|
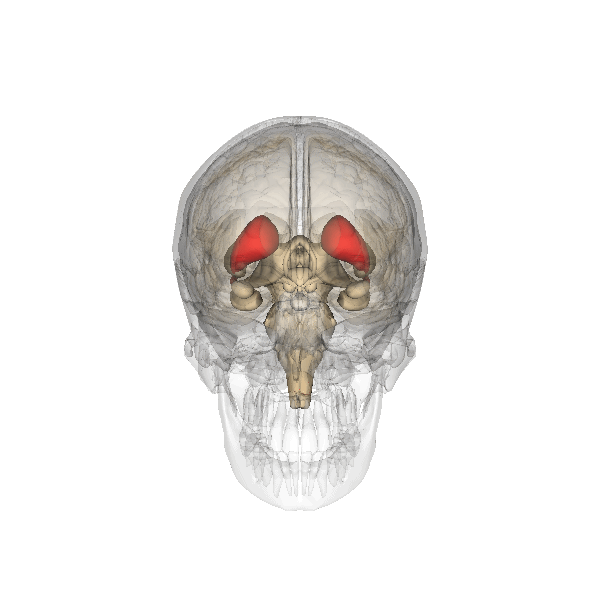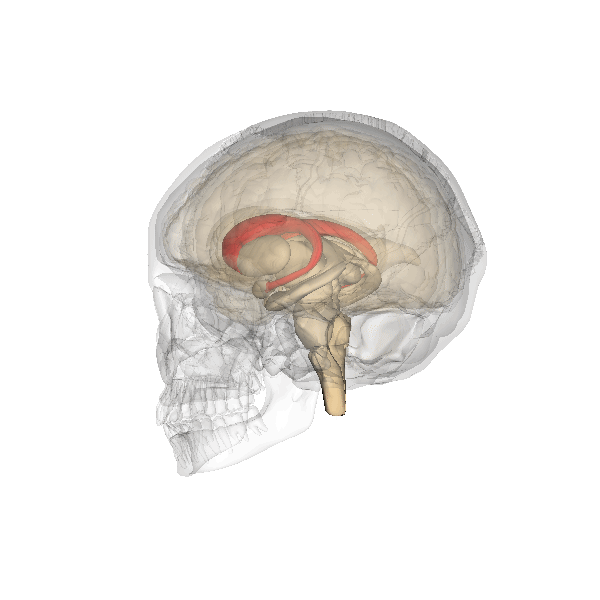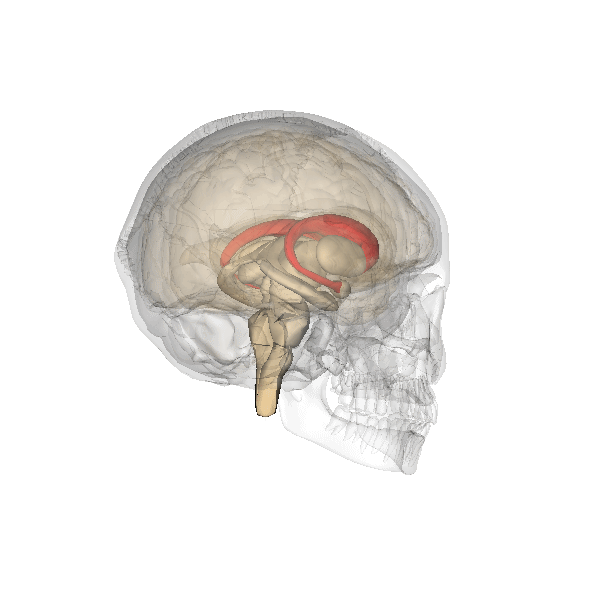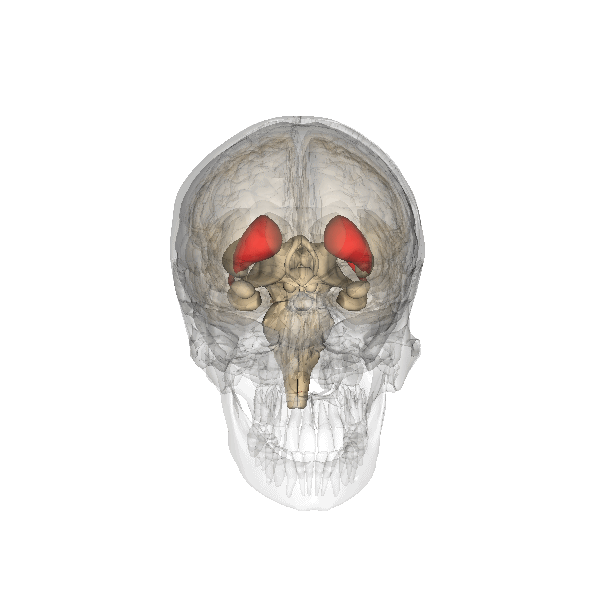
Cortico-basal Ganglia-thalamo-cortical Loop
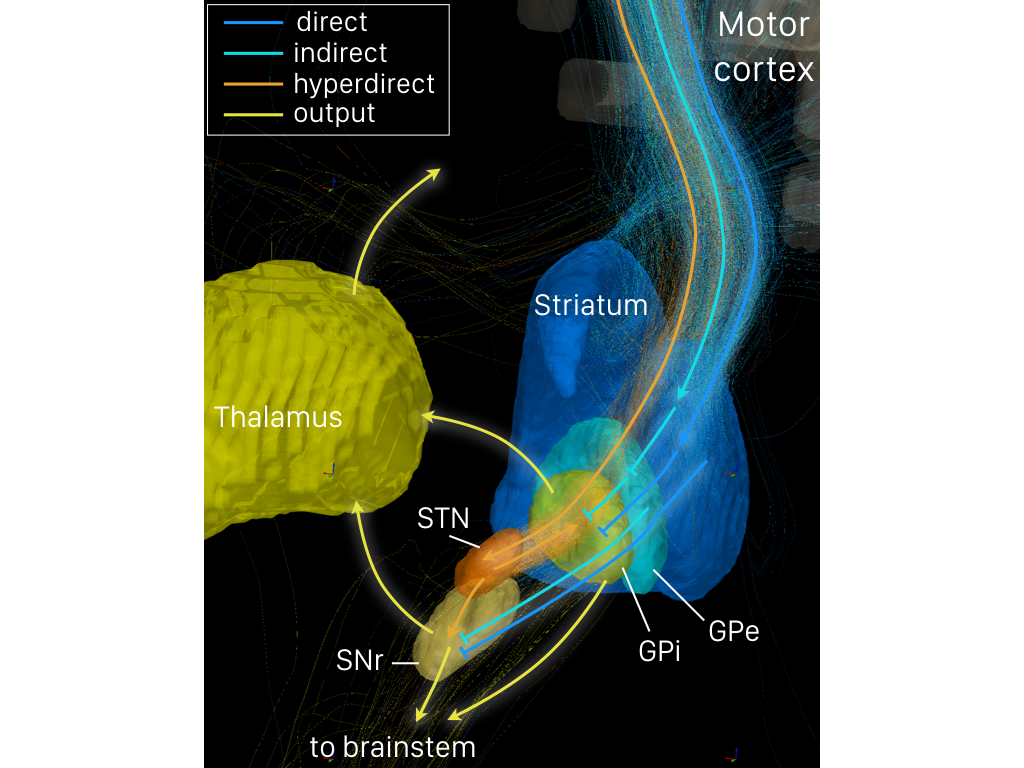
The cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop (CBGTC loop) is a system of neural circuits in the brain. The loop involves connections between the cortex, the basal ganglia, the thalamus, and back to the cortex. It is of particular relevance to hyperkinetic and hypokinetic movement disorders, such as Parkinson's disease and Huntington's disease, as well as to mental disorders of control, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD), and Tourette syndrome. The CBGTC loop primarily consists of modulatory dopaminergic projections from the pars compacta of the substantia nigra, and ventral tegmental area as well as excitatory glutamatergic projections from the cortex to the striatum, where these projections form synapses with excitatory and inhibitory pathways that relay back to the cortex. The loop was originally proposed as a part of a model of the basal ganglia called the ''parallel processing model'', which has bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal Ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG), or basal nuclei, are a group of subcortical nuclei, of varied origin, in the brains of vertebrates. In humans, and some primates, there are some differences, mainly in the division of the globus pallidus into an external and internal region, and in the division of the striatum. The basal ganglia are situated at the base of the forebrain and top of the midbrain. Basal ganglia are strongly interconnected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and brainstem, as well as several other brain areas. The basal ganglia are associated with a variety of functions, including control of voluntary motor movements, procedural learning, habit learning, conditional learning, eye movements, cognition, and emotion. The main components of the basal ganglia – as defined functionally – are the striatum, consisting of both the dorsal striatum ( caudate nucleus and putamen) and the ventral striatum ( nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle), the globus pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pars Compacta
The pars compacta (SNpc) is a portion of the ''substantia nigra'', located in the midbrain. It is formed by dopaminergic neurons and located medial to the pars reticulata. Parkinson's disease is characterized by the death of dopaminergic neurons in this region. Anatomy In humans, the nerve cell bodies of the ''pars compacta'' are coloured black by the pigment neuromelanin. The degree of pigmentation increases with age. This pigmentation is visible as a distinctive black stripe in brain sections and is the origin of the name given to this volume of the brain. The neurons have particularly long and thick dendrites (François et al.). The ventral dendrites, particularly, go down deeply in the pars reticulata. Other similar neurons are more sparsely distributed in the midbrain and constitute "groups" with no well-defined borders, although continuous to the pars compacta, in a prerubral position. These have been given, in early works in rats (with not much respect for the anatomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globus Pallidus
The globus pallidus (GP), also known as paleostriatum or dorsal pallidum, is a subcortical structure of the brain. It consists of two adjacent segments, one external, known in rodents simply as the globus pallidus, and one internal, known in rodents as the entopeduncular nucleus. It is part of the telencephalon, but retains close functional ties with the subthalamus in the diencephalon – both of which are part of the extrapyramidal motor system. The globus pallidus is a major component of the basal ganglia, with principal inputs from the striatum, and principal direct outputs to the thalamus and the substantia nigra. The latter is made up of similar neuronal elements, has similar afferents from the striatum, similar projections to the thalamus, and has a similar synaptology. Neither receives direct cortical afferents, and both receive substantial additional inputs from the intralaminar thalamus. Globus pallidus is Latin for "pale globe". Structure Pallidal nuclei are made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globus Pallidus
The globus pallidus (GP), also known as paleostriatum or dorsal pallidum, is a subcortical structure of the brain. It consists of two adjacent segments, one external, known in rodents simply as the globus pallidus, and one internal, known in rodents as the entopeduncular nucleus. It is part of the telencephalon, but retains close functional ties with the subthalamus in the diencephalon – both of which are part of the extrapyramidal motor system. The globus pallidus is a major component of the basal ganglia, with principal inputs from the striatum, and principal direct outputs to the thalamus and the substantia nigra. The latter is made up of similar neuronal elements, has similar afferents from the striatum, similar projections to the thalamus, and has a similar synaptology. Neither receives direct cortical afferents, and both receive substantial additional inputs from the intralaminar thalamus. Globus pallidus is Latin for "pale globe". Structure Pallidal nuclei are made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indirect Pathway
The indirect pathway, sometimes known as the indirect pathway of movement, is a neuronal circuit through the basal ganglia and several associated nuclei within the central nervous system (CNS) which helps to prevent unwanted muscle contractions from competing with voluntary movements. It operates in conjunction with the direct pathway. Overview of Neuronal Connections and Normal Function The indirect pathway passes through the caudate, putamen, and globus pallidus, which are parts of the basal ganglia. It traverses the subthalamic nucleus, a part of the diencephalon, and enters the substantia nigra, a part of the midbrain. In a resting individual, a specific region of the globus pallidus, known as the internus, and a portion of the substantia nigra, known as the pars reticulata, send spontaneous inhibitory signals to the ventrolateral nucleus (VL) of the thalamus, through the release of GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter. Inhibition of the excitatory neurons within VL, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subthalamic Nucleus
The subthalamic nucleus (STN) is a small lens-shaped nucleus in the brain where it is, from a functional point of view, part of the basal ganglia system. In terms of anatomy, it is the major part of the subthalamus. As suggested by its name, the subthalamic nucleus is located ventral to the thalamus. It is also dorsal to the substantia nigra and medial to the internal capsule. It was first described by Jules Bernard Luys in 1865, and the term ''corpus Luysi'' or ''Luys' body'' is still sometimes used. Anatomy Structure The principal type of neuron found in the subthalamic nucleus has rather long, sparsely spiny dendrites. In the more centrally located neurons, the dendritic arbors have a more ellipsoidal shape. The dimensions of these arbors (1200 μm, 600 μm, and 300 μm) are similar across many species—including rat, cat, monkey and human—which is unusual. However, the number of neurons increases with brain size as well as the external dimensions o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caudate Nucleus
The caudate nucleus is one of the structures that make up the corpus striatum, which is a component of the basal ganglia in the human brain. While the caudate nucleus has long been associated with motor processes due to its role in Parkinson's disease, it plays important roles in various other nonmotor functions as well, including procedural learning, associative learning and inhibitory control of action, among other functions. The caudate is also one of the brain structures which compose the reward system and functions as part of the cortico–basal ganglia–thalamic loop. Structure Together with the putamen, the caudate forms the dorsal striatum, which is considered a single functional structure; anatomically, it is separated by a large white matter tract, the internal capsule, so it is sometimes also referred to as two structures: the medial dorsal striatum (the caudate) and the lateral dorsal striatum (the putamen). In this vein, the two are functionally distinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Putamen
The putamen (; from Latin, meaning "nutshell") is a round structure located at the base of the forebrain (telencephalon). The putamen and caudate nucleus together form the dorsal striatum. It is also one of the structures that compose the basal nuclei. Through various pathways, the putamen is connected to the substantia nigra, the globus pallidus, the claustrum, and the thalamus, in addition to many regions of the cerebral cortex. A primary function of the putamen is to regulate movements at various stages (e.g. preparation and execution) and influence various types of learning. It employs GABA, acetylcholine, and enkephalin to perform its functions. The putamen also plays a role in degenerative neurological disorders, such as Parkinson's disease. History The word "putamen" is from Latin, referring to that which "falls off in pruning", from "putare", meaning "to prune, to think, or to consider". Until recently, most MRI research focused broadly on the basal ganglia as a who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Synapse
Chemical synapses are biological junctions through which neurons' signals can be sent to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie perception and thought. They allow the nervous system to connect to and control other systems of the body. At a chemical synapse, one neuron releases neurotransmitter molecules into a small space (the synaptic cleft) that is adjacent to another neuron. The neurotransmitters are contained within small sacs called synaptic vesicles, and are released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. These molecules then bind to neurotransmitter receptors on the postsynaptic cell. Finally, the neurotransmitters are cleared from the synapse through one of several potential mechanisms including enzymatic degradation or re-uptake by specific transporters either on the presynaptic cell or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Striatum
The striatum, or corpus striatum (also called the striate nucleus), is a nucleus (a cluster of neurons) in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward systems; receives glutamatergic and dopaminergic inputs from different sources; and serves as the primary input to the rest of the basal ganglia. Functionally, the striatum coordinates multiple aspects of cognition, including both motor and action planning, decision-making, motivation, reinforcement, and reward perception. The striatum is made up of the caudate nucleus and the lentiform nucleus. The lentiform nucleus is made up of the larger putamen, and the smaller globus pallidus. Strictly speaking the globus pallidus is part of the striatum. It is common practice, however, to implicitly exclude the globus pallidus when referring to striatal structures. In primates, the striatum is divided into a ventral striatum, and a dorsal striatum, subdivisions that are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting of allocortex. It is separated into two cortices, by the longitudinal fissure that divides the cerebrum into the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The two hemispheres are joined beneath the cortex by the corpus callosum. The cerebral cortex is the largest site of neural integration in the central nervous system. It plays a key role in attention, perception, awareness, thought, memory, language, and consciousness. The cerebral cortex is part of the brain responsible for cognition. In most mammals, apart from small mammals that have small brains, the cerebral cortex is folded, providing a greater surface area in the confined volume of the cranium. Apart from minimising brain and cranial volume, cortical folding is crucial for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |