|
Convergence Of Probability Measures
''Convergence of Probability Measures'' is a graduate textbook in the field of mathematical probability theory. It was written by Patrick Billingsley and published by Wiley in 1968. A second edition in 1999 both simplified its treatment of previous topics and updated the book for more recent developments. The Basic Library List Committee of the Mathematical Association of America has recommended its inclusion in undergraduate mathematics libraries. Readers are expected to already be familiar with both the fundamentals of probability theory and the topology of metric spaces. The subject weak convergence of measures involves rigorous study of how a continuous time (or space) stochastic process arises as a scaling limit of a discrete time (or space) process. A fundamental example, Donsker's theorem, is convergence of rescaled random walk to Brownian motion. The mathematical theory, combining probability and functional analysis, was first developed in the 1950s by Skorokhod a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with probability. Although there are several different probability interpretations, probability theory treats the concept in a rigorous mathematical manner by expressing it through a set of axioms. Typically these axioms formalise probability in terms of a probability space, which assigns a measure taking values between 0 and 1, termed the probability measure, to a set of outcomes called the sample space. Any specified subset of the sample space is called an event. Central subjects in probability theory include discrete and continuous random variables, probability distributions, and stochastic processes (which provide mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic or uncertain processes or measured quantities that may either be single occurrences or evolve over time in a random fashion). Although it is not possible to perfectly predict random events, much can be said about their behavior. Two major results in probability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prokhorov's Theorem
In measure theory Prokhorov's theorem relates tightness of measures to relative compactness (and hence weak convergence) in the space of probability measures. It is credited to the Soviet mathematician Yuri Vasilyevich Prokhorov, who considered probability measures on complete separable metric spaces. The term "Prokhorov’s theorem" is also applied to later generalizations to either the direct or the inverse statements. Statement Let (S, \rho) be a separable metric space. Let \mathcal(S) denote the collection of all probability measures defined on S (with its Borel σ-algebra). Theorem. # A collection K\subset \mathcal(S) of probability measures is tight if and only if the closure of K is sequentially compact in the space \mathcal(S) equipped with the topology of weak convergence. # The space \mathcal(S) with the topology of weak convergence is metrizable. # Suppose that in addition, (S,\rho) is a complete metric space (so that (S,\rho) is a Polish space). Ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1968 Non-fiction Books
The year was highlighted by protests and other unrests that occurred worldwide. Events January–February * January 5 – " Prague Spring": Alexander Dubček is chosen as leader of the Communist Party of Czechoslovakia. * January 10 – John Gorton is sworn in as 19th Prime Minister of Australia, taking over from John McEwen after being elected leader of the Liberal Party the previous day, following the disappearance of Harold Holt. Gorton becomes the only Australian Senate, Senator to become Prime Minister, though he immediately transfers to the Australian House of Representatives, House of Representatives through the 1968 Higgins by-election in Holt's vacant seat. * January 15 – The 1968 Belice earthquake in Sicily kills 380 and injures around 1,000. * January 21 ** Vietnam War: Battle of Khe Sanh – One of the most publicized and controversial battles of the war begins, ending on April 8. ** 1968 Thule Air Base B-52 crash: A U.S. B-52 Stratofortress cras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics Textbooks
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MathSciNet
MathSciNet is a searchable online bibliographic database created by the American Mathematical Society in 1996. It contains all of the contents of the journal ''Mathematical Reviews'' (MR) since 1940 along with an extensive author database, links to other MR entries, citations, full journal entries, and links to original articles. It contains almost 3.6 million items and over 2.3 million links to original articles. Along with its parent publication ''Mathematical Reviews'', MathSciNet has become an essential tool for researchers in the mathematical sciences. Access to the database is by subscription only and is not generally available to individual researchers who are not affiliated with a larger subscribing institution. For the first 40 years of its existence, traditional typesetting was used to produce the Mathematical Reviews journal. Starting in 1980 bibliographic information and the reviews themselves were produced in both print and electronic form. This formed the basis of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZbMATH
zbMATH Open, formerly Zentralblatt MATH, is a major reviewing service providing reviews and abstracts for articles in pure mathematics, pure and applied mathematics, produced by the Berlin office of FIZ Karlsruhe – Leibniz Institute for Information Infrastructure GmbH. Editors are the European Mathematical Society, FIZ Karlsruhe, and the Heidelberg Academy of Sciences. zbMATH is distributed by Springer Science+Business Media. It uses the Mathematics Subject Classification codes for organising reviews by topic. History Mathematicians Richard Courant, Otto Neugebauer, and Harald Bohr, together with the publisher Ferdinand Springer, took the initiative for a new mathematical reviewing journal. Harald Bohr worked in Copenhagen. Courant and Neugebauer were professors at the University of Göttingen. At that time, Göttingen was considered one of the central places for mathematical research, having appointed mathematicians like David Hilbert, Hermann Minkowski, Carl Runge, and Felix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empirical Process
In probability theory, an empirical process is a stochastic process that describes the proportion of objects in a system in a given state. For a process in a discrete state space a population continuous time Markov chain or Markov population model is a process which counts the number of objects in a given state (without rescaling). In mean field theory, limit theorems (as the number of objects becomes large) are considered and generalise the central limit theorem for empirical measures. Applications of the theory of empirical processes arise in non-parametric statistics. Definition For ''X''1, ''X''2, ... ''X''''n'' independent and identically-distributed random variables in R with common cumulative distribution function ''F''(''x''), the empirical distribution function is defined by :F_n(x)=\frac\sum_^n I_(X_i), where I''C'' is the indicator function of the set ''C''. For every (fixed) ''x'', ''F''''n''(''x'') is a sequence of random variables which converge to ''F''(''x'') almost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
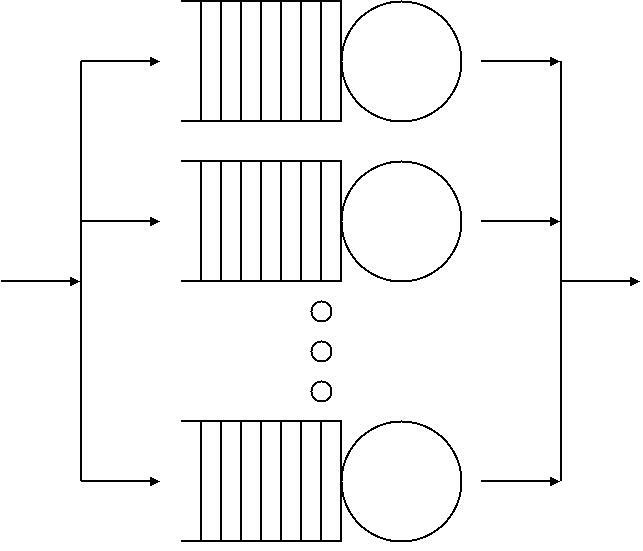
Queueing Theory
Queueing theory is the mathematical study of waiting lines, or queues. A queueing model is constructed so that queue lengths and waiting time can be predicted. Queueing theory is generally considered a branch of operations research because the results are often used when making business decisions about the resources needed to provide a service. Queueing theory has its origins in research by Agner Krarup Erlang when he created models to describe the system of Copenhagen Telephone Exchange company, a Danish company. The ideas have since seen applications including telecommunication, traffic engineering, computing and, particularly in industrial engineering, in the design of factories, shops, offices and hospitals, as well as in project management. Spelling The spelling "queueing" over "queuing" is typically encountered in the academic research field. In fact, one of the flagship journals of the field is ''Queueing Systems''. Single queueing nodes A queue, or queueing node ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Applied Probability
Applied probability is the application of probability theory to statistical problems and other scientific and engineering domains. Scope Much research involving probability is done under the auspices of applied probability. However, while such research is motivated (to some degree) by applied problems, it is usually the mathematical aspects of the problems that are of most interest to researchers (as is typical of applied mathematics in general). Applied probabilists are particularly concerned with the application of stochastic processes, and probability more generally, to the natural, applied and social sciences, including biology, physics (including astronomy), chemistry, medicine, computer science and information technology, and economics. Another area of interest is in engineering: particularly in areas of uncertainty, risk management, probabilistic design, and Quality assurance. See also *Areas of application: **Ruin theory **Statistical physics **Stoichiometry and modelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard M
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from Old Frankish and is a compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'strong in rule'. Nicknames include "Richie", " Dick", "Dickon", " Dickie", "Rich", "Rick", "Rico", "Ricky", and more. Richard is a common English, German and French male name. It's also used in many more languages, particularly Germanic, such as Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, Icelandic, and Dutch, as well as other languages including Irish, Scottish, Welsh and Finnish. Richard is cognate with variants of the name in other European languages, such as the Swedish "Rickard", the Catalan "Ricard" and the Italian "Riccardo", among others (see comprehensive variant list below). People named Richard Multiple people with the same name * Richard Andersen (other) * Richard Anderson (other) * Richard Cartwright (other) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skorokhod's Representation Theorem
In mathematics and statistics, Skorokhod's representation theorem is a result that shows that a weakly convergent sequence of probability measures whose limit measure is sufficiently well-behaved can be represented as the distribution/law of a pointwise convergent sequence of random variables defined on a common probability space. It is named for the Soviet mathematician A. V. Skorokhod. Statement Let (\mu_n)_ be a sequence of probability measures on a metric space S such that \mu_n converges weakly to some probability measure \mu_\infty on S as n \to \infty. Suppose also that the support of \mu_\infty is separable. Then there exist S-valued random variables X_n defined on a common probability space (\Omega,\mathcal,\mathbf) such that the law of X_n is \mu_n for all n (including n=\infty) and such that (X_n)_ converges to X_\infty, \mathbf-almost surely. See also * Convergence in distribution In probability theory, there exist several different notions of convergence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Càdlàg
In mathematics, a càdlàg (French: "''continue à droite, limite à gauche''"), RCLL ("right continuous with left limits"), or corlol ("continuous on (the) right, limit on (the) left") function is a function defined on the real numbers (or a subset of them) that is everywhere right-continuous and has left limits everywhere. Càdlàg functions are important in the study of stochastic processes that admit (or even require) jumps, unlike Brownian motion, which has continuous sample paths. The collection of càdlàg functions on a given domain is known as Skorokhod space. Two related terms are càglàd, standing for "continue à gauche, limite à droite", the left-right reversal of càdlàg, and càllàl for "continue à l'un, limite à l’autre" (continuous on one side, limit on the other side), for a function which at each point of the domain is either càdlàg or càglàd. Definition Let be a metric space, and let . A function is called a càdlàg function if, for every , * the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |