|
Copenhagen Court House
The Copenhagen Court House ( da, Københavns Domhus) is a historic building located on Nytorv in Copenhagen, Denmark. Originally built as a combined city hall and courthouse, it now serves as the seat of the District Court of Copenhagen. Inaugurated in 1815, it was built to the design of Christian Frederik Hansen in Neoclassical style. History A modern style court of justice, ''Hof- og Stadsretten'', was introduced in Denmark, specifically for Copenhagen, by Johann Friedrich Struensee in 1771. Located in Viborg and Copenhagen, two High Courts were introduced as courts of appeal in 1805. It was for this emerging legal system that a new courthouse was needed. In the Great Fire of 1795, Copenhagen's city hall, located between Nytorv and Gammeltorv, was among the many buildings lost to the flames. It was the second consecutive city hall at that spot to meet this fate; the first building, built in 1679 at the same site, had been lost in the Fire of 1728. After the fire, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indre By
Indre By (lit. English, "Inner City"), also known as Copenhagen Center or K or Downtown Copenhagen, is an administrative district (''by'') in central Copenhagen, the capital of Denmark. It covers an area of , has a population of 26,223, and a population density of 5,638 per km². Neighboring city districts are as follows: * to the east and south east is Christianshavn, separated from the Inner City by the Inner Harbour (''Inderhavnen'') and Copenhagen Harbour (''Københavns Havn'') * to the north is Indre Østerbro * to the west is Indre Nørrebro and Frederiksberg municipality, which is not a part of Copenhagen municipality but rather an enclave surrounded by the municipality, with both being separated from the Indre By along the "lakes" (Skt. Jørgens Lake, Peblinge Lake, and Sortedams Lake) * to the southwest is Vesterbro * to the south is Vestamager, separated from the Inner City by the South Harbour (''Sydhavnen'') The Indre By district This district is the historic, ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copenhagen Fire Of 1795
The Copenhagen Fire of 1795 (''Københavns brandes 1795'') started on Friday, 5 June 1795, at or around 3 pm by the Navy's old base south east of Kongens Nytorv on Gammelholm, in the Navy's magazine for coal and timber, the so-called Dellehave. As the workers had already gone home, a considerable length of time passed before efforts to combat the fire started, and out of fear for theft, the fire hydrants had been removed. The people of Holmen also blocked the civilian fire brigade, possibly in the belief that since it was a military area, the military should take care of it. There had been an extended period without rain and the dry wood, combined with the storage of rope work and tar, made the fire spread quickly. The wind blew especially strong from east-southeast, and that meant the countless embers were carried through the air into the city. Because of the strong sunlight, small fires were difficult to detect until they have taken hold. This is why the fire spread from Gammelh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestibule (architecture)
A vestibule (also anteroom, antechamber, or foyer) is a small room leading into a larger space such as a lobby, entrance hall or passage, for the purpose of waiting, withholding the larger space view, reducing heat loss, providing storage space for outdoor clothing, etc. The term applies to structures in both modern and classical architecture since ancient times. In modern architecture, a vestibule is typically a small room next to the outer door and connecting it with the interior of the building. In ancient Roman architecture, a vestibule ( la, vestibulum) was a partially enclosed area between the interior of the house and the street. Ancient usage Ancient Greece Vestibules were common in ancient Greek temples. Due to the construction techniques available at the time, it was not possible to build large spans. Consequently, many entranceways had two rows of columns that supported the roof and created a distinct space around the entrance. In ancient Greek houses, the prothyru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Column
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a compression member. The term ''column'' applies especially to a large round support (the shaft of the column) with a capital and a base or pedestal, which is made of stone, or appearing to be so. A small wooden or metal support is typically called a ''post''. Supports with a rectangular or other non-round section are usually called ''piers''. For the purpose of wind or earthquake engineering, columns may be designed to resist lateral forces. Other compression members are often termed "columns" because of the similar stress conditions. Columns are frequently used to support beams or arches on which the upper parts of walls or ceilings rest. In architecture, "column" refers to such a structural element that also has certain proportional and decorative featur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
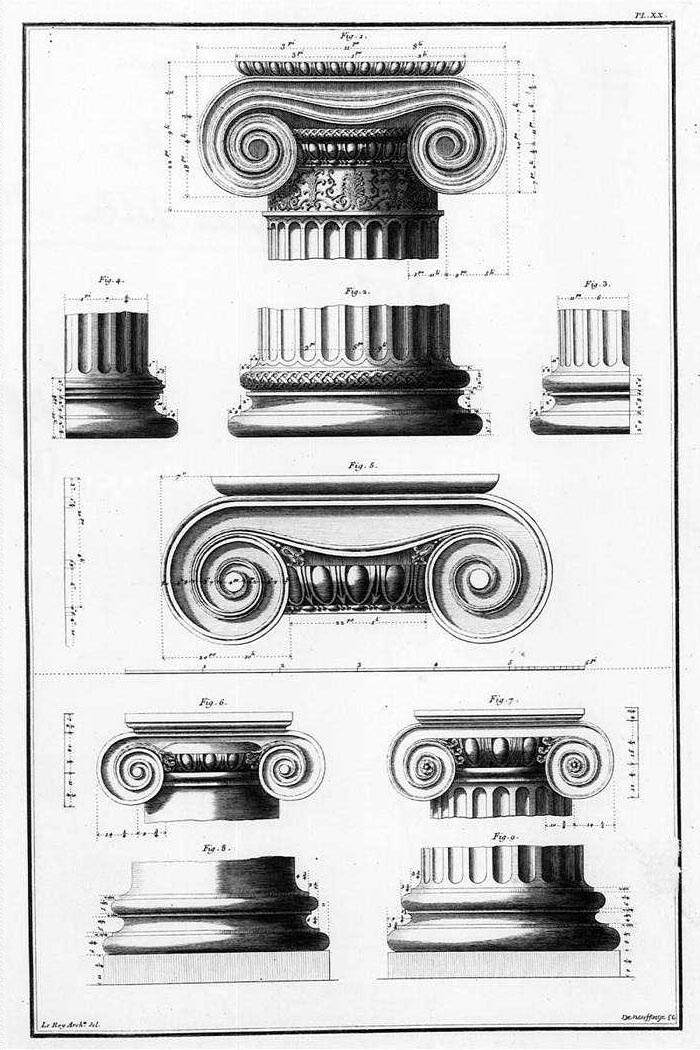
Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. The Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital, which have been the subject of much theoretical and practical discourse, based on a brief and obscure passage i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lavendelstræde Cph
Lavendelstræde ( lit. "Lavender Street") is a street in the old town of Copenhagen, Denmark). It runs from Kattesundet- Hestemøllestræde in the northeast to Vester Voldgade in the west, linking Slutterigade and Nytorv and at Regnbuepladsen and Copenhagen City Hall in the southwest. History The street received its name in 1609. It from the area close to the city's central square Gammeltorv to the Gyldenløve Bastion of the West Rampart which followed present-day Vester Voldgade. The name of the street probably refers to the lavender that grew in a small group of herb gardens located next to the rampart. The street was completely destroyed in the Copenhagen Fire of 1795. Its buildings were rebuilt over the next few years, and a new combined townhall and courthouse was built at its beginning, fronting Nytorv. On the Gyldenløve Bastion stood a stub mill, St. Lucy's Windmill (''Sankt Lucie Mølle''), which was also known as Lavendelstræde Windmill (''Lavendelstræde Mølle'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copenhagen City Hall
Copenhagen City Hall ( da, Københavns Rådhus) is the headquarters of the Copenhagen City Council as well as the Lord mayor of the Copenhagen Municipality, Denmark. The building is situated on City Hall Square in central Copenhagen. Architecture The current building was inaugurated in 1905. It was designed by the architect Martin Nyrop in the National Romantic style but with inspiration from the Siena City Hall. It is dominated by its richly ornamented front, the gilded statue of Absalon just above the balcony and the tall, slim clock tower. The latter is, at 105.6 metres, one of the tallest buildings in the generally low city of Copenhagen. In addition to the tower clock, the City Hall also houses Jens Olsen's World Clock. History The current city hall was designed by architect Martin Nyrop and the design for the building was inspired by the city hall of Siena, Italy. Construction began in 1892 and the hall was opened on 12 September 1905. Before the city hall moved to i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hirschholm Palace
Hirschholm Palace, also known as Hørsholm Palace, was a royal palace located in present-day Hørsholm municipality just north of Copenhagen, Denmark. It was rebuilt in the Baroque style in the 1740s and, one of the finest buildings of its time, it became known as the "Versailles of the North". It developed a notorious reputation in connection with its role in the affair between Johann Friedrich Struensee and Queen Caroline Mathilda in the 1770s. After that it fell into disrepair and was demolished in 1809–1813. The palace was designed by Lauritz de Thurah for King Christian VI and his consort Queen Sophie Magdalene, and was intended as their summer residence. History Early history Hirschholm Palace was built on a site that had been used since the Middle Ages. From around 1100 there was a fortification at site known as Hørningsholm. In 1391 the estate became crown land when Queen Margrete I took possession of the property. At the end of the 16th century Frederik II and Chris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Copenhagen (1807)
The Second Battle of Copenhagen (or the Bombardment of Copenhagen) (16 August – 7 September 1807) was a British bombardment of the Danish capital, Copenhagen, in order to capture or destroy the Dano-Norwegian fleet during the Napoleonic Wars. The incident led to the outbreak of the Anglo-Russian War of 1807, which ended with the Treaty of Örebro in 1812. Britain's first response to Napoleon's Continental System was to launch a major naval attack on Denmark. Although ostensibly neutral, Denmark was under heavy French pressure to pledge its fleet to Napoleon. In September 1807, the Royal Navy bombarded Copenhagen, seizing the Danish fleet and assured use of the sea lanes in the North Sea and Baltic Sea for the British merchant fleet. A consequence of the attack was that Denmark did join the Continental System and the war on the side of France, but without a fleet it had little to offer. The attack gave rise to the term to ''Copenhagenize''. Background Despite the defeat a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prison
A prison, also known as a jail, gaol (dated, standard English, Australian, and historically in Canada), penitentiary (American English and Canadian English), detention center (or detention centre outside the US), correction center, correctional facility, lock-up, hoosegow or remand center, is a facility in which inmates (or prisoners) are confined against their will and usually denied a variety of freedoms under the authority of the state as punishment for various crimes. Prisons are most commonly used within a criminal justice system: people charged with crimes may be imprisoned until their trial; those pleading or being found guilty of crimes at trial may be sentenced to a specified period of imprisonment. In simplest terms, a prison can also be described as a building in which people are legally held as a punishment for a crime they have committed. Prisons can also be used as a tool of political repression by authoritarian regimes. Their perceived opponents may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copenhagen Fire Of 1728
The Copenhagen Fire of 1728 was the largest fire in the history of Copenhagen, Denmark. It began on the evening of 20 October 1728 and continued to burn until the morning of 23 October. It destroyed approximately 28% of the city (measured by counting the number of destroyed lots from the cadastre) and left 20% of the population homeless. The reconstruction lasted until 1737. No less than 47% of the section of the city, which dates back to the Middle Ages, was completely lost, and along with the Copenhagen Fire of 1795, it is the main reason that few traces of medieval Copenhagen can be found in the modern city. Although the number of dead and wounded was relatively low compared to the extent of the fire, the cultural losses were huge. In addition to several private book collections, 35,000 texts including a large number of unique works were lost with the University of Copenhagen library, and at the observatory on top of Rundetårn, instruments and records made by Tycho Brahe and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)