|
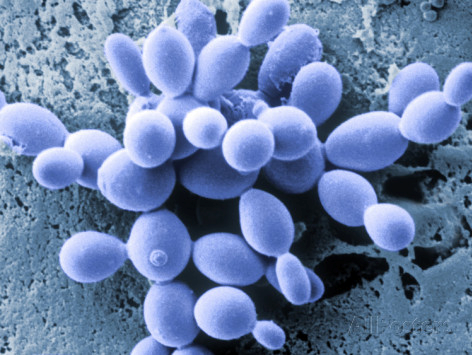
Cordana Musae
''Cordana musae'' is an ascomycete fungus that is a plant pathogen. It produces cordana leaf spot A leaf spot is a limited, discoloured, diseased area of a leaf that is caused by fungal, bacterial or viral plant diseases, or by injuries from nematodes, insects, environmental factors, toxicity or herbicides. These discoloured spots or lesions ... on bananas.''Cordana'' leaf spot of banana produced by ''Cordana musae'' College of Tropical Agriculture and Human Resources (CTAHR), University of Hawai'i at Mānoa, Honolulu, Hawai'i, p. 3. External links [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascomycota
Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The defining feature of this fungal group is the " ascus" (), a microscopic sexual structure in which nonmotile spores, called ascospores, are formed. However, some species of the Ascomycota are asexual, meaning that they do not have a sexual cycle and thus do not form asci or ascospores. Familiar examples of sac fungi include morels, truffles, brewers' and bakers' yeast, dead man's fingers, and cup fungi. The fungal symbionts in the majority of lichens (loosely termed "ascolichens") such as ''Cladonia'' belong to the Ascomycota. Ascomycota is a monophyletic group (it contains all descendants of one common ancestor). Previously placed in the Deuteromycota along with asexual species from other fungal taxa, asexual (or anamorphic) ascomyce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascomycetes
Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The defining feature of this fungal group is the " ascus" (), a microscopic sexual structure in which nonmotile spores, called ascospores, are formed. However, some species of the Ascomycota are asexual, meaning that they do not have a sexual cycle and thus do not form asci or ascospores. Familiar examples of sac fungi include morels, truffles, brewers' and bakers' yeast, dead man's fingers, and cup fungi. The fungal symbionts in the majority of lichens (loosely termed "ascolichens") such as ''Cladonia'' belong to the Ascomycota. Ascomycota is a monophyletic group (it contains all descendants of one common ancestor). Previously placed in the Deuteromycota along with asexual species from other fungal taxa, asexual (or anamorphic) ascomycetes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incertae Sedis
' () or ''problematica'' is a term used for a taxonomic group where its broader relationships are unknown or undefined. Alternatively, such groups are frequently referred to as "enigmatic taxa". In the system of open nomenclature, uncertainty at specific taxonomic levels is indicated by ' (of uncertain family), ' (of uncertain suborder), ' (of uncertain order) and similar terms. Examples *The fossil plant '' Paradinandra suecica'' could not be assigned to any family, but was placed ''incertae sedis'' within the order Ericales when described in 2001. * The fossil ''Gluteus minimus'', described in 1975, could not be assigned to any known animal phylum. The genus is therefore ''incertae sedis'' within the kingdom Animalia. * While it was unclear to which order the New World vultures (family Cathartidae) should be assigned, they were placed in Aves ''incertae sedis''. It was later agreed to place them in a separate order, Cathartiformes. * Bocage's longbill, ''Motacilla bocagii' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cordana
''Cordana'' is an ascomycete fungus genus. In 2020, it was placed within the monotypic family of Cordanaceae, and within the order Coniochaetales. The genus name of ''Cordana'' is in honour of August Carl Joseph Corda (1809–1849), who was a Czech physician and mycologist. The genus was circumscribed by Carl Gottlieb Traugott Preuss in Linnaea Vol.24 on pages 100 and 129 in 1851. Species There are about 24 known species; * '' Cordana abramovii'' * '' Cordana andinopatagonica'' * '' Cordana aquatica'' * '' Cordana bambusae'' * '' Cordana bisbyi'' * '' Cordana boothii'' * '' Cordana crassa'' * '' Cordana ellipsoidea'' * '' Cordana gilibertiae'' * '' Cordana inaequalis'' * '' Cordana indica'' * '' Cordana lignicola'' * '' Cordana lithuanica'' * '' Cordana lushanensis'' * '' Cordana meilingensis'' * '' Cordana mercadoana'' * '' Cordana oblongispora'' * '' Cordana pauciseptata'' * '' Cordana semaniae'' * '' Cordana sinensis'' * '' Cordana solitaria'' * ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascomycete
Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The defining feature of this fungal group is the " ascus" (), a microscopic sexual structure in which nonmotile spores, called ascospores, are formed. However, some species of the Ascomycota are asexual, meaning that they do not have a sexual cycle and thus do not form asci or ascospores. Familiar examples of sac fungi include morels, truffles, brewers' and bakers' yeast, dead man's fingers, and cup fungi. The fungal symbionts in the majority of lichens (loosely termed "ascolichens") such as ''Cladonia'' belong to the Ascomycota. Ascomycota is a monophyletic group (it contains all descendants of one common ancestor). Previously placed in the Deuteromycota along with asexual species from other fungal taxa, asexual (or anamorphic) ascomycetes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Pathogen
Plant pathology (also phytopathology) is the scientific study of diseases in plants caused by pathogens (infectious organisms) and environmental conditions (physiological factors). Organisms that cause infectious disease include fungi, oomycetes, bacteria, viruses, viroids, virus-like organisms, phytoplasmas, protozoa, nematodes and parasitic plants. Not included are ectoparasites like insects, mites, vertebrate, or other pests that affect plant health by eating plant tissues. Plant pathology also involves the study of pathogen identification, disease etiology, disease cycles, economic impact, plant disease epidemiology, plant disease resistance, how plant diseases affect humans and animals, pathosystem genetics, and management of plant diseases. Overview Control of plant diseases is crucial to the reliable production of food, and it provides significant problems in agricultural use of land, water, fuel and other inputs. Plants in both natural and cultivated populat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaf Spot
A leaf spot is a limited, discoloured, diseased area of a leaf that is caused by fungal, bacterial or viral plant diseases, or by injuries from nematodes, insects, environmental factors, toxicity or herbicides. These discoloured spots or lesions often have a centre of necrosis (cell death).Horst, R. (2008). Westcott’s Plant Disease Handbook (Seventh Edition.). Springer Netherlands. Symptoms can overlap across causal agents, however differing signs and symptoms of certain pathogens can lead to the diagnosis of the type of leaf spot disease. Prolonged wet and humid conditions promote leaf spot disease and most pathogens are spread by wind, splashing rain or irrigation that carry the disease to other leaves.Lucas, G., & Campbell, L. (1992). Introduction to Plant Diseases Identification and Management (2nd ed. 1992.). Springer US. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-7294-7 Description Leaf spots are a type of plant disease that are usually caused by pathogens and sometimes othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large herbaceous flowering plants in the genus ''Musa''. In some countries, bananas used for cooking may be called "plantains", distinguishing them from dessert bananas. The fruit is variable in size, color, and firmness, but is usually elongated and curved, with soft flesh rich in starch covered with a rind, which may be green, yellow, red, purple, or brown when ripe. The fruits grow upward in clusters near the top of the plant. Almost all modern edible seedless ( parthenocarp) bananas come from two wild species – ''Musa acuminata'' and ''Musa balbisiana''. The scientific names of most cultivated bananas are ''Musa acuminata'', ''Musa balbisiana'', and ''Musa'' × ''paradisiaca'' for the hybrid ''Musa acuminata'' × ''M. balbisiana'', depending on their genomic constitution. The old scientific name for this hybrid, ''Musa sapientum'', is no longer used. ''Musa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Hawaii At Manoa
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school. The word ''university'' is derived from the Latin ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". The first universities were created in Europe by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (''Università di Bologna''), founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *Being a high degree-awarding institute. *Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy. *Using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *Issuing secular and non-secular degrees: grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascomycota Enigmatic Taxa
Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The defining feature of this fungal group is the " ascus" (), a microscopic sexual structure in which nonmotile spores, called ascospores, are formed. However, some species of the Ascomycota are asexual, meaning that they do not have a sexual cycle and thus do not form asci or ascospores. Familiar examples of sac fungi include morels, truffles, brewers' and bakers' yeast, dead man's fingers, and cup fungi. The fungal symbionts in the majority of lichens (loosely termed "ascolichens") such as ''Cladonia'' belong to the Ascomycota. Ascomycota is a monophyletic group (it contains all descendants of one common ancestor). Previously placed in the Deuteromycota along with asexual species from other fungal taxa, asexual (or anamorphic) ascom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungal Plant Pathogens And Diseases
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |