|
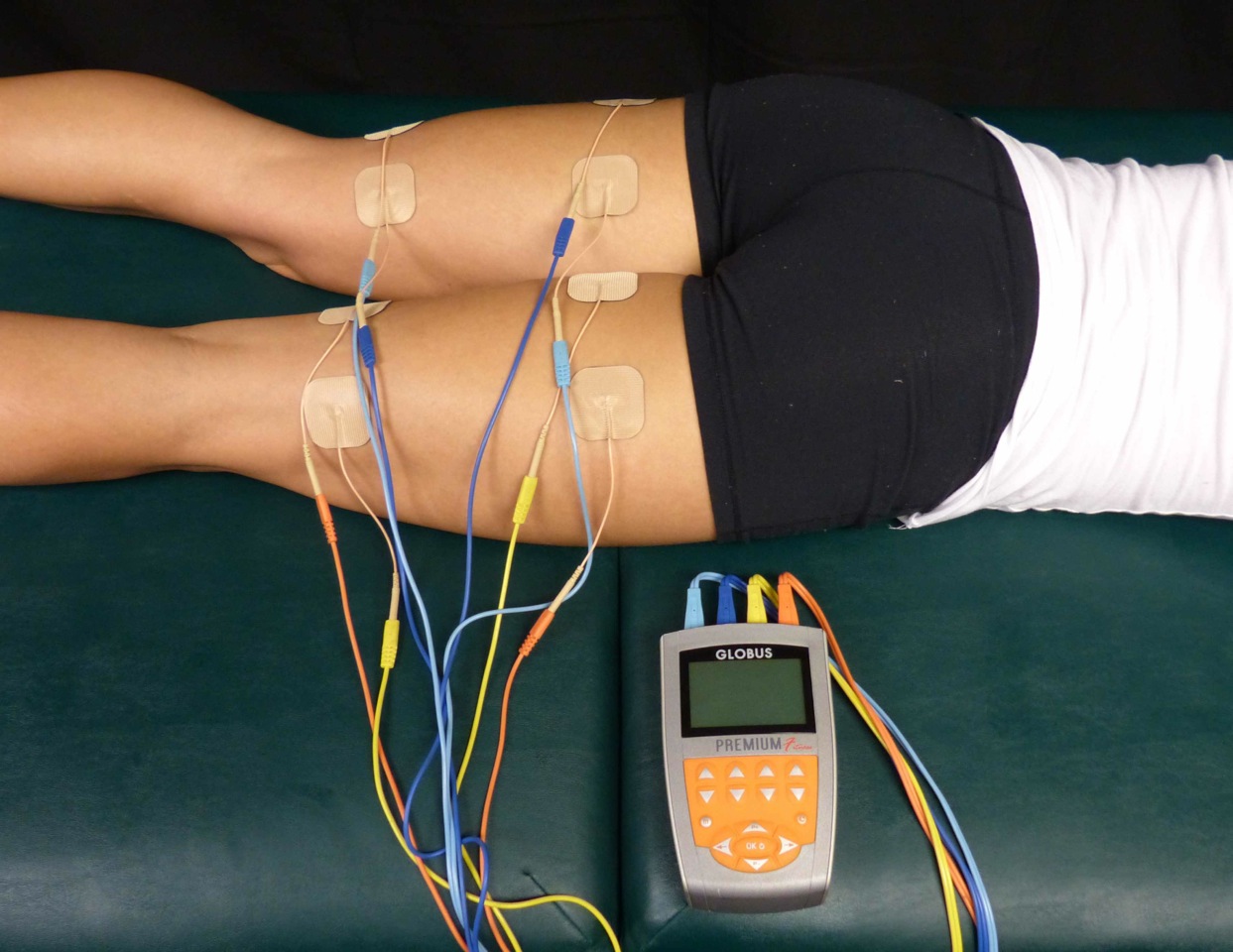
Cosmetic Electrotherapy
Cosmetic electrotherapy is a range of beauty treatments that uses low electric currents passed through the skin to produce several therapeutic effects such as muscle toning in the body and micro-lifting of the face.Dawn Mernagh-Ward, Jennifer Cartwright, ''Health and beauty therapy: a practical approach for NVQ level 3'', Edition 3, Publisher Nelson Thornes, 2004, , . 420 pagespage 109 It is based on electrotherapy, which has been researched and accepted in the field of rehabilitation, though the "scientific and medical communities have tended to sideline or dismiss the use of electrotherapy for healthy muscles". The use of electricity in cosmetics goes back to the end of the 19th century, almost a hundred years after Luigi Galvani discovered that electricity can make the muscle in a frog's leg twitch (see galvanism). Subsequent research in electrophysiology has been carried out by people such as Robert O. Becker, Dr Björn Nordenström, a former chair of the Nobel Selection Comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrotherapy Machine (cosmetic)
Electrotherapy is the use of electrical energy as a medical treatment. In medicine, the term ''electrotherapy'' can apply to a variety of treatments, including the use of electrical devices such as deep brain stimulators for neurological disease. The term has also been applied specifically to the use of electric current to speed wound healing. Additionally, the term "electrotherapy" or "electromagnetic therapy" has also been applied to a range of alternative medical devices and treatments. Medical uses Electrotherapy is primarily used in physical therapy for: * relaxation of muscle spasms * prevention and retardation of disuse atrophy * increase of local blood circulation * muscle rehabilitation and re-education * electrical muscle stimulation * maintaining and increasing range of motion * management of chronic and intractable pain including diabetic neuropathy * acute post-traumatic and post-surgical pain * post-surgical stimulation of muscles to prevent venous thrombosis * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular System
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels (from Greek ''kardia'' meaning ''heart'', and from Latin ''vascula'' meaning ''vessels''). The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms ''cardiovascular system'' and ''vascular system'' interchangeably with the ''circulatory system''. The network of blood vessels are the great vessels of the heart including large elastic arteries, and large veins; other arteries, smaller arterioles, capillaries that join with venules (small veins), and other veins. The circulatory system is closed in vertebrates, which means that the blood never leaves the network of blood vessels. Some invertebrates such as arthro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golgi Tendon Organ
The Golgi tendon organ (GTO) (also called Golgi organ, tendon organ, neurotendinous organ or neurotendinous spindle) is a proprioceptor – a type of sensory receptor that senses changes in muscle tension. It lies at the interface between a muscle and its tendon known as the musculotendinous junction also known as the myotendinous junction. It provides the sensory component of the Golgi tendon reflex. The Golgi tendon organ is one of several eponymous terms named after the Italian physician Camillo Golgi. Structure The body of the Golgi tendon organ is made up of braided strands of collagen (intrafusal fasciculi) that are less compact than elsewhere in the tendon and are encapsulated. The capsule is connected in series (along a single path) with a group of muscle fibers () at one end, and merge into the tendon proper at the other. Each capsule is about long, has a diameter of about , and is perforated by one or more afferent type Ib sensory nerve fibers ( Aɑ fiber), w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scar
A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other organs, and tissues of the body. Thus, scarring is a natural part of the healing process. With the exception of very minor lesions, every wound (e.g., after accident, disease, or surgery) results in some degree of scarring. An exception to this are animals with complete regeneration, which regrow tissue without scar formation. Scar tissue is composed of the same protein ( collagen) as the tissue that it replaces, but the fiber composition of the protein is different; instead of a random basketweave formation of the collagen fibers found in normal tissue, in fibrosis the collagen cross-links and forms a pronounced alignment in a single direction. This collagen scar tissue alignment is usually of inferior functional quality to the normal collagen randomised alignment. For example, scars in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellulite
Cellulite is the herniation of subcutaneous fat within fibrous connective tissue that manifests as skin dimpling and nodularity, often on the pelvic region (specifically the buttocks), lower limbs, and abdomen. Cellulite occurs in most postpubescent females. A review gives a prevalence of 85–98% of women, indicating that it is physiological rather than pathological. It can result from a complex combination of factors ranging from hormones to heredity. Causes The causes of cellulite include changes in metabolism, physiology, diet and exercise habits, obesity, sex-specific dimorphic skin architecture, alteration of connective tissue structure, hormonal factors, genetic factors, the microcirculatory system, the extracellular matrix, and subtle inflammatory alterations. Hormonal factors Hormones play a dominant role in the formation of cellulite. Estrogen may be the important hormone in the development of cellulite. However, there has been no reliable clinical evidence to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stretch Mark
Stretch marks, also known as striae () or striae distensae, are a form of scarring on the skin with an off-color hue. Over time they may diminish, but will not disappear completely. Striae are caused by tearing of the dermis during periods of rapid growth of the body, such as during puberty or pregnancy, in which they usually form during the last trimester. Usually on the stomach, these striae also commonly occur on the breasts, thighs, hips, lower back, and buttocks. Pregnancy-related striae are known as ''striae gravidarum''. Striae may also be influenced by the hormonal changes associated with puberty, pregnancy, bodybuilding, or hormone replacement therapy. There is no evidence that creams used during pregnancy prevent stretch marks. Once they have formed there is no clearly effective treatment, though various methods have been attempted and studied. Signs and symptoms Striae, or "stretch marks", begin as reddish or purple lesions, which can appear anywhere on the body, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
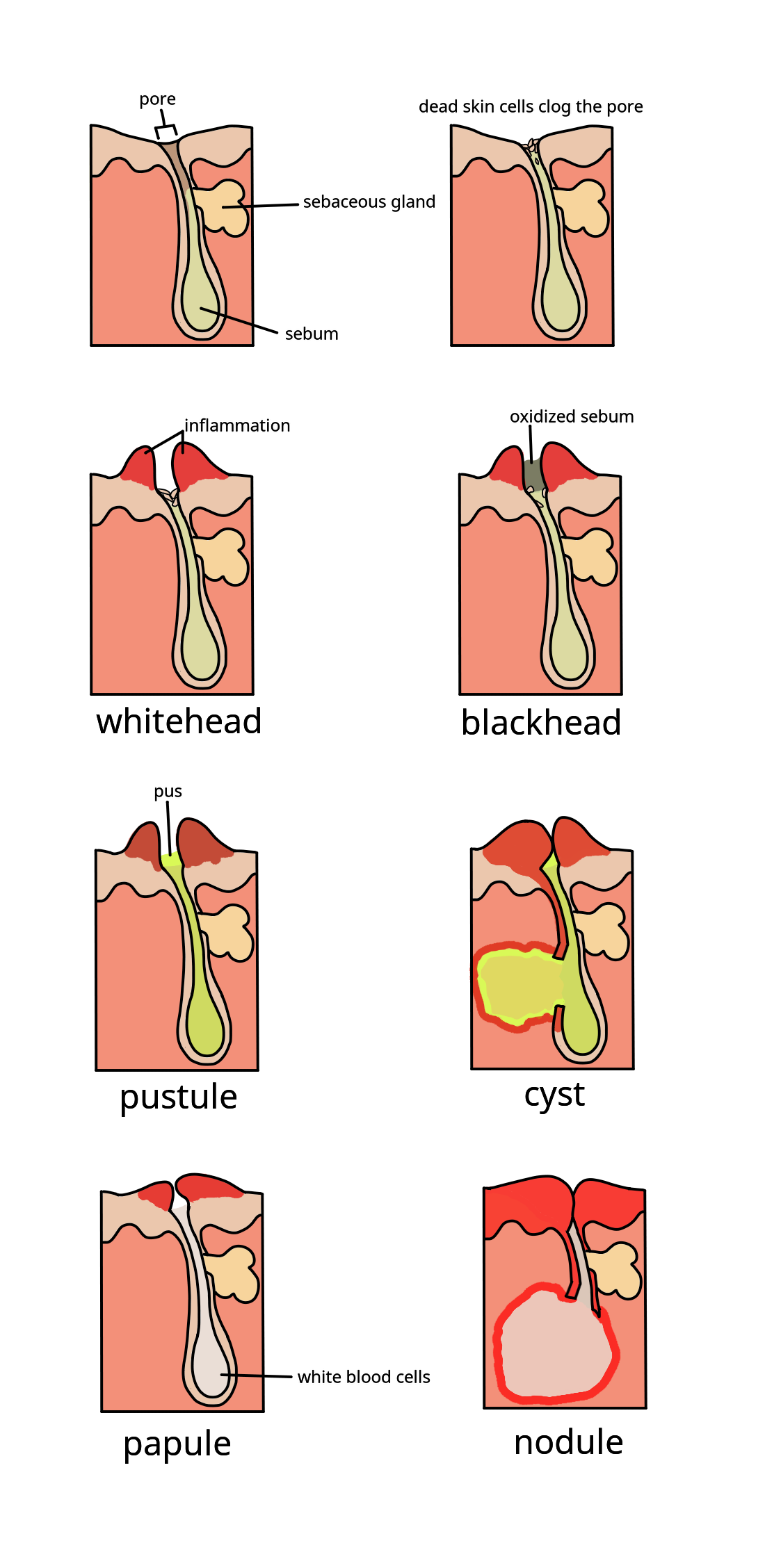
Acne
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term skin condition that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and possible scarring. It primarily affects skin with a relatively high number of oil glands, including the face, upper part of the chest, and back. The resulting appearance can lead to anxiety, reduced self-esteem, and, in extreme cases, depression or thoughts of suicide. Susceptibility to acne is primarily genetic in 80% of cases. The roles of diet and cigarette smoking in the condition are unclear, and neither cleanliness nor exposure to sunlight appear to play a part. In both sexes, hormones called androgens appear to be part of the underlying mechanism, by causing increased production of sebum. Another common factor is the excessive growth of the bacterium '' Cutibacterium acnes'', which is present on the skin. Treatments for ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunburn
Sunburn is a form of radiation burn that affects living tissue, such as skin, that results from an overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, usually from the Sun. Common symptoms in humans and animals include: red or reddish skin that is hot to the touch or painful, general fatigue, and mild dizziness. Other symptoms include blistering, peeling skin, swelling, itching, and nausea. Excessive UV radiation is the leading cause of (primarily) non-malignant skin tumors,World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cance"Do sunscreens prevent skin cancer" Press release No. 132, 5 June 2000World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cance"Solar and ultraviolet radiation"IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, Volume 55, November 1997 and in extreme cases can be life-threatening. Sunburn is an inflammatory response in the tissue triggered by direct DNA damage by UV radiation. When the cells' DNA is overl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek , ''ēlektron'', "amber" Electron#Etymology">etymology of "electron" , ''physis'', "nature, origin"; and , ''-logia'') is the branch of physiology that studies the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage changes or electric current or manipulations on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and, in particular, action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system, such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings. They are useful for electrodiagnosis and monitoring. Definition and scope Classical electrophysiological techniques Principle and mechanisms Electrophysiology is the branch of physiology that pertains broadly to the flow of ions ( ion current) in biological tissues and, in pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ampere
The ampere (, ; symbol: A), often Clipping (morphology), shortened to amp,SI supports only the use of symbols and deprecates the use of abbreviations for units. is the unit of electric current in the International System of Units (SI). One ampere is equal to electrons worth of charge moving past a point in a second. It is named after France, French mathematician and physicist André-Marie Ampère (1775–1836), considered the father of electromagnetism along with Denmark, Danish physicist Hans Christian Ørsted. As of the 2019 redefinition of the SI base units, the ampere is defined by fixing the elementary charge to be exactly C (coulomb), which means an ampere is an electrical current equivalent to elementary charges moving every seconds or elementary charges moving in a second. Prior to the redefinition the ampere was defined as the current that would need to be passed through 2 parallel wires 1 metre apart to produce a magnetic force of Newton (unit), newtons per me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcurrent Electrical Neuromuscular Stimulator
A microcurrent electrical neuromuscular stimulator or MENS (also microamperage electrical neuromuscular stimulator) is a device used to send weak electrical signals into the body. Such devices apply extremely small microamp Aelectrical currents (less than 1 milliampere A to the tissues using electrodes placed on the skin. One microampere Ais 1 millionth of an ampere and the uses of MENS are distinct from those of "TENS" which runs at one milliamp Aor one thousandth of an amp. Uses MENS uses include treatments for pain, diabetic neuropathy, age-related macular degeneration, wound healing, tendon repair, plantar fasciitis and ruptured ligament recovery. Most microcurrent treatments concentrate on pain and/or speeding healing and recovery. It is commonly used by professional and performance athletes with acute pain and/or muscle tenderness as it is drug-free and non-invasive, thus avoiding testing and recovery issues. It is also used as a cosmetic treatment. History The bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slendertone
Electrical muscle stimulation (EMS), also known as neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) or electromyostimulation, is the elicitation of muscle contraction using electric impulses. EMS has received an increasing amount of attention in the last few years for many reasons: it can be utilized as a strength training tool for healthy subjects and athletes; it could be used as a rehabilitation and preventive tool for people who are partially or totally immobilized; it could be utilized as a testing tool for evaluating the neural and/or muscular function in vivo; it could be used as a post-exercise recovery tool for athletes. The impulses are generated by a device and are delivered through electrodes on the skin near to the muscles being stimulated. The electrodes are generally pads that adhere to the skin. The impulses mimic the action potential that comes from the central nervous system, causing the muscles to contract. The use of EMS has been cited by sports scientists as a comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



.jpg)