|
Corycae
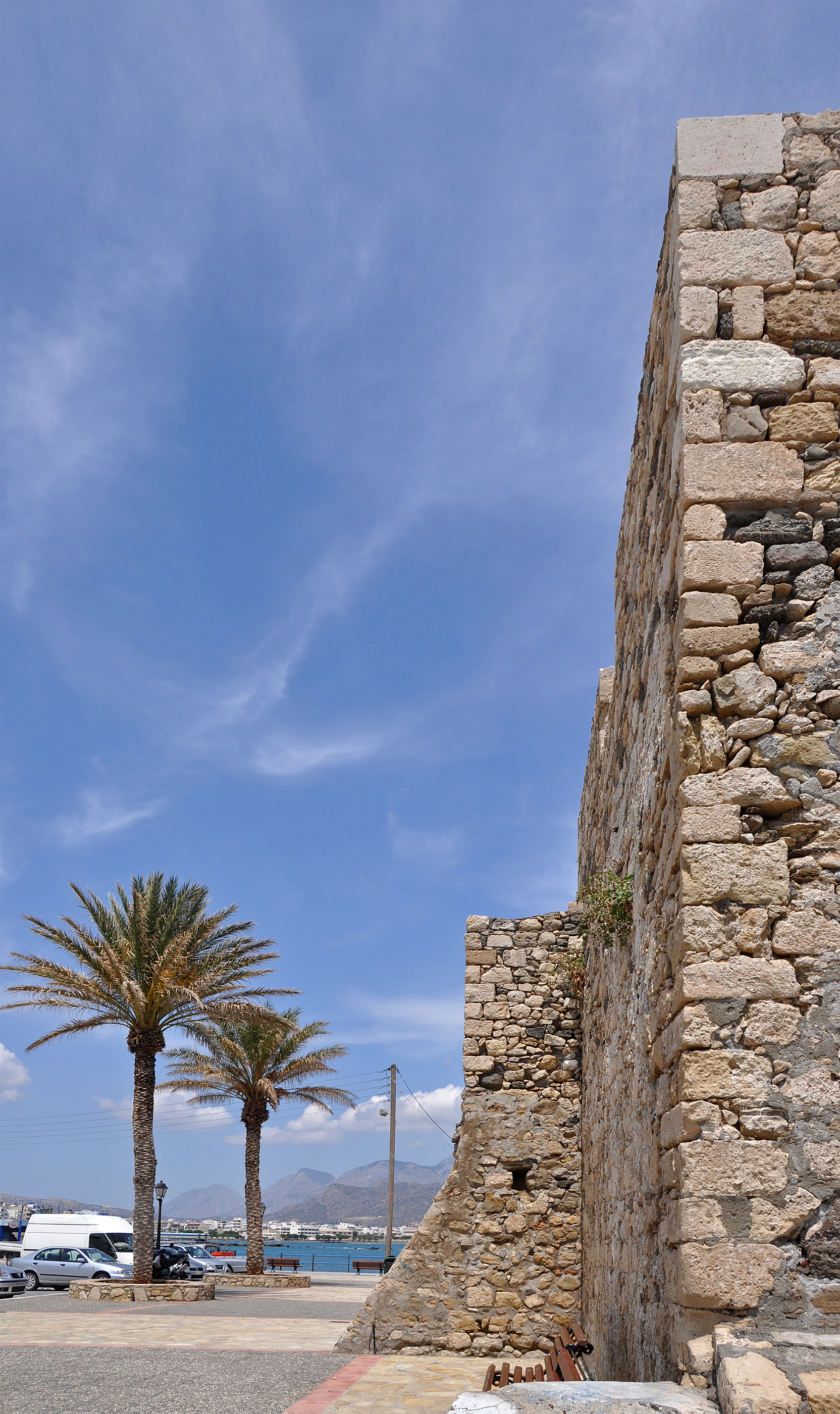
Gramvousa also Grampousa ( el, Γραμβούσα or Γραμπούσα, further names include ''Akra'', ''Cavo Buso'', ''Cavo Bouza'', ''Garabusa'' and ''Grabusa'') refers to two small uninhabited islands off the coast of a peninsula also known Gramvousa Peninsula (Greek: ''Χερσόνησος Γραμβούσας'') in north-western Crete in the regional unit of Chania. The Gramvousa Peninsula forms the westernmost of the two pairs of peninsulae in north-western Crete (the other being Rodopos Peninsula) and is the western part of Kissamos Bay. The Gramvousa islands are administered by the municipality of Kissamos. Naming Imeri Gramvousa ( el, Ήμερη Γραμβούσα), which translates to ''Tame Gramvousa'', hosts the remains of a Venetian fort and the remains of buildings left behind by Cretan insurgents, who were compelled to live as pirates during the Greek War of Independence. Today, Imeri Gramvousa is a popular tourist attraction. Agria Gramvousa ( el, Άγρια ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gramvousa Peninsula
Gramvousa Peninsula ( el, Χερσόνησος Γραμβούσας, Chersonesos Gramvousas) is a peninsula at the northwestern end of the island of Crete, Greece. Anciently, it was known as Corycus or Korykos ( grc, Κώρυκος), or as Cimarus or Kimaros (Κίμαρος); although the latter is ascribed to the cape at the northern extremity of the peninsula ( Cape Vouxa). Strabo states that Corycus was the point whence the distances to the several ports of Peloponnesus were measured. According to Pliny, the islands which lie off this promontory were called Corycae (modern Gramvousa), and that part of the mass of rock which forms this point went by the name of Mount Corycus. Ptolemy mentions a city also called Corycus, and there is a passage in which Juvenal mentions a Corycian vessel which evidently belonged to this Cretan town. When the Florentine traveller Cristoforo Buondelmonti visited the island in 1415, he found remains existing.Cornelius, ''Creta Sacra'', vol. i. p. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
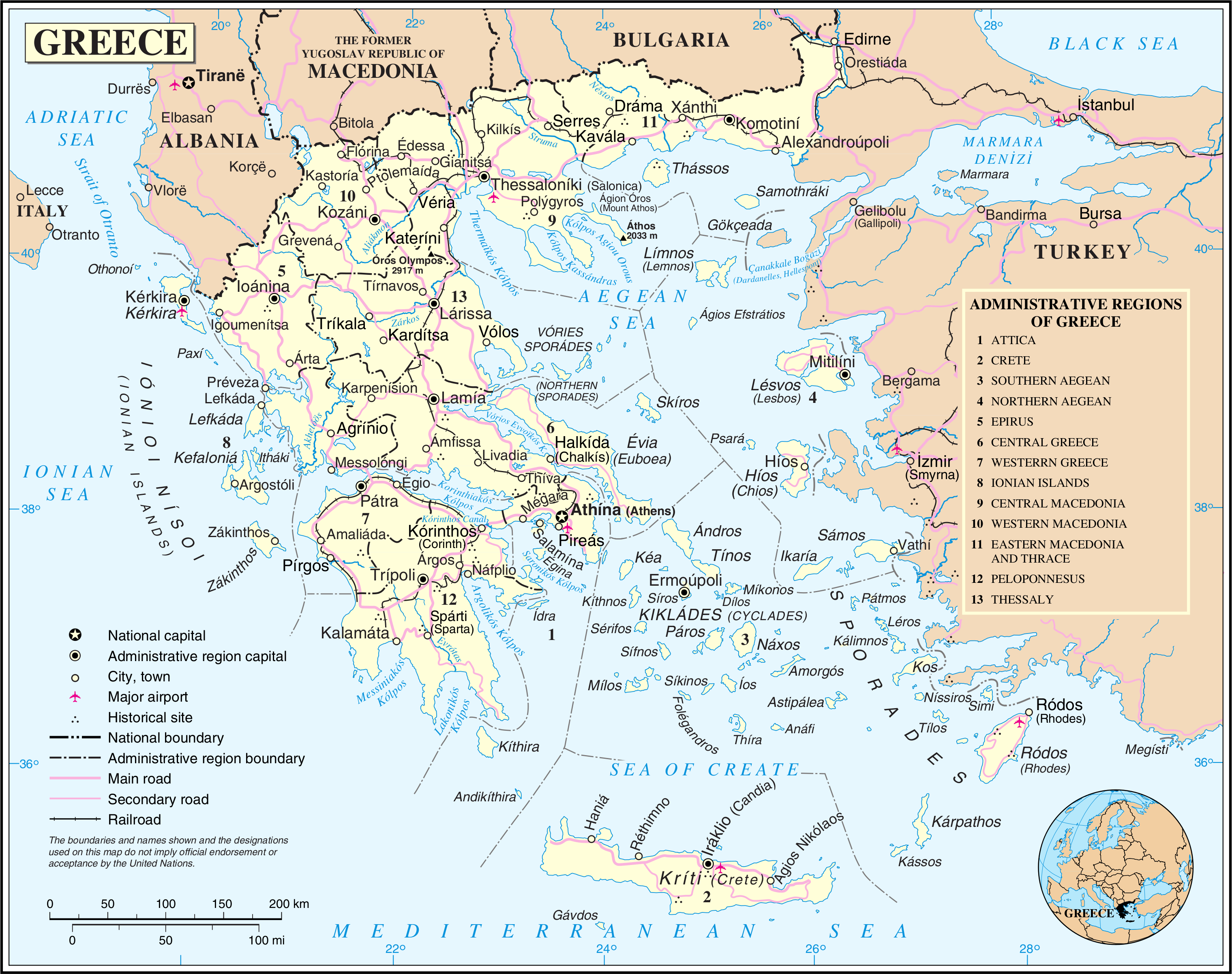
Modern Regions Of Greece
The regions of Greece ( el, περιφέρειες, translit=periféries) are the country's thirteen first-level administrative entities, each comprising several second-level units, originally known as prefectures and, since 2011, as regional units. History The current regions were established in July 1986 (the presidential decree officially establishing them was signed in 1987), by decision of the interior minister, Menios Koutsogiorgas, as second-level administrative entities, complementing the prefectures (Law 1622/1986). Ν.1622/86 "Τοπική Αυτοδιοίκηση - Περιφερειακή Ανάπτυξη - Δημοκρατικός Προγραμματισμός", (ΦΕΚ 92/τ.Α΄/14-7-1986) Before 1986, there was a traditional division into broad historical–geographical regions (γεωγραφικά διαμερίσματα), which, however, was often arbitrary; not all of the pre-1986 traditional historical-geographic regions had official administrative bodie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morean War
The Morean War ( it, Guerra di Morea), also known as the Sixth Ottoman–Venetian War, was fought between 1684–1699 as part of the wider conflict known as the "Great Turkish War", between the Republic of Venice and the Ottoman Empire. Military operations ranged from Dalmatia to the Aegean Sea, but the war's major campaign was the Venetian conquest of the Morea (Peloponnese) peninsula in southern Greece. On the Venetian side, the war was fought to avenge the loss of Crete in the Cretan War (1645–1669). It happened while the Ottomans were entangled in their northern struggle against the Habsburgsbeginning with the failed Ottoman attempt to conquer Vienna and ending with the Habsburgs gaining Buda and the whole of Hungary, leaving the Ottoman Empire unable to concentrate its forces against the Venetians. As such, the Morean War was the only Ottoman–Venetian conflict from which Venice emerged victorious, gaining significant territory. Venice's expansionist revival would be shor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hania
Chania ( el, Χανιά ; vec, La Canea), also spelled Hania, is a city in Greece and the capital of the Chania regional unit. It lies along the north west coast of the island Crete, about west of Rethymno and west of Heraklion. The municipality has 108,642 inhabitants (2011). This consists of the city of Chania and several nearby areas, including Kounoupidiana (pop. 8,620), Mournies (pop. 7,614), Souda (pop. 6,418), Nerokouros (pop. 5,531), Daratsos (pop. 4,732), Perivolia (pop. 3,986), Galatas (pop. 3,166) and Aroni (pop. 3,003). History Early history Chania is the site of the Minoan settlement the Greeks called Kydonia, the source of the word quince. It appears on Linear B as ''ku-do-ni-ja''. Some notable archaeological evidence for the existence of this Minoan city below some parts of today's Chania was found by excavations in the district of Kasteli in the Old Town. This area appears to have been inhabited since the Neolithic era. The city reemerged after the end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rethymnon
Rethymno ( el, Ρέθυμνο, , also ''Rethimno'', ''Rethymnon'', ''Réthymnon'', and ''Rhíthymnos'') is a city in Greece on the island of Crete. It is the capital of Rethymno regional unit, and has a population of more than 30,000 inhabitants (near 40,000 for the municipal unit). It is a former Latin Catholic bishopric as Retimo(–Ario) and former Latin titular see. Rethymno was originally built during the Minoan civilization (ancient Rhithymna and Arsinoe). The city was prominent enough to mint its own coins and maintain urban growth. One of these coins is today depicted as the crest of the town: two dolphins in a circle. History This region as a whole is rich with ancient history, most notably through the Minoan civilisation centred at Knossos east of Rethymno. Rethymno itself began a period of growth when the Venetian conquerors of the island decided to put an intermediate commercial station between Heraklion and Chania, acquiring its own bishop and nobility in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heraklion
Heraklion or Iraklion ( ; el, Ηράκλειο, , ) is the largest city and the administrative capital of the island of Crete and capital of Heraklion regional unit. It is the fourth largest city in Greece with a population of 211,370 (Urban Area) according to the 2011 census. The population of the municipality was 177,064. The Bronze Age palace of Knossos, also known as the Palace of Minos, is located 5.5 km (3.1m) southeast of the city. Heraklion was Europe's fastest growing tourism destination for 2017, according to Euromonitor, with an 11.2% growth in international arrivals. According to the ranking, Heraklion was ranked as the 20th most visited region in Europe, as the 66th area on the planet and as the 2nd in Greece for the year 2017, with 3.2 million visitors and the 19th in Europe for 2018, with 3.4 million visitors. Etymology The Arab traders from al-Andalus (Iberia) who founded the Emirate of Crete moved the island's capital from Gortyna to a new castle they called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ierapetra
Ierapetra ( el, Ιεράπετρα, lit=sacred stone; ancient name: ) is a Greece, Greek town and municipality located on the southeast coast of Crete. History The town of Ierapetra (in the local dialect: Γεράπετρο ''Gerapetro'') is located on the southeast coast of Crete, situated on the beach of Ierapetra Bay. This town lies south of Agios Nikolaos, Crete, Agios Nikolaos and southwest of Sitia, and is an important regional center. With 16,139 inhabitants (in 2011), Ierapetra is the most populous town in the regional unit of Lasithi and the fourth most populous town in Crete. Ierapetra is nicknamed "the bride of the Libyan Sea" because of its position as the only town on Crete's southern coast. Antiquity Ierapetra has retained a prominent place in the history of Crete since the Minoan civilization, Minoan period. The Greek and later Ancient Rome, Roman town of Hierapytna was located on the same site as present-day Ierapetra. In the Classical antiquity, Classical Age, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatzimichalis Dalianis
Hatzimichalis Dalianis ( el, Χατζημιχάλης Νταλιάνης, 1775 – 17 March 1828) was a revolutionary leader of the Greek War of Independence and commander in Crete in 1828. Greek War of Independence According to some Greek historians, the Greek speaking towns of Argyrokastro, Vouliarates, Premeti, and Delvinaki argue over his origin. Some believe he was born in the Greek-speaking town of Delvinaki, Epirus, when the region was under Ottoman rule.Detorakis, Turkish rule in Crete, p. 383 Consequent research, however, by other Greek historians disputes this fact. Nevertheless, all agree that he was born in Epirus. Alexander Mammopoulos attributes his birthplace conclusively to an Albanian-speaking village of the same name in modern Përmet District, while Stavros Karkaletsis, claims that he was born in the Greek-speaking village of Bularat, in Dropull. He grew up in Trieste, where his father worked as a merchant. In 1816 he became a member of the Greek patriotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Mavrocordatos
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history. Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Aleksander and Aleksandr. Related names and diminutives include Iskandar, Alec, Alek, Alex, Alexandre, Aleks, Aleksa and Sander; feminine forms include Alexandra, Alexandria, and Sasha. Etymology The name ''Alexander'' originates from the (; 'defending men' or 'protector of men'). It is a compound of the verb (; 'to ward off, avert, defend') and the noun (, genitive: , ; meaning 'man'). It is an example of the widespread motif of Greek names expressing "battle-prowess", in this case the ability to withstand or push back an enemy battle line. The earliest attested form of the name, is the Mycenaean Greek feminine anthroponym , , (/Alexandra/), written in the Linear B syllabic script. Alaksandu, alternatively called ''Alakasandu'' or ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ioannis Kapodistrias
Count Ioannis Antonios Kapodistrias (10 or 11 February 1776 – 9 October 1831), sometimes anglicized as John Capodistrias ( el, Κόμης Ιωάννης Αντώνιος Καποδίστριας, Komis Ioannis Antonios Kapodistrias; russian: граф Иоанн Каподистрия, Graf Ioann Kapodistriya; it, Giovanni Antonio Capodistria, Conte Capo d'Istria), was a Greek statesman who served as the Foreign Minister of the Russian Empire and was one of the most distinguished politicians and diplomats of Europe. After a long and distinguished career in European politics and diplomacy he was elected as the first head of state of independent Greece (1827–31). He is considered the founder of the modern Greek state, and the architect of Greek independence. Background and early career Ioannis Kapodistrias was born in Corfu, the most populous Ionian Island (then under Venetian rule) to a distinguished Corfiote family. Kapodistrias's father was the nobleman, artist and pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klephts
Klephts (; Greek κλέφτης, ''kléftis'', pl. κλέφτες, ''kléftes'', which means "thieves" and perhaps originally meant just "brigand": "Other Greeks, taking to the mountains, became unofficial, self-appointed armatoles and were known as klephts (from the Greek ''kleptes'', "brigand").") were highwaymen turned self-appointed armatoloi, anti-Ottoman insurgents, and warlike mountain-folk who lived in the countryside when Greece was a part of the Ottoman Empire. They were the descendants of Greeks who retreated into the mountains during the 15th century in order to avoid Ottoman rule.: "The klephts were descendants of Greeks who fled into the mountains to avoid the Turks in the fifteenth century and who remained active as brigands into the nineteenth century." They carried on a continuous war against Ottoman rule and remained active as brigands until the 19th century. The terms kleptomania and kleptocracy are derived from the same Greek root, κλέπτειν (''klépte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
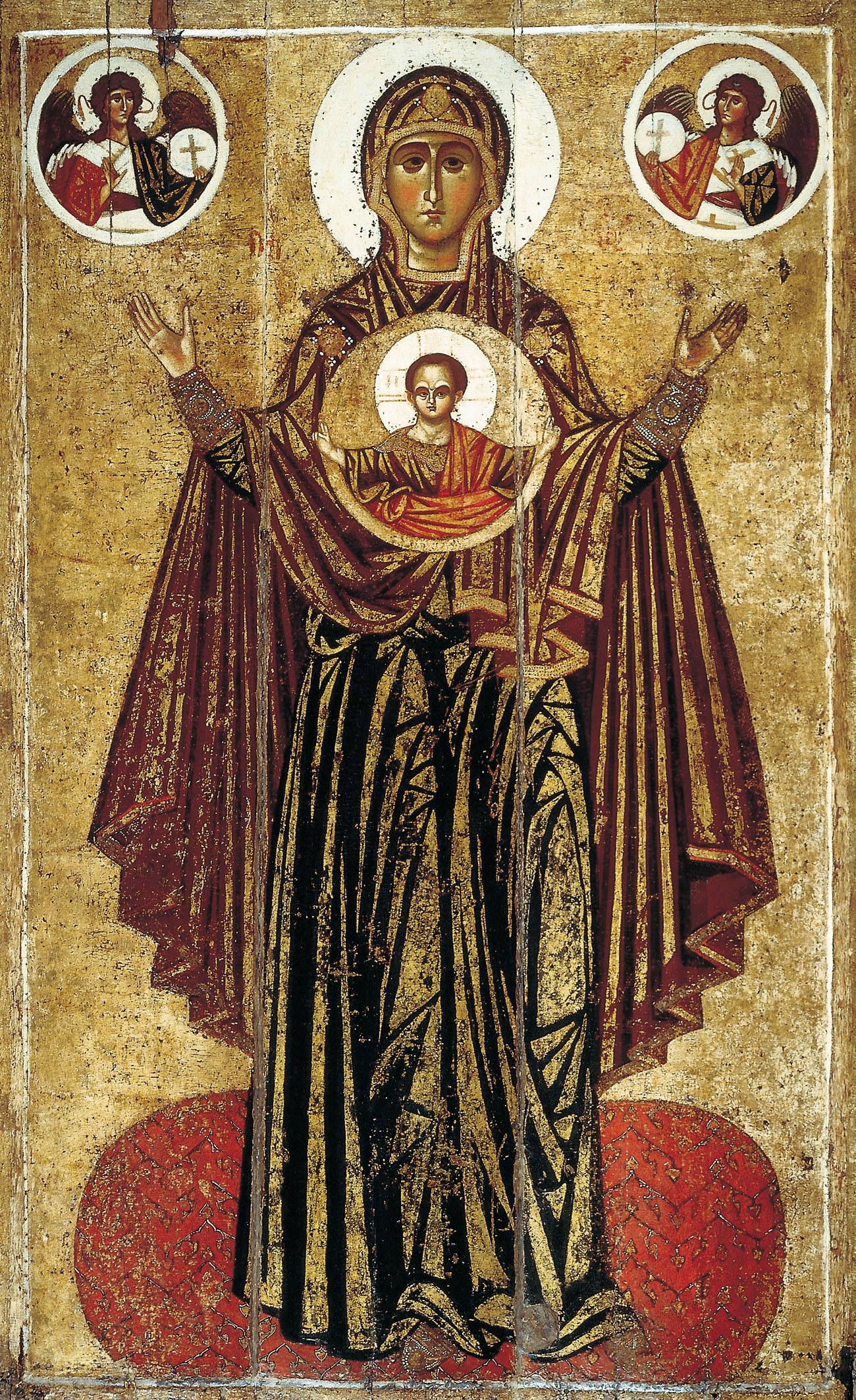
Panagia
Panagia ( el, Παναγία, fem. of , + , the ''All-Holy'', or the ''Most Holy''; pronounced ) (also transliterated Panaghia or Panajia), in Medieval and Modern Greek, is one of the titles of Mary, mother of Jesus, used especially in Eastern Catholicism and Orthodox Christianity. Most Greek churches dedicated to the Virgin Mary are called ''Panagia''; the standard western Christian designation of "St. Mary" is rarely used in the Orthodox East, as Mary is considered the holiest of all created beings and therefore of higher status than the Saints. Iconography ''Panagia'' is also the term for a particular type of icon of the Theotokos, wherein she is facing the viewer directly, usually depicted full length with her hands in the ''orans'' position, and with a medallion showing the image of Christ as a child in front of her chest. This medallion symbolically represents Jesus within the womb of the Virgin Mary at the moment of the Incarnation. This type of icon is also called t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)