|
Corselitze
Corselitze, or Korselitse, is a manor house on the island of Falster in the south-east of Denmark. The Neoclassical house was built in 1777 by Johan Frederik Classen, who at the time of his death founded Det Classenske Fideicommis, which owns the estate today. History Early history ''Corselitze'' derives from Wendish and means 'settlement of Chotel's heirs'. The estate shares much of its early history with the island of Falster. Like most of the island, it belonged to the Crown in the 13th century and is mentioned in King Valdemar II's Danish Census Book which dates from about 1231. In 1354 Corselitze was acquired by Jens Falster, a member of the local nobility, and it remained in the possession of his family until 1600 when it was sold to . A few years later, in 1603, it was reacquired by the Crown in exchange for Eskebjerg on Funen. Between 1560 and 1650 the entire island of Falster once again came under the Crown through such transactions. Initially it was used as , a Danish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corselitze Forest
Corselitze Forest (alternate, Corselitz; da, Corselitze skov) is located on the Denmark, Danish island of Falster. Situated in the northeast of the island, it contains white pine plantations, although beech is the most common tree species. History The forest, a manor house also named Corselitze, a summerhouse, an extensive garden, farmland, and additional surrounding forests were developed by Major general Johan Frederik Classen, a successful businessman who made his fortune running a number of companies in Frederiksværk in the north of Zealand. He had acquired the Corselitze estate from the Crown in 1768. When he died in 1792, he left all his possessions to a charitable foundation known as ''Det Classenske Fideicommis'' which continues to manage the forest today. The forest The forest covers an area of and consists mainly of deciduous trees including beech and oak although there are also some Pinophyta, conifers. It is typical of eastern Denmark with beech the most important ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johan Frederik Classen
Johan Frederik Classen, frequently also J. F. Classen, (11 February 1725 – 24 March 1792) was a Danish-Norwegian industrialist, major general, landowner and founder of Det Classenske Fideicommis. He served as chancellery adviser to King Frederik V. Classen built the manor house Arresødal in 1773, he renovated the Neoclassical manor house Corselitze in 1777, and built the General's Summerhouse by the Corselitze Forest. Early years Classen was born in Oslo (then called Christiania), where his father (from Sønderborg on the Danish island of Als), was an organist. The father, who had the same name as his son, was born 1697 and died 1775; his mother, Maria, born Walter (1702-1768 ), was from a Norwegian farmer family. After having gone through grammar school in his hometown, he became a theology candidate at University of Copenhagen in 1741, taking his examinations three years later. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generalens Lysthus
Generalens Lysthus (the General's Summer House) is a small, thatched cottage in Tromnæs Forest on the Denmark, Danish island of Falster. It was built in 1786 by the industrialist Johan Frederik Classen who also built nearby Corselitze. Architecture The house is located near the sea at the end of the road from Corselitze manor which lies to the west. It bears a close resemblance to the larger thatched country home at Liselund on the island of Møn. Designed by Andreas Kirkerup and completed in 1786 in the Neoclassical style, the one-storey, half-timbered whitewashed building has a covered veranda and a living room. The hipped thatched roof has wooden thatching supports along the ridge. In addition to the cottages's small-paned casement windows on all sides, the veranda has larger round-arched windows while the tops of the double doors are also glazed. As a result, the interior has a pleasantly bright look. The windows, doors and woodwork are painted green. The veranda is supported b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Det Classenske Fideicommis
Det Classenske Fideicommis (literally "The Classen Fideicommiss") is a Danish charitable foundation. By testament in 1789 and his codicil of March 23, 1792, the industrialist Major General Johan Frederik Classen left behind his wealth and possessions as a fund, among other things, to "alleviate poverty and misery". It grants about 2 million kroner ($340,000) annually. Retrieved 26 November 2012. Background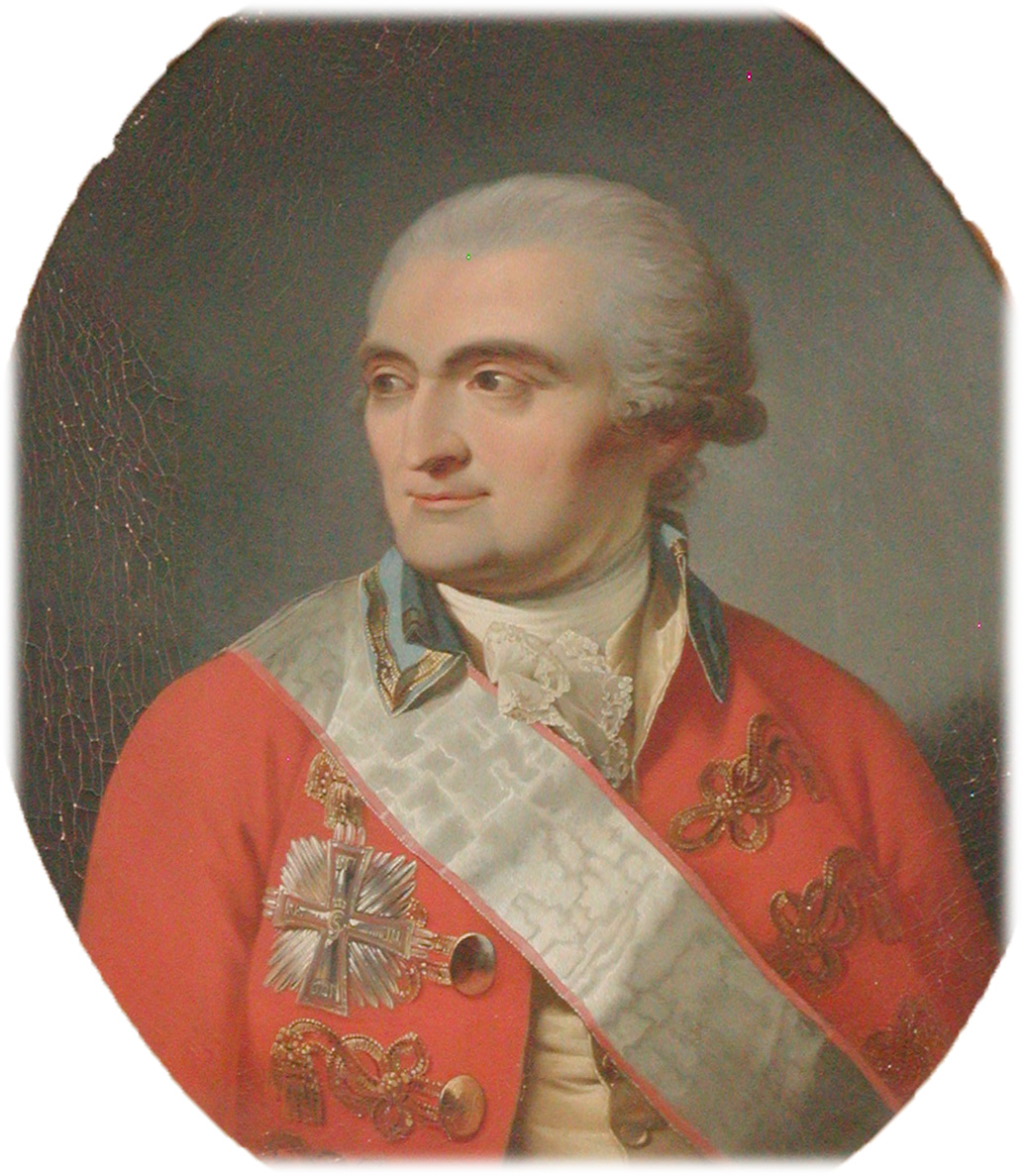  Classen (1725–1792) was an enterprising businessman and industrialist who developed an armaments and munitions factory in northwest
Classen (1725–1792) was an enterprising businessman and industrialist who developed an armaments and munitions factory in northwest
|
Andreas Kirkerup
Andreas Johannes Kirkerup (9 June 1749 – 22 October 1810) was a Danish architect and master builder, one of the most significant pupils of Caspar Frederik Harsdorff. Together with architects such as Andreas Hallander and Johan Martin Quist, he played a major role in the rebuilding of Copenhagen after the Great Fire of 1795. Early life and education Kirkerup was born in on 9 June 1749 Copenhagen, the son of carpenter Johannes Andreasen Kirkerup (død 1755) and Dorothea Pedersdatter Wiese. Kirkerup followed in his father's footsteps, training under master builder Johan Boye Junge (1735–1807) who endorsed him to study architecture at the Royal Danish Academy of Fine Arts where he studied under Caspar Frederik Harsdorff (1735 – 1799). He won the Academy's small and large silver medals in 1768, the small gold medal in 1771 and finally the large gold medal in 1773. Career Kirkerup set up a business as master carpenter in 1774 and was appointed architect for the engineering tro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falster
Falster () is an island in south-eastern Denmark with an area of and 43,398 inhabitants as of 1 January 2010."Danmarks Statistik." Retrieved 28 June 2010. Located in the , it is part of and is administered by Guldborgsund Municipality. Falster includes Denmark's southernmost point, , near |
Hesnæs
Hesnæs is a little fishing village located southeast of Stubbekøbing on the Danish island of Falster. It is best known for its thatched, straw-clad houses, not found elsewhere in Denmark. History The first documented reference to Hesnæs (then ''Hesnes'') dates from 1551 when it is mentioned as a fishing village. In 1585, the Crown acquired Hesnæs from Peter Gyldenstjerne of Bønnet. It had 11 fishing huts and five net-making stalls. In 1771, it was bought by Johan Frederik Classen of Corselitze, founder of Det Classenske Fideicommis."Hesnæs" ''Historisk Atlas''. Retrieved 21 November 2012. In 1801, Hesnæs was a small fishing community consisting of 18 families in clay-plastered, whitewashed houses set out in rows beside the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassical Architecture
Neoclassical architecture is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy and France. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing styles of architecture in most of Europe for the previous two centuries, Renaissance architecture and Baroque architecture, already represented partial revivals of the Classical architecture of ancient Rome and (much less) ancient Greek architecture, but the Neoclassical movement aimed to strip away the excesses of Late Baroque and return to a purer and more authentic classical style, adapted to modern purposes. The development of archaeology and published accurate records of surviving classical buildings was crucial in the emergence of Neoclassical architecture. In many countries, there was an initial wave essentially drawing on Roman architecture, followed, from about the start of the 19th century, by a second wave of Greek Revival architec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Wiedewelt
Johannes Wiedewelt (1 July 1731 – 17 December 1802), Danish neoclassical sculptor. He became a court sculptor, introducing neoclassical ideals to Denmark in the form of palace decorations, garden sculptures and artifacts and, especially, memorial monuments. He was undoubtedly the best known Danish sculptor before Bertel Thorvaldsen. Life Early training He was born in Copenhagen to royal sculptor to the Danish Court, Just Wiedewelt (1677–1757) and his wife Birgitte Lauridsdatter. The elder Wiedewelt recognised his son's talents early, and the boy trained under the Italian history painter Hieronimo Miani, one of the two leaders of the Drawing and Painting Academy (''Tegne- og Malerakademiet'') in Copenhagen along with Louis August le Clerc (1688–1771), as early as perhaps 1744. This Academy was the precursor to the still-extant Royal Danish Academy of Art (''Det Kongelige Danske Kunstakademi'') established ten years later. When Miani left Denmark in 1745 to retu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landscape Garden
The English landscape garden, also called English landscape park or simply the English garden (french: Jardin à l'anglaise, it, Giardino all'inglese, german: Englischer Landschaftsgarten, pt, Jardim inglês, es, Jardín inglés), is a style of "landscape" garden which emerged in England in the early 18th century, and spread across Europe, replacing the more formal, symmetrical French formal garden which had emerged in the 17th century as the principal gardening style of Europe. The English garden presented an idealized view of nature. Created and pioneered by William Kent and others, the “informal” garden style originated as a revolt against the architectural garden and drew inspiration from paintings of landscapes by Salvator Rosa, Claude Lorrain, and Nicolas Poussin.Bris, Michel Le. 1981. ''Romantics and Romanticism.'' Skira/Rizzoli International Publications, Inc. New York 1981. 215 pp. age 17Tomam, Rolf, editor. 2000. ''Neoclassicism and Romanticism: Architecture, S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reed (plant)
Reed is a common name for several tall, grass-like plants of wetlands. Varieties They are all members of the order Poales (in the modern, expanded circumscription), and include: In the grass family, Poaceae * Common reed (''Phragmites australis''), the original species named reed * Giant reed (''Arundo donax''), used for making reeds for musical instruments * Burma reed (''Neyraudia reynaudiana'') * Reed canary-grass (''Phalaris arundinacea'') * Reed sweet-grass (''Glyceria maxima'') * Small-reed (''Calamagrostis'' species) In the sedge family, Cyperaceae * Paper reed or papyrus ('' Cyperus papyrus''), the source of the Ancient Egyptian writing material, also used for making boats In the family Typhaceae * Bur-reed (''Sparganium'' species) * Reed-mace (''Typha'' species), also called bulrush or cattail In the family Restionaceae * Cape thatching reed ('' Elegia tectorum''), a restio originating from the South-western Cape, South Africa. * Thatching reed (''Thamnochortus ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liselund
Liselund is an 18th-century aesthetically landscaped park, complete with several exotic buildings and monuments. Located close to Møns Klint on the north-eastern corner of the Danish island of Møn, it is deemed to be one of the finest examples in Scandinavia of Romantic English gardening. The park was created in the 1790s by French nobleman Antoine de Bosc de la Calmette for his wife Elisabeth, commonly known as Lisa. Liselund, roughly translated, means Lise's grove. Background Arrival of the De la Calmette family in Denmark Antoine de Bosc de la Calmette was a Huguenot whose family had been forced to leave France for Holland. His father was a diplomat who after terms in Switzerland and Portugal, finally arrived in Denmark where, in 1776, the family was naturalised and recognised as Danish nobility. In January 1777, he married Catharina Elisabeth Iselin, the daughter of the Swiss baron Reinhard Iselin who had also emigrated to Denmark. In 1783, Antoine was appointed prefect of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_-_facade_on_Piazza_dei_signori.jpg)
.jpg)

