|
Contagium Vivum Fluidum
''Contagium vivum fluidum'' (Latin: "contagious living fluid") was a phrase first used to describe a virus, and underlined its ability to slip through the finest-mesh filters then available, giving it almost liquid properties. Martinus Beijerinck (1851–1931), a Dutch microbiologist and botanist, first used the term when studying the tobacco mosaic virus, becoming convinced that the virus had a liquid nature. In 1892, Dmitri Ivanovsky had discovered that the cause of tobacco mosaic disease could pass through Chamberland's porcelain filter. He noted these findings but felt that they could only have resulted from a cracked filter. It was left to Beijerinck, in 1898, to put forward the idea that the pathogen was small enough to pass through the filter routinely used to trap bacteria. Ivanovsky, irked that Beijerinck had not cited him, recreated Beijerinck's experimental set-up and demonstrated that particles of ink were small enough to pass through the filter, thus leaving the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
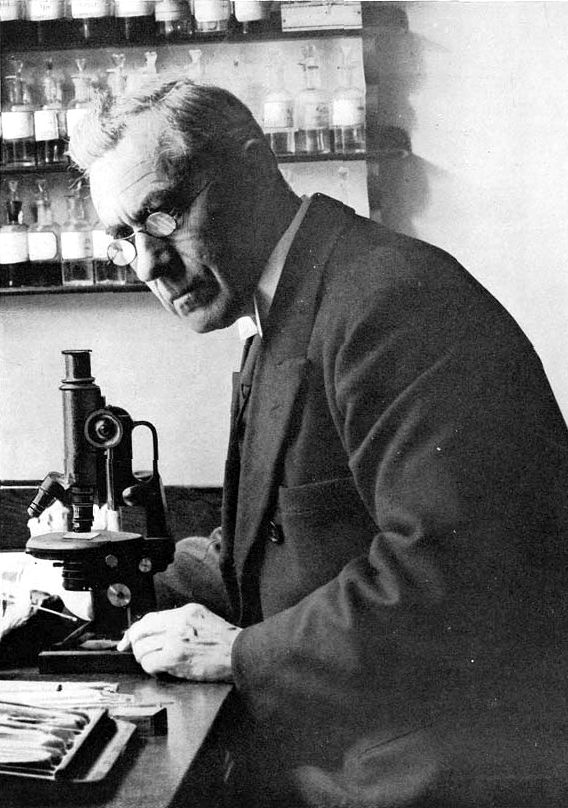
Martinus Beijerinck
Martinus Willem Beijerinck (, 16 March 1851 – 1 January 1931) was a Dutch microbiologist and botanist who was one of the founders of virology and environmental microbiology. He is credited with the discovery of viruses, which he called "''contagium vivum fluidum''". Life Early life and education Born in Amsterdam, Beijerinck studied at the Technical School of Delft, where he was awarded the degree of Chemical Engineer in 1872. He obtained his Doctor of Science degree from the University of Leiden in 1877. At the time, Delft, then a Polytechnic, did not have the right to confer doctorates, so Leiden did this for them. He became a teacher in microbiology at the Agricultural School in Wageningen (now Wageningen University) and later at the ''Polytechnische Hogeschool Delft'' (Delft Polytechnic, currently Delft University of Technology) (from 1895). He established the Delft School of Microbiology. His studies of agricultural and industrial microbiology yielded fundamental disco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) the genetic material, i. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tobacco Mosaic Virus
''Tobacco mosaic virus'' (TMV) is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus species in the genus ''Tobamovirus'' that infects a wide range of plants, especially tobacco and other members of the family Solanaceae. The infection causes characteristic patterns, such as "mosaic"-like mottling and discoloration on the leaves (hence the name). TMV was the first virus to be discovered. Although it was known from the late 19th century that a non-bacterial infectious disease was damaging tobacco crops, it was not until 1930 that the infectious agent was determined to be a virus. It is the first pathogen identified as a virus. The virus was crystallised by W.M. Stanley. It has a similar size to the largest synthetic molecule, known as PG5 History In 1886, Adolf Mayer first described the tobacco mosaic disease that could be transferred between plants, similar to bacterial infections. In 1892, Dmitri Ivanovsky gave the first concrete evidence for the existence of a non-bacterial infect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dmitri Ivanovsky
Dmitri Iosifovich Ivanovsky (alternative spelling ''Dmitrii'' or ''Dmitry Iwanowski''; russian: Дми́трий Ио́сифович Ивано́вский; 28 October 1864 – 20 June 1920) was a Russian botanist, the co-discoverer of :viruses (1892) and one of the founders of virology. Life Ivanovsky was born in the village of Nizy, Gdov Uyezd. He studied at the University of Saint Petersburg under Andrei Famintsyn in 1887, when he was sent to Ukraine and Bessarabia to investigate a tobacco disease causing great damage to plantations located there at the time. Three years later, he was assigned to look into a similar disease occurrence of tobacco plants, this time raging in the Crimea region. He discovered that both incidents of disease were caused by an extremely minuscule infectious agent, capable of permeating porcelain Chamberland filters, something which bacteria could never do. He described his findings in an article (1892) and a dissertation (1902). Then he worked at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamberland Filter
A Chamberland filter, also known as a Pasteur–Chamberland filter, is a porcelain water filter invented by Charles Chamberland in 1884. It was developed after Henry Doulton, Henry Doulton's ceramic water filter of 1827. It is similar to the Berkefeld filter in principle. Design The filter consists of a permeable unglazed porcelain tube (called bisque) that contains a ring of enameled porcelain through which the inflow pipe fits. The core of the porcelain is made up of a metal pipe with holes through which water flows out and is collected. Inflow is pressurized so filtration occurs under force. There are 13 types: ''L1'' to ''L13''. L1 filters have the coarsest pore size while L13 have the finest. Usefulness The Pasteur-Chamberland filter is as useful as other ceramic and porcelain filters. It is a good bacterial water filter used mainly as a high volume water filter.Textbook of Microbiology by Ananthanarayan and Panikar, The filter works more quickly when the water suppli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Microscope
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a higher resolving power than light microscopes and can reveal the structure of smaller objects. A scanning transmission electron microscope has achieved better than 50 pm resolution in annular dark-field imaging mode and magnifications of up to about 10,000,000× whereas most light microscopes are limited by diffraction to about 200 nm resolution and useful magnifications below 2000×. Electron microscopes use shaped magnetic fields to form electron optical lens systems that are analogous to the glass lenses of an optical light microscope. Electron microscopes are used to investigate the ultrastructure of a wide range of biological and inorganic specimens including microorganisms, cells, large molecules, biopsy samples, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wendell Meredith Stanley
Wendell Meredith Stanley (16 August 1904 – 15 June 1971) was an American biochemist, virologist and Nobel laureate. Biography Stanley was born in Ridgeville, Indiana, and earned a BSc in Chemistry at Earlham College in Richmond, Indiana. He then studied at the University of Illinois, gaining an MS in science in 1927 followed by a PhD in chemistry two years later. His later accomplishments include writing the book "Chemistry: A Beautiful Thing" and being a Pulitzer Prize nominee. Research As a member of National Research Council he moved temporarily for academic work with Heinrich Wieland in Munich before he returned to the States in 1931. On return he was approved as an assistant at The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research. He remained with the Institute until 1948, becoming an Associate Member in 1937, and a Member in 1940. In 1948, he became Professor of Biochemistry at the University of California, Berkeley and built the Virus Laboratory and a free-standing Depart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
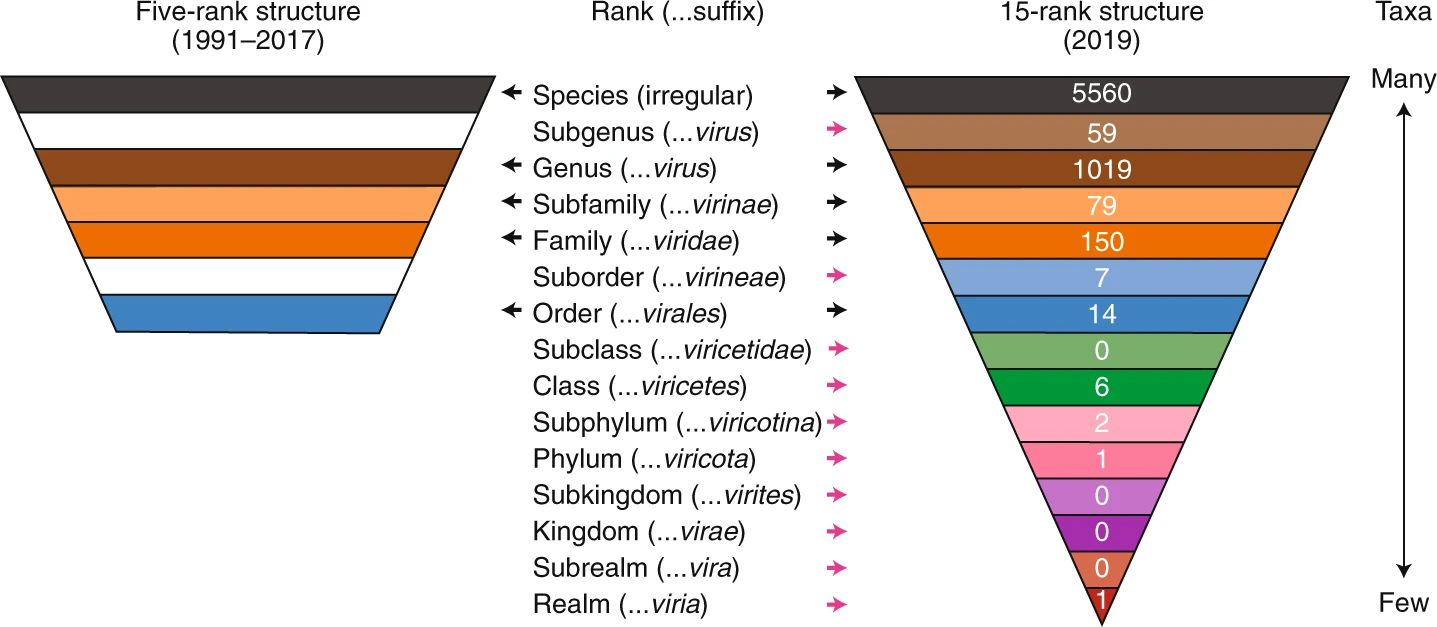
Virus Species
Virus classification is the process of naming viruses and placing them into a taxonomic system similar to the classification systems used for cellular organisms. Viruses are classified by phenotypic characteristics, such as morphology, nucleic acid type, mode of replication, host organisms, and the type of disease they cause. The formal taxonomic classification of viruses is the responsibility of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) system, although the Baltimore classification system can be used to place viruses into one of seven groups based on their manner of mRNA synthesis. Specific naming conventions and further classification guidelines are set out by the ICTV. A catalogue of all the world's known viruses has been proposed and, in 2013, some preliminary efforts were underway. Definitions Species definition Species form the basis for any biological classification system. Before 1982, it was thought that viruses could not be made to fit Ernst Mayr's r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) the genetic material, i.e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Words And Phrases
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a fusional language, highly inflected language, with three distinct grammatical gender, genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven grammatical case, noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


%2C_one_of_the_founders_of_virology).jpg)