|
Cosmos 672
Kosmos 672 (russian: Космос 672 meaning ''Cosmos 672'') was the second uncrewed test of the ASTP Soyuz spacecraft. Also had APAS-75 androgynous docking system. This was preceded by another uncrewed test of this spacecraft type, Kosmos 638. It was a Soyuz 7K-TM The 1975 Apollo–Soyuz Test Project version of the Soyuz spacecraft (Soyuz 7K-TM) served as a technological bridge to the third generation Soyuz-T (T - транспортный, ''Transportnyi'' meaning transport) spacecraft (1976–1986). ... spacecraft. Mission parameters *Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-TM *Mass: 6510 to 6680 kg *Crew: None *Launched: August 12, 1974 *Landed: August 18, 1974 References *Mir Hardware Heritage Mir Hardware Heritage - NASA report (PDF format)** Mir Hardware Heritage (wikisource) Kosmos 0672 1974 in the Soviet Union Spacecraft launched in 1974 Soyuz uncrewed test flights Apollo–Soyuz Test Project {{USSR-spacecraft-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz Spacecraft In Orbit - GPN-2002-000155
Soyuz is a transliteration of the Cyrillic text Союз (Russian and Ukrainian, 'Union'). It can refer to any union, such as a trade union (''profsoyuz'') or the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (Сою́з Сове́тских Социалисти́ческих Респу́блик, ''Soyuz Sovetskikh Sotsialisticheskikh Respublik''). As terminological shorthand "soyuz" by itself was often used interchangeably with each of the slightly longer terms Сове́тский Сою́з (''Sovetskiy Soyuz'', 'Soviet Union'). It was also a shorthand for the citizenry as a whole. Soyuz is also the designated name of various projects the country commissioned during the Space Race. Space program uses * Soyuz programme, a human spaceflight program initiated by the Soviet Union, continued by the Russian Federation * Soyuz (spacecraft), used in that program * Soyuz (rocket), initially used to launch that spacecraft * Soyuz (rocket family), derivatives of that rocket design * Soyuz Launch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo–Soyuz Test Project
Apollo–Soyuz was the first crewed international space mission, carried out jointly by the United States and the Soviet Union in July 1975. Millions of people around the world watched on television as a United States Apollo spacecraft docked with a Soviet Soyuz capsule. The project, and its handshake in space, was a symbol of détente between the two superpowers during the Cold War. The mission was officially known as the Apollo–Soyuz Test Project (ASTP; russian: Экспериментальный полёт «Союз» – «Аполлон» (ЭПАС), translit=Eksperimentalniy polyot Soyuz–Apollon (EPAS), lit=Experimental flight Soyuz-Apollo, and commonly referred to in the Soviet Union as Soyuz–Apollo; the Soviets officially designated the mission as Soyuz 19). The unnumbered American vehicle was left over from the canceled Apollo missions, and was the last Apollo module to fly. The three American astronauts, Thomas P. Stafford, Vance D. Brand, and Deke Slayt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
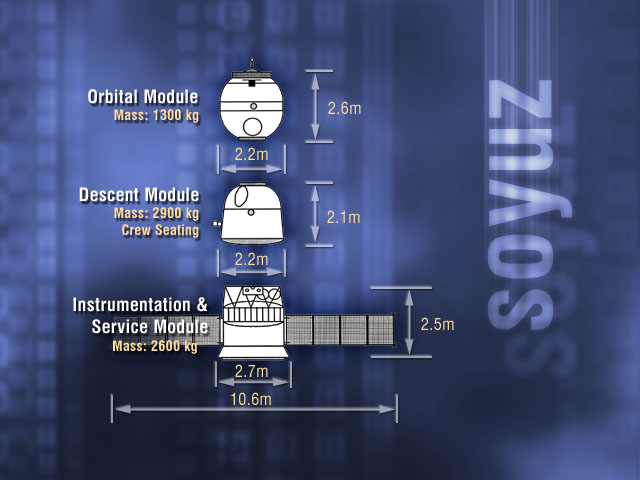
Soyuz Spacecraft
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraft and was originally built as part of the Soviet crewed lunar programs. It is launched on a Soyuz rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Between the 2011 retirement of the Space Shuttle and the 2020 demo flight of SpaceX Crew Dragon, the Soyuz served as the only means to ferry crew to or from the International Space Station, for which it remains heavily used. Although China did launch crewed Shenzhou flights during this time, none of them docked with the ISS. History The first Soyuz flight was uncrewed and started on 28 November 1966. The first Soyuz mission with a crew, Soyuz 1, launched on 23 April 1967 but ended with a crash due to a parachute failure, killing cosmonaut Vladimir Komarov. The following flight was uncr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APAS-75
The terms Androgynous Peripheral Attach System (APAS), Androgynous Peripheral Assembly System (APAS) and Androgynous Peripheral Docking System (APDS), are used interchangeably to describe a family of spacecraft docking mechanisms, and are also sometimes used as a generic name for any docking system in that family. A system similar to APAS-89/95 is used by the Chinese Shenzhou spacecraft. Overview The name of the system is Russian in origin, and is an acronym, , in the Cyrillic alphabet, from the Russian (''Androginno-periferiynyy agregat stykovki''). The English acronym was designed to be just the same letters but in the Latin alphabet, for which the first two words are direct counterparts of those in the original. The third word in Russian comes from the German , meaning "complicated mechanism", and the last means "docking". The last two words in the English name were picked to begin with the same equivalent letters as in the Russian name. The idea behind the design is that unli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmos 638
Kosmos 638 (russian: Космос 638) was an uncrewed test of the 1975 Apollo–Soyuz Test Project Soyuz. It carried an APAS-75 androgynous docking system. This was followed by another uncrewed test of this spacecraft type, Kosmos 672. It was a Soyuz 7K-TM The 1975 Apollo–Soyuz Test Project version of the Soyuz spacecraft (Soyuz 7K-TM) served as a technological bridge to the third generation Soyuz-T (T - транспортный, ''Transportnyi'' meaning transport) spacecraft (1976–1986). ... spacecraft. When the air was released from the orbital module (which is ejected before re-entry of the capsule) it caused unexpected motions with the spacecraft. This led to the next test also being uncrewed. Mission parameters *Spacecraft: Soyuz-7K-TM №71 *Mass: 6510 to 6680 kg *Crew: None *Launched: April 3, 1974 *Landed: April 13, 1974 References *Mir Hardware Heritage ''Mir Hardware Heritage'' (NASA report RP 1357) (PDF format)** ''Mir Hardware Heritage'' (NASA rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz 7K-TM
The 1975 Apollo–Soyuz Test Project version of the Soyuz spacecraft (Soyuz 7K-TM) served as a technological bridge to the third generation Soyuz-T (T - транспортный, ''Transportnyi'' meaning transport) spacecraft (1976–1986). The Soyuz ASTP spacecraft was designed for use during the Apollo Soyuz Test Project as Soyuz 19. It featured design changes to increase compatibility with the American craft. The Soyuz ASTP featured new solar panels for increased mission length, an APAS-75 docking mechanism instead of the standard male mechanism and modifications to the environmental control system to lower the cabin pressure to 0.68 atmospheres (69 kPa) prior to docking with Apollo. The ASTP Soyuz backup craft flew as the Soyuz 22 mission, replacing the docking port with a camera. Uncrewed Missions * Cosmos 638 * Cosmos 672 Manned missions * Soyuz 16 * Soyuz 19 ( ASTP) * Soyuz 22 Soyuz 22 (russian: Союз 22, ''Union 22'') was a September, 1976, Soviet crewed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mir Hardware Heritage
''Mir'' (russian: Мир, ; ) was a space station that operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, operated by the Soviet Union and later by Russia. ''Mir'' was the first modular space station and was assembled in orbit from 1986 to 1996. It had a greater mass than any previous spacecraft. At the time it was the largest artificial satellite in orbit, succeeded by the International Space Station (ISS) after ''Mir'''s orbital decay, orbit decayed. The station served as a microgravity research laboratory in which crews conducted experiments in biology, human biology, physics, astronomy, meteorology, and spacecraft systems with a goal of developing technologies required for permanent occupation of Outer space, space. ''Mir'' was the first continuously inhabited long-term research station in orbit and held the record for the longest continuous human presence in space at 3,644 days, until it was surpassed by the ISS on 23 October 2010. It holds the record for the longes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmos Satellites
The cosmos (, ) is another name for the Universe. Using the word ''cosmos'' implies viewing the universe as a complex and orderly system or entity. The cosmos, and understandings of the reasons for its existence and significance, are studied in cosmologya broad discipline covering scientific, religious or philosophical aspects of the cosmos and its nature. Religious and philosophical approaches may include the cosmos among spiritual entities or other matters deemed to exist outside the physical universe. Etymology The philosopher Pythagoras first used the term ''kosmos'' ( grc, κόσμος, Latinized ''kósmos'') for the order of the universe. Greek κόσμος "order, good order, orderly arrangement" is a word with several main senses rooted in those notions. The verb κοσμεῖν (''κοσμεῖν'') meant generally "to dispose, prepare", but especially "to order and arrange (troops for battle), to set (an army) in array"; also "to establish (a government or regime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1974 In The Soviet Union
Major events in 1974 include the aftermath of the 1973 oil crisis and the resignation of President of the United States, United States President Richard Nixon following the Watergate scandal. In the Middle East, the aftermath of the 1973 Yom Kippur War determined politics; following List of Prime Ministers of Israel, Israeli Prime Minister Golda Meir's resignation in response to high Israeli casualties, she was succeeded by Yitzhak Rabin. In Europe, the Turkish invasion of Cyprus, invasion and occupation of northern Cyprus by Turkey, Turkish troops initiated the Cyprus dispute, the Carnation Revolution took place in Portugal, and Chancellor of Germany, Chancellor of West Germany Willy Brandt resigned following an Guillaume affair, espionage scandal surrounding his secretary Günter Guillaume. In sports, the year was primarily dominated by the 1974 FIFA World Cup, FIFA World Cup in West Germany, in which the Germany national football team, German national team won the championshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Launched In 1974
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit (space stations) only, whereas those used for robotic space missions operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft used to supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz Uncrewed Test Flights
Soyuz is a transliteration of the Cyrillic text Союз (Russian and Ukrainian, 'Union'). It can refer to any union, such as a trade union (''profsoyuz'') or the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (Сою́з Сове́тских Социалисти́ческих Респу́блик, ''Soyuz Sovetskikh Sotsialisticheskikh Respublik''). As terminological shorthand "soyuz" by itself was often used interchangeably with each of the slightly longer terms Сове́тский Сою́з (''Sovetskiy Soyuz'', 'Soviet Union'). It was also a shorthand for the citizenry as a whole. Soyuz is also the designated name of various projects the country commissioned during the Space Race. Space program uses * Soyuz programme, a human spaceflight program initiated by the Soviet Union, continued by the Russian Federation * Soyuz (spacecraft), used in that program * Soyuz (rocket), initially used to launch that spacecraft * Soyuz (rocket family), derivatives of that rocket design * Soyuz Launch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |