|
Consumer Needs
The theory of consumer choice is the branch of microeconomics that relates Preference (economics), preferences to consumption expenditures and to supply and demand, consumer demand curves. It analyzes how consumers maximize the desirability of their consumption (as measured by their preferences subject to limitations on their expenditures), by maximizing utility subject to a consumer budget constraint. Factors influencing consumers' evaluation of the utility of goods include: income level, cultural factors, product information and physio-psychological factors. Consumption is separated from production, logically, because two different economic agents are involved. In the first case, consumption is determined by the individual. Their specific tastes or preferences determine the amount of utility they derive from goods and services they consume. In the second case, a producer has different motives to the consumer in that they are focussed on the profit they make. This is explained f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microeconomics
Microeconomics is a branch of economics that studies the behavior of individuals and Theory of the firm, firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of scarcity, scarce resources and the interactions among these individuals and firms. Microeconomics focuses on the study of individual markets, sectors, or industries as opposed to the economy as a whole, which is studied in macroeconomics. One goal of microeconomics is to analyze the market mechanisms that establish relative prices among goods and services and allocate limited resources among alternative uses. Microeconomics shows conditions under which free markets lead to desirable allocations. It also analyzes market failure, where markets fail to produce Economic efficiency, efficient results. While microeconomics focuses on firms and individuals, macroeconomics focuses on the total of economic activity, dealing with the issues of Economic growth, growth, inflation, and unemployment—and with national policies relati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heuristics
A heuristic or heuristic technique (''problem solving'', '' mental shortcut'', ''rule of thumb'') is any approach to problem solving that employs a pragmatic method that is not fully optimized, perfected, or rationalized, but is nevertheless "good enough" as an approximation or attribute substitution. Where finding an optimal solution is impossible or impractical, heuristic methods can be used to speed up the process of finding a satisfactory solution. Heuristics can be mental shortcuts that ease the cognitive load of making a decision. Context Gigerenzer & Gaissmaier (2011) state that sub-sets of ''strategy'' include heuristics, regression analysis, and Bayesian inference. Heuristics are strategies based on rules to generate optimal decisions, like the anchoring effect and utility maximization problem. These strategies depend on using readily accessible, though loosely applicable, information to control problem solving in human beings, machines and abstrac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
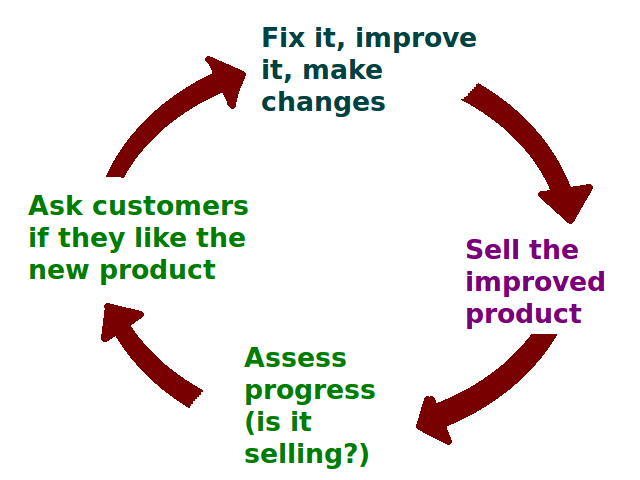
Online Shopping
Online shopping is a form of electronic commerce which allows consumers to directly buy goods or services from a seller over the Internet using a web browser or a mobile app. Consumers find a product of interest by visiting the website of the retailer directly or by searching among alternative vendors using a shopping search engine, which displays the same product's availability and pricing at different e-retailers. customers can shop online using a range of different computers and devices, including desktop computers, laptops, tablet computers and smartphones. Online stores that evoke the physical analogy of buying products or services at a regular "brick-and-mortar" retailer or shopping center follow a process called business-to-consumer (B2C) online shopping. When an online store is set up to enable businesses to buy from another business, the process is instead called business-to-business (B2B) online shopping. A typical online store enables the customer to browse t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Investment
Investment is traditionally defined as the "commitment of resources into something expected to gain value over time". If an investment involves money, then it can be defined as a "commitment of money to receive more money later". From a broader viewpoint, an investment can be defined as "to tailor the pattern of expenditure and receipt of resources to optimise the desirable patterns of these flows". When expenditures and receipts are defined in terms of money, then the net monetary receipt in a time period is termed cash flow, while money received in a series of several time periods is termed cash flow stream. In finance, the purpose of investing is to generate a Return (finance), return on the invested asset. The return may consist of a capital gain (profit) or loss, realised if the investment is sold, unrealised capital appreciation (or depreciation) if yet unsold. It may also consist of periodic income such as dividends, interest, or rental income. The return may also inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunk Cost
In economics and business decision-making, a sunk cost (also known as retrospective cost) is a cost that has already been incurred and cannot be recovered. Sunk costs are contrasted with '' prospective costs'', which are future costs that may be avoided if action is taken. In other words, a sunk cost is a sum paid in the past that is no longer relevant to decisions about the future. Even though economists argue that sunk costs are no longer relevant to future rational decision-making, people in everyday life often take previous expenditures in situations, such as repairing a car or house, into their future decisions regarding those properties. Bygones principle According to classical economics and standard microeconomic theory, only prospective (future) costs are relevant to a rational decision. At any moment in time, the best thing to do depends only on ''current'' alternatives. The only things that matter are the ''future'' consequences. Past mistakes are irrelevant. Any cos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumer Constraint Choice Price Shift
A consumer is a person or a group who intends to order, or use purchased goods, products, or services primarily for personal, social, family, household and similar needs, who is not directly related to entrepreneurial or business activities. The term most commonly refers to a person who purchases goods and services for personal use. Rights "Consumers, by definition, include us all", said President John F. Kennedy, offering his definition to the United States Congress on March 15, 1962. This speech became the basis for the creation of World Consumer Rights Day, now celebrated on March 15. In his speech, John Fitzgerald Kennedy outlined the integral responsibility to consumers from their respective governments to help exercise consumers' rights, including: *The right to safety: To be protected against the marketing of goods that are hazardous to health or life. *The right to be informed: To be protected against fraudulent, deceitful, or grossly misleading information, advertisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardinal Utility
In economics, a cardinal utility expresses not only which of two outcomes is preferred, but also the intensity of preferences, i.e. ''how much'' better or worse one outcome is compared to another. In consumer choice theory, economists originally attempted to replace cardinal utility with the apparently weaker concept of ordinal utility. Cardinal utility appears to impose the assumption that levels of absolute satisfaction exist, so magnitudes of increments to satisfaction can be compared across different situations. However, economists in the 1940s proved that under mild conditions, ordinal utilities imply cardinal utilities. This result is now known as the von Neumann–Morgenstern utility theorem; many similar utility representation theorems exist in other contexts. History In 1738, Daniel Bernoulli was the first to theorize about the marginal value of money. He assumed that the value of an additional amount is inversely proportional to the pecuniary possessions which a per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is a term frequently used in marketing to evaluate customer experience. It is a measure of how products and services supplied by a company meet or surpass customer expectation. Customer satisfaction is defined as "the number of customers, or percentage of total customers, whose reported experience with a firm, its products, or its services (ratings) exceeds specified satisfaction goals".. Enhancing customer satisfaction and fostering customer loyalty are pivotal for businesses, given the significant importance of improving the balance between customer attitudes before and after the consumption process. Expectancy disconfirmation theory is the most widely accepted theoretical framework for explaining customer satisfaction. However, other frameworks, such as equity theory, attribution theory, contrast theory, assimilation theory, and various others, are also used to gain insights into customer satisfaction. However, traditionally applied satisfaction survey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumer Constraint Choice
A consumer is a person or a group who intends to order, or use purchased goods, products, or services primarily for personal, social, family, household and similar needs, who is not directly related to entrepreneurial or business activities. The term most commonly refers to a person who purchases goods and services for personal use. Rights "Consumers, by definition, include us all", said President John F. Kennedy, offering his definition to the United States Congress on March 15, 1962. This speech became the basis for the creation of World Consumer Rights Day, now celebrated on March 15. In his speech, John Fitzgerald Kennedy outlined the integral responsibility to consumers from their respective governments to help exercise consumers' rights, including: *The right to safety: To be protected against the marketing of goods that are hazardous to health or life. *The right to be informed: To be protected against fraudulent, deceitful, or grossly misleading information, advertisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indifference Curves
In economics, an indifference curve connects points on a graph representing different quantities of two goods, points between which a consumer is ''indifferent''. That is, any combinations of two products indicated by the curve will provide the consumer with equal levels of utility, and the consumer has no preference for one combination or bundle of goods over a different combination on the same curve. One can also refer to each point on the indifference curve as rendering the same level of utility (satisfaction) for the consumer. In other words, an indifference curve is the locus of various points showing different combinations of two goods providing equal utility to the consumer. Utility is then a device to represent preferences rather than something from which preferences come. The main use of indifference curves is in the representation of potentially observable demand patterns for individual consumers over commodity bundles. Indifference curve analysis is a purely technolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |