|
Continuous Electron Beam Accelerator Facility
Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility (TJNAF), commonly called Jefferson Lab or JLab, is a US National Laboratory located in Newport News, Virginia. Its stated mission is "to provide forefront scientific facilities, opportunities and leadership essential for discovering the fundamental structure of nuclear matter; to partner in industry to apply its advanced technology; and to serve the nation and its communities through education and public outreach." Since June 1, 2006, it has been operated by Jefferson Science Associates, LLC, a limited liability company created by Southeastern Universities Research Association and PAE Applied Technologies. Until 1996 it was known as the Continuous Electron Beam Accelerator Facility (CEBAF); commonly, this name is still used for the main accelerator. Founded in 1984, Jefferson Lab employs more than 750 people, and more than 2,000 scientists from around the world have conducted research using the facility. History The facility ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JLab Logo White2
jLab is a numerical computational environment implemented in Java. The main scripting engine of jLab is GroovySci, an extension of Groovy. Additionally, the interpreted J-Scripts (similar to MATLAB MATLAB (an abbreviation of "MATrix LABoratory") is a proprietary multi-paradigm programming language and numeric computing environment developed by MathWorks. MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementa ...) and dynamic linking to Java class code are supported. The jLab environment aims to provide a MATLAB/Scilab like scientific computing platform that is supported by scripting engines implemented in the Java language. In the current implementation of jLab there coexist two scripting engines: # the interpreted j-Script scripting engine and # the compiled Groovy scripting engine. The later (i.e. Groovy) seems to be the preferred choice, since it is much faster, can execute directly Java code using only the familiar Java packaging rules ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picosecond
A picosecond (abbreviated as ps) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to 10−12 or (one trillionth) of a second. That is one trillionth, or one millionth of one millionth of a second, or 0.000 000 000 001 seconds. A picosecond is to one second as one second is to approximately 31,689 years. Multiple technical approaches achieve imaging within single-digit picoseconds: for example, the streak camera or intensified CCD (ICCD) cameras are able to picture the motion of light. One picosecond is equal to 1000 femtoseconds, or 1/1000 nanoseconds. Because the next SI unit is 1000 times larger, measurements of 10−11 and 10−10 second are typically expressed as tens or hundreds of picoseconds. Some notable measurements in this range include: * 1.0 picoseconds (1.0 ps) – cycle time for electromagnetic frequency 1 terahertz (THz) (1 x 1012 hertz), an inverse unit. This corresponds to a wavelength of 0.3 mm, as can be calculated b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
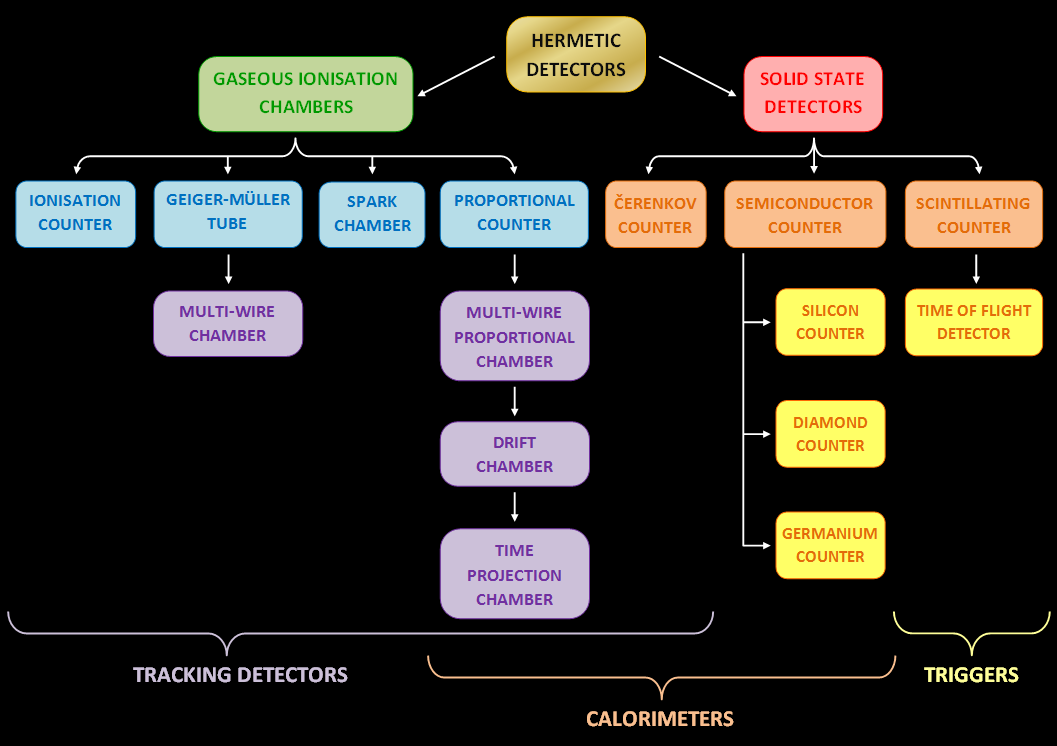
Particle Detector
In experimental and applied particle physics, nuclear physics, and nuclear engineering, a particle detector, also known as a radiation detector, is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify ionizing particles, such as those produced by nuclear decay, cosmic radiation, or reactions in a particle accelerator. Detectors can measure the particle energy and other attributes such as momentum, spin, charge, particle type, in addition to merely registering the presence of the particle. Examples and types Many of the detectors invented and used so far are ionization detectors (of which gaseous ionization detectors and semiconductor detectors are most typical) and scintillation detectors; but other, completely different principles have also been applied, like Čerenkov light and transition radiation. Historical examples * Bubble chamber * Wilson cloud chamber (diffusion chamber) *Photographic plate ;Detectors for radiation protection The following types of particle detec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subatomic Particle
In physical sciences, a subatomic particle is a particle that composes an atom. According to the Standard Model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a proton, neutron, or meson), or an elementary particle, which is not composed of other particles (for example, an electron, photon, or muon). Particle physics and nuclear physics study these particles and how they interact. Experiments show that light could behave like a stream of particles (called photons) as well as exhibiting wave-like properties. This led to the concept of wave–particle duality to reflect that quantum-scale behave like both particles and waves; they are sometimes called wavicles to reflect this. Another concept, the uncertainty principle, states that some of their properties taken together, such as their simultaneous position and momentum, cannot be measured exactly. The wave–particle duality has been shown to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LINAC
A linear particle accelerator (often shortened to linac) is a type of particle accelerator that accelerates charged subatomic particles or ions to a high speed by subjecting them to a series of oscillating electric potentials along a linear beamline. The principles for such machines were proposed by Gustav Ising in 1924, while the first machine that worked was constructed by Rolf Widerøe in 1928 at the RWTH Aachen University. Linacs have many applications: they generate X-rays and high energy electrons for medicinal purposes in radiation therapy, serve as particle injectors for higher-energy accelerators, and are used directly to achieve the highest kinetic energy for light particles (electrons and positrons) for particle physics. The design of a linac depends on the type of particle that is being accelerated: electrons, protons or ions. Linacs range in size from a cathode ray tube (which is a type of linac) to the linac at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , which has a neutral (not positive or negative) charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the nuclei of atoms. Since protons and neutrons behave similarly within the nucleus, and each has a mass of approximately one atomic mass unit, they are both referred to as nucleons. Their properties and interactions are described by nuclear physics. Protons and neutrons are not elementary particles; each is composed of three quarks. The chemical properties of an atom are mostly determined by the configuration of electrons that orbit the atom's heavy nucleus. The electron configuration is determined by the charge of the nucleus, which is determined by the number of protons, or atomic number. The number of neutrons is the neutron number. Neutrons do not affect the electron configuration, but the sum of atomic and neutron numbers is the mass of the nucleus. Atoms of a chemical element t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron mass ratio). Protons and neutrons, each with masses of approximately one atomic mass unit, are jointly referred to as "nucleons" (particles present in atomic nuclei). One or more protons are present in the Atomic nucleus, nucleus of every atom. They provide the attractive electrostatic central force which binds the atomic electrons. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as the atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z''). Since each chemical element, element has a unique number of protons, each element has its own unique atomic number, which determines the number of atomic electrons and consequently the chemical characteristics of the element. The word ''proton'' is Greek language, G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quark
A quark () is a type of elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. Quarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons, the most stable of which are protons and neutrons, the components of atomic nuclei. All commonly observable matter is composed of up quarks, down quarks and electrons. Owing to a phenomenon known as '' color confinement'', quarks are never found in isolation; they can be found only within hadrons, which include baryons (such as protons and neutrons) and mesons, or in quark–gluon plasmas. There is also the theoretical possibility of more exotic phases of quark matter. For this reason, much of what is known about quarks has been drawn from observations of hadrons. Quarks have various intrinsic properties, including electric charge, mass, color charge, and spin. They are the only elementary particles in the Standard Model of particle physics to experience all four fundamental interactions, also known as ''fundamental forces' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Nucleus
The atomic nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom, discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden experiments, Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. An atom is composed of a positively charged nucleus, with a cloud of negatively charged electrons surrounding it, bound together by electrostatic force. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force. The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of () for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about for uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrometer
A spectrometer () is a scientific instrument used to separate and measure spectral components of a physical phenomenon. Spectrometer is a broad term often used to describe instruments that measure a continuous variable of a phenomenon where the spectral components are somehow mixed. In visible light a spectrometer can separate white light and measure individual narrow bands of color, called a spectrum. A mass spectrometer measures the spectrum of the masses of the atoms or molecules present in a gas. The first spectrometers were used to split light into an array of separate colors. Spectrometers were developed in early studies of physics, astronomy, and chemistry. The capability of spectroscopy to determine chemical composition drove its advancement and continues to be one of its primary uses. Spectrometers are used in astronomy to analyze the chemical composition of stars and planets, and spectrometers gather data on the origin of the universe. Examples of spectrometer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CLAS Detector
CEBAF Large Acceptance Spectrometer (CLAS) is a nuclear and particle physics detector located in the experimental Hall B at Jefferson Laboratory in Newport News, Virginia, United States. It is used to study the properties of the nuclear matter by the collaboration of over 200 physicists (CLAS Collaboration) from many countries all around the world. The 0.5 to 12.0 GeV electron beam from the accelerator of Jefferson Laboratory is brought into "Hall B", the experimental hall that houses the CLAS system. Electrons or photons in the incoming beam collide with the nuclei of atoms in the physics "target" located at the center of CLAS. These collisions generally produce new particles, often after the target nucleons (protons and neutrons) are briefly excited to heavier-mass versions of the familiar protons and neutrons. A whole variety of intermediate-mass short-lived particles called "mesons" can be created. Scattered electron as well as the longer-lived produced particles travel throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and physicist William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin (1824–1907). The Kelvin scale is an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale, meaning it uses absolute zero as its null (zero) point. Historically, the Kelvin scale was developed by shifting the starting point of the much-older Celsius scale down from the melting point of water to absolute zero, and its increments still closely approximate the historic definition of a degree Celsius, but since 2019 the scale has been defined by fixing the Boltzmann constant to be exactly . Hence, one kelvin is equal to a change in the thermodynamic temperature that results in a change of thermal energy by . The temperature in degree Celsius is now defined as the temperature in kelvins minus 273.15, meanin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |