|
Cosijoeza
Cosijoeza, Cocijoeza o Cosiioeza ( Zapotec: Gzio'za'a or Kosi'ioeza) (1450–1504) was a Coquitao (King in Zapotec) of Zaachila (the kingdom not to be confused with the homonymous city), its name in Zapotec means "Storm of obsidian knives" or "time of obsidian knives", was named by Aztecs as Huizquiauitl. He ascended the throne in 1487, faced the expansionism of the Aztec Empire and built the city of Guiengola. The geostrategic importance of the kingdom of Zaachila is due to its condition as a bridge between the highlands of the Anáhuac center and the Mayan lands of what is now Chiapas and Guatemala, as well as its important salt production industry on the coast, goldsmith and grana cochineal (these activities continue to be industries in the region although with less economic influence than in the past) because of this Zaachila was seen under the ambition of the Aztecs. In the face of the threat posed by the Aztecs, in 1494 King Cosiioeza ordered the killing of the children ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosijopii
Cosijopii I also Cosiiopii I (December 30, 1502–1563) was the last sovereign of the Kingdom of Zaachila, that was named by the Aztecs as Teotzapotlan. Such kingdom was located in the west side of the current Mexican state of Oaxaca and during the last period reached the Pacific coast of the current Chiapas and Guatemala, the Zaachila Kingdom fell after the Spanish colonization. Cosijopii was the son of Cosijoeza, Zapoteca king, and Coyolicaltzin, daughter of Aztec tlatoani Ahuízotl. His siblings were Bitoopa, Natipa, Pinopia, Cosijopi, and Donají. Cosijopii succeeded his father Cosijoeza to the throne in 1529. Cosijopii moved his capital from Zaachila city to Guiengola at some point in the mid-sixteenth century. His sister, Donají Sicasibí was kidnapped by the Mixtecos and taken to Tehuantepec. He formed an alliance with the Spanish, commanded by Pedro de Alvarado Pedro de Alvarado (; c. 1485 – 4 July 1541) was a Spanish conquistador and governor of Gua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diego Rivera
Diego María de la Concepción Juan Nepomuceno Estanislao de la Rivera y Barrientos Acosta y Rodríguez, known as Diego Rivera (; December 8, 1886 – November 24, 1957), was a prominent Mexican painter. His large frescoes helped establish the Mexican muralism, mural movement in Mexican art, Mexican and international art. Between 1922 and 1953, Rivera painted murals in, among other places, Mexico City, Chapingo, and Cuernavaca, Mexico; and San Francisco, Detroit, and New York City, United States. In 1931, a retrospective exhibition of his works was held at the Museum of Modern Art in New York; this was before he completed his 27-mural series known as ''Detroit Industry Murals''. Rivera had four wives and numerous children, including at least one natural daughter. His first child and only son died at the age of two. His third wife was fellow Mexican artist Frida Kahlo, with whom he had a volatile relationship that continued until her death. His fourth and final wife was his agen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
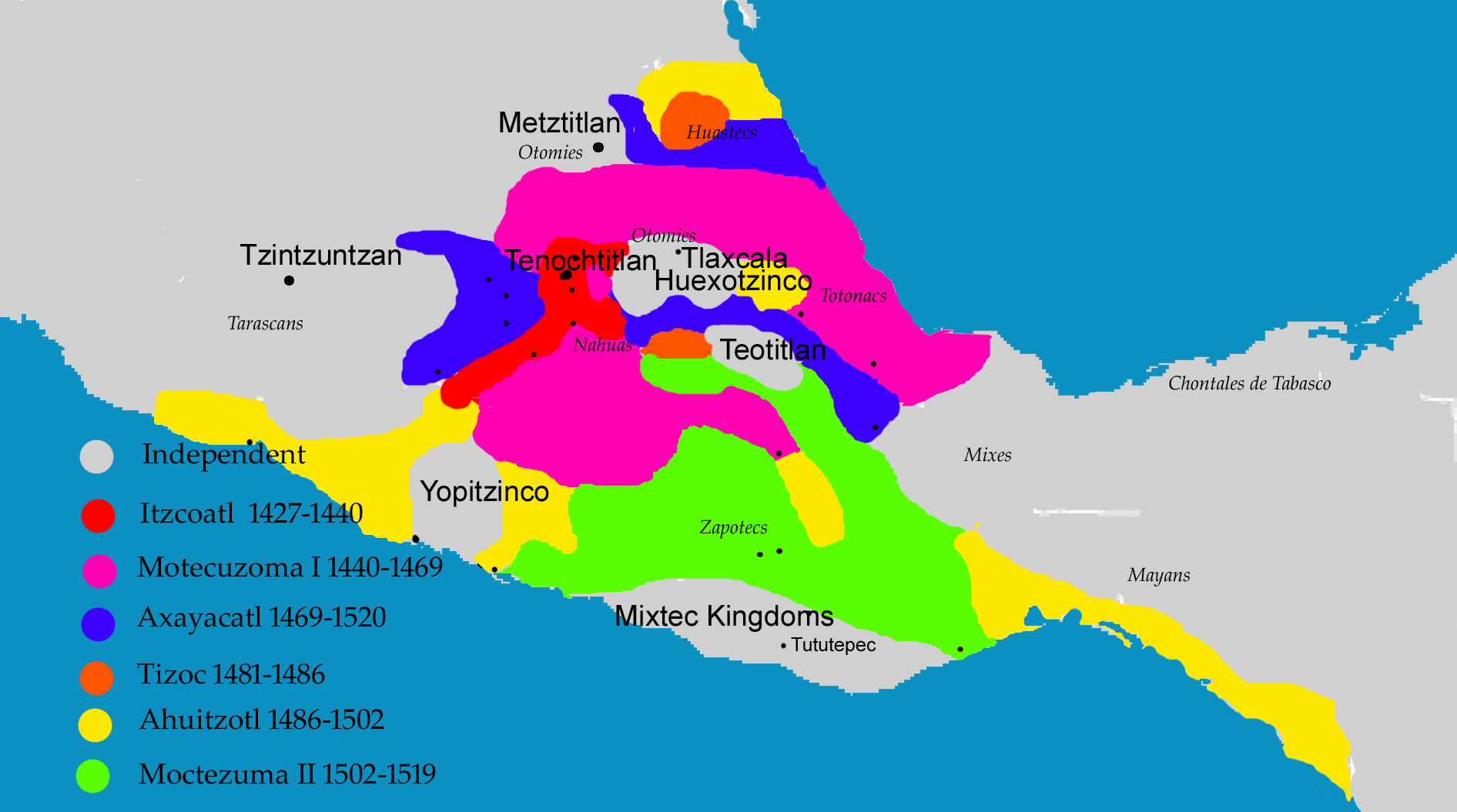
Zaachila III
Zaachila (the Zapotec name; Nahuatl: ''Teotzapotlan''; Mixtec: ''Ñuhu Tocuisi'') was a powerful Mesoamerican city in what is now Oaxaca, Mexico, from the city of Oaxaca. The city is named after Zaachila Yoo, the Zapotec ruler, in the late 14th and early 15th century. Zaachila was home of Donaji- the last Zapotec princess. Zaachila is now an archaeological site. A large unexplored pyramid mound is in the center in which two tombs were discovered in 1962. These tombs are thought to belong to important Mixtec persons. Following the fall of Monte Alban, Zaachila became the last Zapotec capital. Sometime before the arrival of the Spaniards, the capital was conquered by the Mixtecs. The history of the pre-Hispanic city is unclear. One theory is that the site flourished 1100 and 1521 AD. Another theory is that the city was founded in 1399 and could be compared to Tenochtitlan, as it was a city in the middle of a lake. The full extent of the ancient city is not known either, princi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zapotec Languages
The Zapotec languages are a group of around 50 closely related indigenous Mesoamerican languages that constitute a main branch of the Oto-Manguean language family and which is spoken by the Zapotec people from the southwestern-central highlands of Mexico. A 2020 census reports nearly half a million speakers, with the majority inhabiting the state of Oaxaca. Zapotec-speaking communities are also found in the neighboring states of Puebla, Veracruz, and Guerrero. Labor migration has also brought a number of native Zapotec speakers to the United States, particularly in California and New Jersey. Most Zapotec-speaking communities are highly bilingual in Spanish. Name The name of the language in Zapotec itself varies according to the geographical variant. In Juchitán (Isthmus) it is ''Diidxazá'' , in Mitla it is ''Didxsaj'' , in Zoogocho it is ''Diža'xon'' , in Coatec Zapotec it is ''Di'zhke , in Miahuatec Zapotec it is ''Dí'zdéh'' and in Santa Catarina Quioquitani it is ''Tii ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zapotec Language
The Zapotec languages are a group of around 50 closely related indigenous Mesoamerican languages that constitute a main branch of the Oto-Manguean language family and which is spoken by the Zapotec people from the southwestern-central highlands of Mexico. A 2020 census reports nearly half a million speakers, with the majority inhabiting the state of Oaxaca. Zapotec-speaking communities are also found in the neighboring states of Puebla, Veracruz, and Guerrero. Labor migration has also brought a number of native Zapotec speakers to the United States, particularly in California and New Jersey. Most Zapotec-speaking communities are highly bilingual in Spanish. Name The name of the language in Zapotec itself varies according to the geographical variant. In Juchitán (Isthmus) it is ''Diidxazá'' , in Mitla it is ''Didxsaj'' , in Zoogocho it is ''Diža'xon'' , in Coatec Zapotec it is ''Di'zhke , in Miahuatec Zapotec it is ''Dí'zdéh'' and in Santa Catarina Quioquitani it is ''T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiapas
Chiapas (; Tzotzil and Tzeltal: ''Chyapas'' ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Chiapas), is one of the states that make up the 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises 124 municipalities and its capital and largest city is Tuxtla Gutiérrez. Other important population centers in Chiapas include Ocosingo, Tapachula, San Cristóbal de las Casas, Comitán, and Arriaga. Chiapas is the southernmost state in Mexico, and it borders the states of Oaxaca to the west, Veracruz to the northwest, and Tabasco to the north, and the Petén, Quiché, Huehuetenango, and San Marcos departments of Guatemala to the east and southeast. Chiapas has a significant coastline on the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. In general, Chiapas has a humid, tropical climate. In the northern area bordering Tabasco, near Teapa, rainfall can average more than per year. In the past, natural vegetation in this region was lowland, tall perennial rainforest, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by Honduras; to the southeast by El Salvador and to the south by the Pacific Ocean. With an estimated population of around million, Guatemala is the most populous country in Central America and the 11th most populous country in the Americas. It is a representative democracy with its capital and largest city being Nueva Guatemala de la Asunción, also known as Guatemala City, the most populous city in Central America. The territory of modern Guatemala hosted the core of the Maya civilization, which extended across Mesoamerica. In the 16th century, most of this area was conquered by the Spanish and claimed as part of the viceroyalty of New Spain. Guatemala attained independence in 1821 from Spain and Mexico. In 1823, it became part of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tlatoani
''Tlatoani'' ( , "one who speaks, ruler"; plural ' or tlatoque) is the Classical Nahuatl term for the ruler of an , a pre-Hispanic state. It is the noun form of the verb "tlahtoa" meaning "speak, command, rule". As a result, it has been variously translated in English as "king", "ruler", or "speaker" in the political sense. Above a tlahtoani is the ''Weyi Tlahtoani,'' sometimes translated as "Great Speaker", though more usually as "Emperor" (the term is often seen as the equivalent to the European " great king"). A ' () is a female ruler, or queen regnant. The term refers to "vice-leader". The leaders of the Mexica prior to their settlement are sometimes referred to as , as well as colonial rulers who were not descended from the ruling dynasty. The ruler's lands were called , and the ruler's house was called ''Nahuatl dictionary'' (1997). Wired humanities project. Retrieved January 1, 2012, frolink/ref> The city-states of the Aztec Empire each had their own tlatoani, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahuitzotl
Ahuitzotl ( nah, āhuitzotl, ) was the eighth Aztec ruler, the '' Huey Tlatoani'' of the city of Tenochtitlan, son of princess Atotoztli II. His name literally means "Water Thorny" and was also applied to the otter. It is also theorized that more likely, the animal called ahuitzotl is actually the water opossum, the hand symbolizing its prehensile tail, which otters notably lack. Either Ahuitzotl or his predecessor Tizoc was the first ''tlatoani'' of Tenochtitlan to assume the title ''Huey Tlatoani'' ("supreme ''tlatoani''") to make their superiority over the other cities in the Triple Alliance (Aztec Empire) clear. Ahuitzotl was responsible for much of the expansion of the Mexica domain, and consolidated the empire's power after emulating his predecessor. He took power as Emperor in the year 7 Rabbit (1486), after the death of his predecessor and brother, Tizoc. He had two sons, the kings Chimalpilli II and Cuauhtémoc, and one daughter. Biography Perhaps the greatest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casus Belli
A (; ) is an act or an event that either provokes or is used to justify a war. A ''casus belli'' involves direct offenses or threats against the nation declaring the war, whereas a ' involves offenses or threats against its ally—usually one bound by a mutual defense pact. Either may be considered an A declaration of war usually contains a description of the ''casus belli'' that has led the party in question to declare war on another party. Terminology The term ''casus belli'' came into widespread use in Europe in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries through the writings of Hugo Grotius (1653), Cornelius van Bynkershoek (1707), and Jean-Jacques Burlamaqui (1732), among others, and due to the rise of the political doctrine of '' jus ad bellum'' or "just war theory". The term is also used informally to refer to any "just cause" a nation may claim for entering into a conflict. It is used retrospectively to describe situations that arose before the term came into wide us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1450 Births
*
{{Number disambiguation ...
145 may refer to: *145 (number), a natural number * AD 145, a year in the 2nd century AD *145 BC, a year in the 2nd century BC *145 (dinghy), a two-person intermediate sailing dinghy *145 (South) Brigade *145 (New Jersey bus) See also * List of highways numbered 145 The following highways are numbered 145: Australia * Lower Barrington Road, Paloona Road, Melrose Road, Bellamy Road, Forthside Road (Tasmania) * Inverleigh–Winchelsea Road (Victoria) Canada * Winnipeg Route 145 * New Brunswick Route 145 * P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |