|
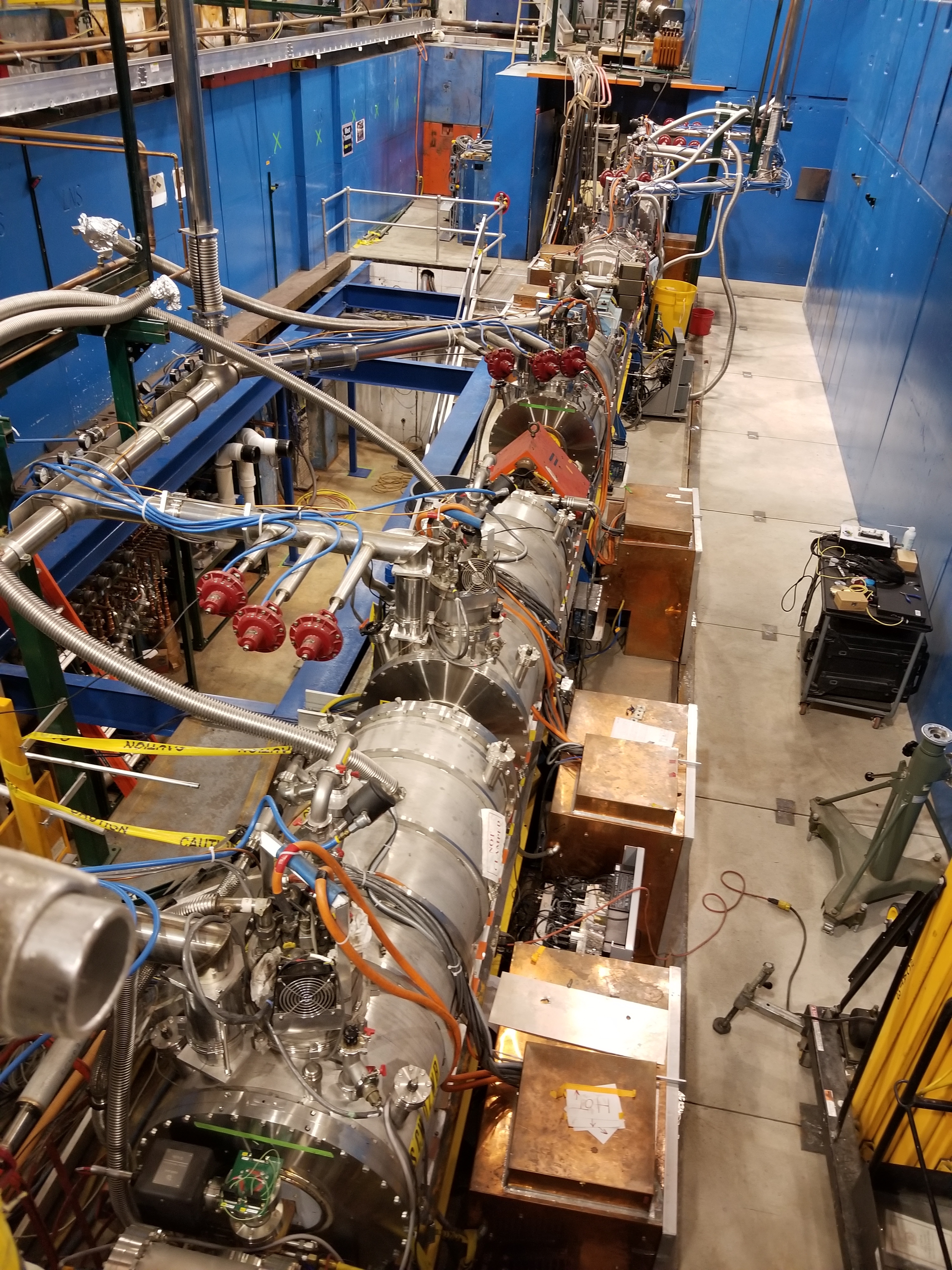
Cornell Electron Storage Ring
The Cornell Electron Storage Ring (CESR, pronounced Caesar) is a particle accelerator operated by Cornell University and located 40 feet beneath a football field on their Ithaca campus. The accelerator has contributed to fundamental research in high energy physics and accelerator physics, as well as solid state physics, biology, art history and other fields through its use as a synchrotron light source. For many years, CESR held the world luminosity record for electron-positron collisions. CESR pioneered several new accelerator techniques, including superconducting radio-frequency cavities and pretzel orbits. Electron Positron Collider CESR was built in the already existing tunnel for the 10 GeV synchrotron and was originally constructed as an electron- positron collider. The project was led by Cornell physicist Maury Tigner who devised a "fiendishly clever" method of filling the ring with positrons generated by the synchrotron. It delivered its first collisions in April ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CESR Detector Area
CESR may refer to: * Center for Economic and Social Rights, an international human rights organization * Centre d'Etude Spatiale des Rayonnements, now the Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planétologie (IRAP), in France * Committee of European Securities Regulators, replaced since 2011 by the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) * Cornell Electron Storage Ring The Cornell Electron Storage Ring (CESR, pronounced Caesar) is a particle accelerator operated by Cornell University and located 40 feet beneath a football field on their Ithaca campus. The accelerator has contributed to fundamental research in hi ..., a particle accelerator operated by Cornell University, in Ithaca (state of New York) * Carrier Ethernet Switches and Routers, a marketing term {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maury Tigner
Maury Tigner (born 22 April 1937) is an American physicist working on particle accelerators and experimental particle physics. Tigner studied physics at the Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute until 1958 and received a PhD degree from Cornell University in 1964. He stayed there and became a professor of physics from 1977 to 1994. After a stay at DESY he led the development and construction of the Cornell Electron Storage Ring, which started operation in 1979. From 1994 to 2000 Tigner worked at the Institute of High Energy Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing, contributing to the development of BEPC II. In 2000 he moved back to Cornell, leading the laboratory of elementary particle physics until 2006. Tigner played a major role in the development of the Superconducting Super Collider, leading the Central Design Group at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory formed in 1984, and worked on development of the International Linear Collider. Tigner became a member ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Accelerators In Particle Physics
A list of particle accelerators used for particle physics experiments. Some early particle accelerators that more properly did nuclear physics, but existed prior to the separation of particle physics from that field, are also included. Although a modern accelerator complex usually has several stages of accelerators, only accelerators whose output has been used directly for experiments are listed. Early accelerators These all used single beams with fixed targets. They tended to have very briefly run, inexpensive, and unnamed experiments. Cyclotrons [1] The magnetic pole pieces and return yoke from the 60-inch cyclotron were later moved to UC Davis and incorporated into a 76-inch isochronous cyclotron which is still in use today Other early accelerator types Synchrotrons Fixed-target accelerators More modern accelerators that were also run in fixed target mode; often, they will also have been run as colliders, or accelerated particles for use in subsequently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Prize In Chemistry
) , image = Nobel Prize.png , alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "MDCCCXXXIII" above, followed by (smaller) "OB•" then "MDCCCXCVI" below. , awarded_for = Outstanding contributions in chemistry , presenter = Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences , location = Stockholm, Sweden , reward = 9 million SEK (2017) , year = 1901 , holder = Carolyn R. Bertozzi, Morten P. Meldal and Karl Barry Sharpless (2022) , most_awards = Frederick Sanger and Karl Barry Sharpless (2) , website nobelprize.org, previous = 2021 , year2=2022, main=2022, next=2023 The Nobel Prize in Chemistry is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of chemistry. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895, awarded for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Review Letters
''Physical Review Letters'' (''PRL''), established in 1958, is a peer-reviewed, scientific journal that is published 52 times per year by the American Physical Society. As also confirmed by various measurement standards, which include the ''Journal Citation Reports'' impact factor and the journal ''h''-index proposed by Google Scholar, many physicists and other scientists consider ''Physical Review Letters'' to be one of the most prestigious journals in the field of physics. ''According to Google Scholar, PRL is the journal with the 9th journal h-index among all scientific journals'' ''PRL'' is published as a print journal, and is in electronic format, online and CD-ROM. Its focus is rapid dissemination of significant, or notable, results of fundamental research on all topics related to all fields of physics. This is accomplished by rapid publication of short reports, called "Letters". Papers are published and available electronically one article at a time. When published in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B Meson
In particle physics, B mesons are mesons composed of a bottom antiquark and either an up (), down (), strange () or charm quark (). The combination of a bottom antiquark and a top quark is not thought to be possible because of the top quark's short lifetime. The combination of a bottom antiquark and a bottom quark is not a B meson, but rather ''bottomonium'', which is something else entirely. Each B meson has an antiparticle that is composed of a bottom quark and an up (), down (), strange () or charm () antiquark respectively. List of B mesons – oscillations The neutral B mesons, and , spontaneously transform into their own antiparticles and back. This phenomenon is called flavor oscillation. The existence of neutral B meson oscillations is a fundamental prediction of the Standard Model of particle physics. It has been measured in the – system to be about , and in the – system to be measured by CDF experiment at Fermilab. A first estimation of the lower an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleopatra VII Of Egypt
Cleopatra VII Philopator ( grc-gre, Κλεοπάτρα Φιλοπάτωρ}, "Cleopatra the father-beloved"; 69 BC10 August 30 BC) was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and its last active ruler.She was also a diplomat, naval commander, linguist, and medical author; see and . A member of the Ptolemaic dynasty, she was a descendant of its founder Ptolemy I Soter, a Macedonian Greek general and companion of Alexander the Great. writes about Ptolemy I Soter: "The Ptolemaic dynasty, of which Cleopatra was the last representative, was founded at the end of the fourth century BC. The Ptolemies were not of Egyptian extraction, but stemmed from Ptolemy Soter, a Macedonian Greek in the entourage of Alexander the Great."For additional sources that describe the Ptolemaic dynasty as " Macedonian Greek", please see , , , and . Alternatively, describes them as a "Macedonian, Greek-speaking" dynasty. Other sources such as and describe the Ptolemies a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CLEO (particle Detector)
CLEO was a general purpose particle detector at the Cornell Electron Storage Ring (CESR), and the name of the collaboration of physicists who operated the detector. The name CLEO is not an acronym; it is short for Cleopatra and was chosen to go with CESR (pronounced Caesar). CESR was a particle accelerator designed to collide electrons and positrons at a center-of-mass energy of approximately 10 GeV. The energy of the accelerator was chosen before the first three bottom quark Upsilon resonances were discovered between 9.4 GeV and 10.4 GeV in 1977. The fourth Υ resonance, the Υ(4S), was slightly above the threshold for, and therefore ideal for the study of, B meson production. CLEO was a hermetic detector that in all of its versions consisted of a tracking system inside a solenoid magnet, a calorimeter, particle identification systems, and a muon detector.CLEO I NIMCLEO II NIM The detector underwent five major upgrades over the course of its thirty-year lifetime, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collider
A collider is a type of particle accelerator which brings two opposing particle beams together such that the particles collide. Colliders may either be ring accelerators or linear accelerators. Colliders are used as a research tool in particle physics by accelerating particles to very high kinetic energy and letting them impact other particles. Analysis of the byproducts of these collisions gives scientists good evidence of the structure of the subatomic world and the laws of nature governing it. These may become apparent only at high energies and for tiny periods of time, and therefore may be hard or impossible to study in other ways. Explanation In particle physics one gains knowledge about elementary particles by accelerating particles to very high kinetic energy and letting them impact on other particles. For sufficiently high energy, a reaction occurs that transforms the particles into other particles. Detecting these products gives insight into the physics involved. To do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and subsequently became dictator from 49 BC until his assassination in 44 BC. He played a critical role in the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. In 60 BC, Caesar, Crassus and Pompey formed the First Triumvirate, an informal political alliance that dominated Roman politics for several years. Their attempts to amass power as were opposed by the within the Roman Senate, among them Cato the Younger with the frequent support of Cicero. Caesar rose to become one of the most powerful politicians in the Roman Republic through a string of military victories in the Gallic Wars, completed by 51 BC, which greatly extended Roman territory. During this time he both invaded Britain and built a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positron
The positron or antielectron is the antiparticle or the antimatter counterpart of the electron. It has an electric charge of +1 '' e'', a spin of 1/2 (the same as the electron), and the same mass as an electron. When a positron collides with an electron, annihilation occurs. If this collision occurs at low energies, it results in the production of two or more photons. Positrons can be created by positron emission radioactive decay (through weak interactions), or by pair production from a sufficiently energetic photon which is interacting with an atom in a material. History Theory In 1928, Paul Dirac published a paper proposing that electrons can have both a positive and negative charge. This paper introduced the Dirac equation, a unification of quantum mechanics, special relativity, and the then-new concept of electron spin to explain the Zeeman effect. The paper did not explicitly predict a new particle but did allow for electrons having either positive or negative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |