncrewed and started on 28 November 1966. The first Soyuz mission with a crew, Soyuz 1, launched on 23 April 1967 but ended with a crash due to a parachute failure, killing cosmonaut Vladimir Komarov. The following flight was uncrew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna (radio), antenna. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the Antenna (radio), antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna radiates radio waves. Transmitters are necessary component parts of all electronic devices that communicate by radio communication, radio, such as radio broadcasting, radio and television broadcasting stations, cell phones, walkie-talkies, Wireless LAN, wireless computer networks, Bluetooth enabled devices, garage door openers, two-way radios in aircraft, ships, spacecraft, radar sets and navigational beacons. The term ''transmitter'' is usually limited to equipment that generates radio waves for Communication engineering, communication purposes; or radiolocation, such as radar and navigational transmitters. Generators of radio waves for heatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz 7K-ST
The Soyuz-T (russian: Союз-T, ''Union-T'') spacecraft was the third generation Soyuz spacecraft, in service for seven years from 1979 to 1986. The ''T'' stood for transport (, ). The revised spacecraft incorporated lessons learned from the Apollo Soyuz Test Project, Soyuz 7K-TM and Military Soyuz. The Soyuz-T was a major upgrade over previous Soyuz spacecraft, sporting solid-state electronics for the first time and a much more advanced onboard computer to help overcome the chronic docking problems that affected cosmonauts during space station missions. In addition, solar panels returned, allowing the Soyuz-T to fly up to 11 days independently as well as a redesigned propulsion system, the KTDU-426. Finally, it could at last carry three cosmonauts with pressure suits. Missions *Soyuz T-1 Soyuz T-1 (russian: link=no, Союз Т-1, also called Soyuz T) was a 1979-80 unmanned Soviet space flight, a test flight of a new Soyuz craft which docked with the orbiting Salyut 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jane's Information Group
Jane's Information Group, now styled Janes, is a global open-source intelligence company specialising in military, national security, aerospace and transport topics, whose name derives from British author Fred T. Jane. History Jane's Information Group was founded in 1898 by Fred T. Jane, who had begun sketching ships as an enthusiast naval artist while living in Portsmouth. This gradually developed into an encyclopedic knowledge, culminating in the publishing of ''All the World's Fighting Ships'' (1898). The company then gradually branched out into other areas of military expertise. The books and trade magazines published by the company are often considered the ''de facto'' public source of information on warfare and transportation systems. Based in Greater London for most of its existence, the group was owned by the Thomson Corporation, The Woodbridge Company, then IHS Markit, before being acquired by Montagu Private Equity in 2019. Description The company name is officially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyndon B
Lyndon may refer to: Places * Lyndon, Alberta, Canada * Lyndon, Rutland, East Midlands, England * Lyndon, Solihull, West Midlands, England United States * Lyndon, Illinois * Lyndon, Kansas * Lyndon, Kentucky * Lyndon, New York * Lyndon, Ohio * Lyndon, Pennsylvania * Lyndon, Vermont * Lyndon, Sheboygan County, Wisconsin, a town * Lyndon, Juneau County, Wisconsin, a town Other uses * Lyndon State College, a public college located in Lyndonville, Vermont People * Lyndon (name), given name and surname See also * Lyndon School (other) * Lyndon Township (other) * * Lydon (other) * Lynden (other) * Lindon (other) * Linden (other) {{disambig, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perigee
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion. General description There are two apsides in any elliptic orbit. The name for each apsis is created from the prefixes ''ap-'', ''apo-'' (), or ''peri-'' (), each referring to the farthest and closest point to the primary body the affixing necessary suffix that describes the primary body in the orbit. In this case, the suffix for Earth is ''-gee'', so the apsides' names are ''apogee'' and ''perigee''. For the Sun, its suffix is ''-helion'', so the names are ''aphelion'' and ''perihelion''. According to Newton's laws of motion, all periodic orbits are ellipses. The barycenter of the two bodies may lie well within the bigger body—e.g., the Earth–Moon barycenter is about 75% of the way from Earth's center to its surface. If, compared to the larger mass, the smaller mass is negligible (e.g., f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)