|
Corseia
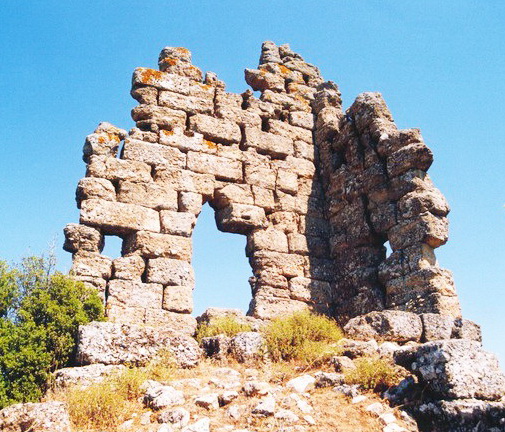
Corseia or Korseia ( grc, Κορσεία), or Chorsia (Χορσία), was town of ancient Boeotia, sometimes included in Opuntian Locris, was the first place which the traveller reached after crossing the mountains from Cyrtones. In the Third Sacred War it was taken by the Phocians, along with Orchomenus and Coroneia. In the plain below, the river Platanius joined the sea. When Pausanias visited in the 2nd century, he found a sacred grove of yews with a small image of Hermes Hermes (; grc-gre, Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology. Hermes is considered the herald of the gods. He is also considered the protector of human heralds, travellers, thieves, merchants, and orat ... in the open air, half a stadion from Corseia. Corseia's site is located near the modern Neochori.There are remains of the walled enclosure and three towers that have been studied by John M. Fossey. References Populated places in ancient Boeotia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Boeotia
Boeotia ( ), sometimes Latinized as Boiotia or Beotia ( el, Βοιωτία; modern: ; ancient: ), formerly known as Cadmeis, is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Central Greece. Its capital is Livadeia, and its largest city is Thebes. Boeotia was also a region of ancient Greece, from before the 6th century BC. Geography Boeotia lies to the north of the eastern part of the Gulf of Corinth. It also has a short coastline on the Gulf of Euboea. It bordered on Megaris (now West Attica) in the south, Attica in the southeast, Euboea in the northeast, Opuntian Locris (now part of Phthiotis) in the north and Phocis in the west. The main mountain ranges of Boeotia are Mount Parnassus in the west, Mount Helicon in the southwest, Cithaeron in the south and Parnitha in the east. Its longest river, the Cephissus, flows in the central part, where most of the low-lying areas of Boeotia are found. Lake Copais was a large lake in the center of Boeotia. It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opuntian Locris
Opuntian Locris or Eastern Locris was an ancient Greek region inhabited by the eastern division of the Locrians, the so-called tribe of the Locri Epicnemidii ( el, ) or Locri Opuntii (Greek: ). Geography Opuntian Locris consisted of a narrow slip upon the eastern coast of central Greece, from the pass of Thermopylae to the mouth of the river Cephissus. The northern frontier town was Alpeni, which bordered upon the Malians, and the southern frontier town was Larymna, which at a later time belonged to Boeotia. The Locrians, however, did not inhabit this coast continuously, but were separated by a narrow slip of Phocis, which extended to the North Euboean Gulf, and contained the Phocian seaport town of Daphnus. The Locrians north of Daphnus were called ''Epicnemidii'', from Mount Cnemis; and those south of this town were named ''Opuntii'', from Opus, their principal city. On the west, the Locrians were separated from Phocis and Boeotia by a range of mountains, extending from Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrtones
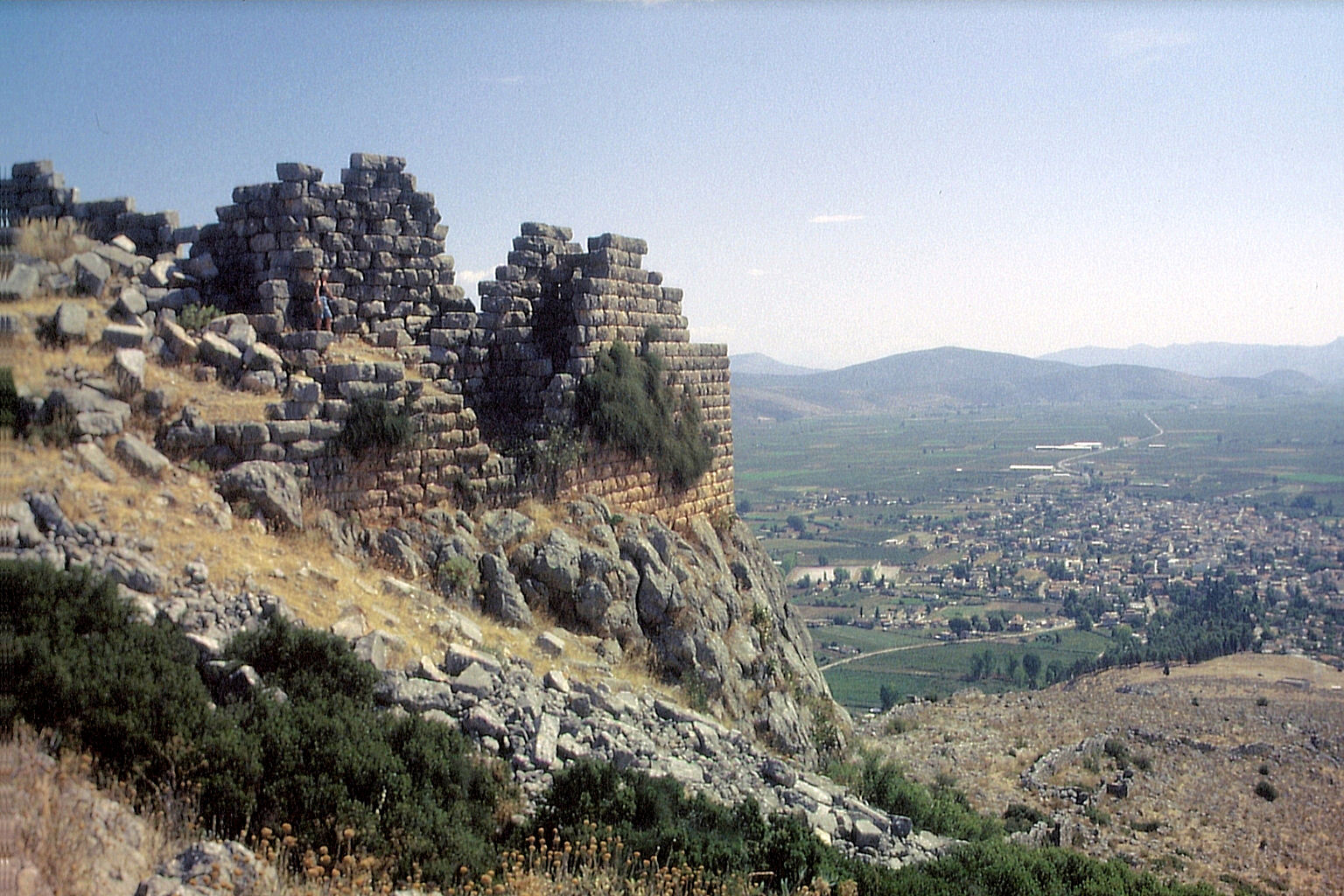
Cyrtones or Kyrtones ( grc, Κύρτωνες), anciently called Cyrtone or Kyrtone (Κυρτώνη), was a city of Boeotia, east of the Lake Copais, and 20 stadia from Hyettus, situated upon a lofty mountain, after crossing which the traveller arrived at Corsia. Cyrtones contained a grove and temple of Apollo, in which were statues of Apollo and Artemis, and a fountain of cold water, at the source of which was a chapel of the nymphs. The site of Cyrtones is tentatively located at Kastron Kolakas/Karaouli, near the modern village of Kyrtoni Kyrtoni ( el, Κυρτώνη, before 1987: Κολάκα - ''Kolaka'') is a village in the southeastern part of Phthiotis, Greece. It is part of the municipality of Lokroi since 2010. It was an independent commune between the 1820s and 1907, and w ..., which was renamed from Kolaka to reflect association with the ancient town. The remains of a walled enclosure, and of a building, possibly a temple, have been found. This ancient fortification h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
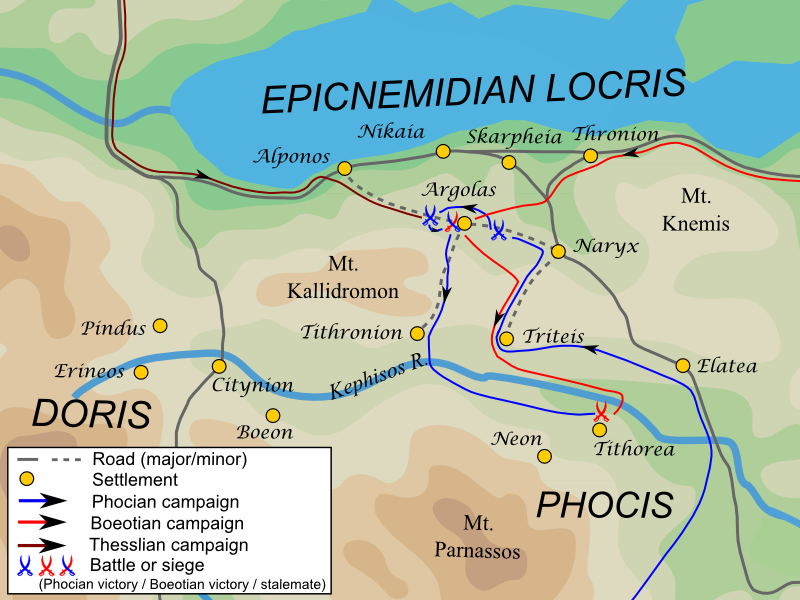
Third Sacred War
The Third Sacred War (356–346 BC) was fought between the forces of the Delphic Amphictyonic League, principally represented by Thebes, and latterly by Philip II of Macedon, and the Phocians. The war was caused by a large fine imposed in 357 BC on the Phocians by the Amphictyonic League (dominated at that moment by Thebes), for the offense of cultivating sacred land; refusing to pay, the Phocians instead seized the Temple of Apollo in Delphi, and used the accumulated treasures to fund large mercenary armies. Thus, although the Phocians suffered several major defeats, they were able to continue the war for many years, until eventually all parties were nearing exhaustion. Philip II used the distraction of the other states to increase his power in northern Greece, in the process becoming ruler of Thessaly. In the end, Philip's growing power, and the exhaustion of the other states, allowed him to impose a peaceful settlement of the war, marking a major step in the rise of Maced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Phocis
Phocis was an ancient region in the central part of Ancient Greece, which included Delphi. A modern administrative unit, also called Phocis, is named after the ancient region, although the modern region is substantially larger than the ancient one. Geopolitically, Phocis was the country of the Phocians, who spoke their own version of Doric Greek, one of the three main dialects of ancient Greek. They were one of several small mountain states of Central Greece, whose dialects are classified as Northwest Doric. It was from their region that the Dorians crossed the Gulf of Corinth at the beginning of the Greek Iron Age to burn Pylos and other southern Greek strongholds and seize control of the Peloponnesus. The dialects of the two groups of Dorians north and south of the Gulf then began to diverge. One of the states around Phocis was still called Doris in classical times. As there is considerable evidence that the invasion began about 1000 BC, the ancestors of the classical Phocia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orchomenus (Boeotia)
Orchomenus ( grc, Ὀρχομενός ''Orchomenos''), the setting for many early Greek myths, is best known today as a rich archaeological site in Boeotia, Greece, that was inhabited from the Neolithic through the Hellenistic periods. It is often referred to as " Minyan Orchomenus", to distinguish it from a later city of the same name in Arcadia. Ancient history According to the founding myth of Orchomenos, its royal dynasty was established by the Minyans, who had followed their eponymous leader Minyas from coastal Thessaly to settle the site. In the Bronze Age, during the fourteenth and thirteenth centuries BCE, Orchomenos became a rich and important centre of civilisation in Mycenaean Greece and a rival to Thebes. The palace with its frescoed walls and the great beehive tomb show the power of Orchomenos in Mycenaean Greece. A massive hydraulic undertaking drained the marshes of Lake Kopaïs, making it a rich agricultural area. Like many sites around the Aegean Sea, Orcho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coroneia (Boeotia)
Coroneia ( grc-gre, Κορώνεια), or Coronea, was a town of ancient Boeotia, and a member of the Boeotian League. It is described by Strabo as situated upon a height near Mount Helicon; its territory was called Κορωνειακή. The town stood upon an insulated hill at the entrance of a valley leading southwards to Mt. Helicon, the principal summit of which is seen at the head of the valley. From this hill there was a fine view over the Lake Copais, and at its foot there was a broad plain extending as far as the marshes of the lake. On either side of the hill flowed two streams, one on the eastern or right hand side, called Coralius or Cuarius, and the other on the left, named Phalarus: a tributary of the latter was the Isomantus or Hoplias. Coroneia is said to have been founded by the Boeotians from Arne in Thessaly, after they had been driven out of their original homes by the Thessalians; and they appear to have called it Coroneia after the Thessalian town of this na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pausanias (geographer)
Pausanias ( /pɔːˈseɪniəs/; grc-gre, Παυσανίας; c. 110 – c. 180) was a Greek traveler and geographer of the second century AD. He is famous for his ''Description of Greece'' (, ), a lengthy work that describes ancient Greece from his firsthand observations. ''Description of Greece'' provides crucial information for making links between classical literature and modern archaeology. Biography Not much is known about Pausanias apart from what historians can piece together from his own writing. However, it is mostly certain that he was born c. 110 AD into a Greek family and was probably a native of Lydia in Asia Minor. From c. 150 until his death in 180, Pausanias travelled through the mainland of Greece, writing about various monuments, sacred spaces, and significant geographical sites along the way. In writing ''Description of Greece'', Pausanias sought to put together a lasting written account of "all things Greek", or ''panta ta hellenika''. Living in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
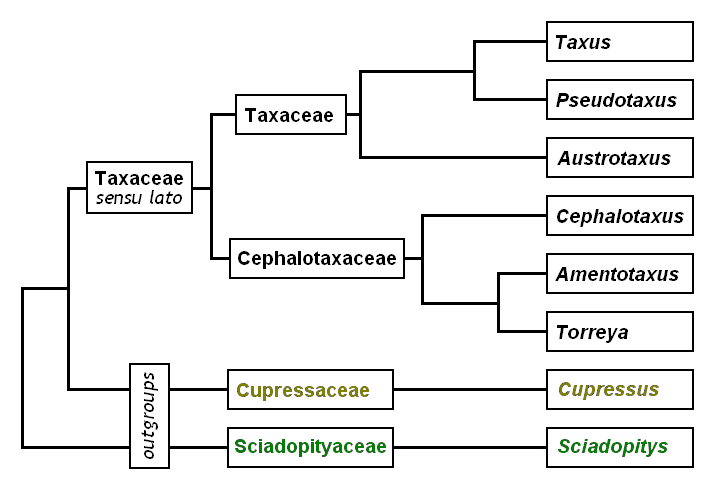
Yews
Yew is a common name given to various species of trees. It is most prominently given to any of various coniferous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Taxus'': * European yew or common yew (''Taxus baccata'') * Pacific yew or western yew (''Taxus brevifolia'') * Canadian yew (''Taxus canadensis'') * Chinese yew (''Taxus chinensis'') * Japanese yew (''Taxus cuspidata'') * Florida yew (''Taxus floridana'') * Mexican yew (''Taxus globosa'') * Sumatran yew (''Taxus sumatrana'') * Himalayan yew (''Taxus wallichiana'') * ''Taxus masonii'' (Eocene fossil yew) It is also used for any of various coniferous plants in the families Taxaceae and Cephalotaxaceae: * White-berry yew (''Pseudotaxus chienii'') * New Caledonian yew or southern yew (''Austrotaxus spicata'') * Catkin-yew (''Amentotaxus sp.'') * Plum-yew (''Cephalotaxus sp.'') Various coniferous plants in the family Podocarpaceae, superficially similar to other yews, are also known by this name: * Prince Albert's yew (''Saxegothaea cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermes
Hermes (; grc-gre, Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology. Hermes is considered the herald of the gods. He is also considered the protector of human heralds, travellers, thieves, merchants, and orators. He is able to move quickly and freely between the worlds of the mortal and the divine, aided by his winged sandals. Hermes plays the role of the psychopomp or "soul guide"—a conductor of souls into the afterlife. In myth, Hermes functions as the emissary and messenger of the gods, and is often presented as the son of Zeus and Maia, the Pleiad. Hermes is regarded as "the divine trickster," about which the '' Homeric Hymn to Hermes'' offers the most well-known account. His attributes and symbols include the herma, the rooster, the tortoise, satchel or pouch, talaria (winged sandals), and winged helmet or simple petasos, as well as the palm tree, goat, the number four, several kinds of fish, and incense. However, his main symbol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stadion (unit)
The stadion (plural stadia, grc-gre, ; Romanization, latinized as stadium), also anglicized as stade, list of obsolete units of measurement, was an ancient Greek units of measurement, ancient Greek unit of length, consisting of 600 Ancient Greek feet (''podes''). Calculations According to Herodotus, one stadium was equal to 600 pous, Greek feet (''podes''). However, the length of the foot varied in different parts of the Greek world, and the length of the stadion has been the subject of argument and hypothesis for hundreds of years. An empirical determination of the length of the stadion was made by Lev Vasilevich Firsov, who compared 81 distances given by Eratosthenes and Strabo with the straight-line distances measured by modern methods, and averaged the results. He obtained a result of about . Various equivalent lengths have been proposed, and some have been named. Among them are: Which measure of the stadion is used can affect the interpretation of ancient texts. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |