|
Constituent Cortes Of 1820
The Constituent Cortes of 1820, formal title The General and Extraordinary Cortes of the Portuguese Nation, also frequently known as the Sovereign Congress or the Cortes Constituintes Vintistas, was the first modern Portuguese parliament. Created after the Liberal Revolution of 1820 to prepare a constitution for Portugal and its overseas territories, it used a different system from the traditional General Cortes for choosing representatives, and the three traditional feudal estates (Clergy, Nobility, and Commoners) no longer sat separately. The Cortes sat between January 24, 1821 and November 4, 1822 at the Palácio das Necessidades in Lisbon. The work of the Constitutional Cortes culminated in the approval of the Portuguese Constitution of 1822. Elections The government installed after the Oporto Revolution, known as the Provisional Junta of the Supreme Government of the Kingdom, decided to convene the Cortes and on September 1, 1820 set up a preparatory commission. On November 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oscar Pereira Da Silva - Sessão Das Cortes De Lisboa, Acervo Do Museu Paulista Da USP 2
Oscar, OSCAR, or The Oscar may refer to: People * Oscar (given name), an Irish- and English-language name also used in other languages; the article includes the names Oskar, Oskari, Oszkár, Óscar, and other forms. * Oscar (Irish mythology), legendary figure, son of Oisín and grandson of Finn mac Cumhall Places * Oscar, Kentucky, an unincorporated community * Oscar, Louisiana, an unincorporated community * Oscar, Missouri, an unincorporated community * Oscar, Oklahoma, an unincorporated community * Oscar, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community * Oscar, Texas, an unincorporated community * Oscar, West Virginia, an unincorporated community * Lake Oscar (other) * Oscar Township, Otter Tail County, Minnesota, a civil township Animals * Oscar (bionic cat), a cat that had implants after losing both hind paws * Oscar (bull), #16, (d. 1983) a ProRodeo Hall of Fame bucking bull * Oscar (fish), ''Astronotus ocellatus'' * Oscar (therapy cat), cat purported to predict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John VI Of Portugal
, house = Braganza , father = Peter III of Portugal , mother = Maria I of Portugal , birth_date = , birth_place = Queluz Palace, Queluz, Portugal , death_date = , death_place = Bemposta Palace, Lisbon, Portugal , burial_date = , burial_place = Pantheon of the House of Braganza , signature = Assinatura D. João VI.svg , religion = Roman Catholicism Dom John VI (Portuguese: ''João VI''; 13 May 1767 – 10 March 1826), nicknamed "the Clement", was King of the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves from 1816 to 1825. Although the United Kingdom of Portugal ceased to exist ''de facto'' beginning in 1822, he remained its monarch ''de jure'' between 1822 and 1825. After the recognition of the independence of Brazil under the Treaty of Rio de Janeiro of 1825, he continued as King of Portugal until his death in 1826. Under the same treaty, he also became titular Emperor of Brazil for life, while his son, Emperor Dom Pedr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cipriano Barata
Cipriano Barata, also known as Cipriano José Barata de Almeida (26 September 1762 – 7 June 1838) was a Brazilian physician and politician who was in favor of Brazilian independence. He was a founding member of a Masonic Lodge, "The Knights of the Light Shop." He was also a journalist who started a newspaper in Portugal called ''Sentinel of Liberty''. Early life and education Barata was born in Bahia, Brazil in 1762. Barata graduated from the University of Coimbra, where he studied surgery, philosophy and mathematics and was introduced to Enlightenment ideas that were popular in academia at the time. Career and political activity Together with professor Francisco Muniz Barreto and others, he was a member of the first Masonic Lodge in Brazil, the "Knights of the Light Shop", founded in Salvador in 1797. The following year, he attended the casting Bahia, being held by legal authorities afterward. Some say that he was the editor of the Manifesto to the People from Bahia, which u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amazonas Province (Brazil)
Amazonas Province was one of the provinces of the Empire of Brazil. It was created in 1850 from territory of Grão-Pará Province Grão-Pará may refer to: *Grão Pará, a municipality in the state of Santa Catarina in the South region of Brazil. *Grão-Pará Ecological Station, the largest strictly protected tropical forest conservation area in the world *Palácio do Grão-P .... In 1889 it became Amazonas (Brazilian state). 1850 establishments in Brazil 1889 disestablishments in Brazil Former countries in South America Provinces of Brazil {{AmazonasBR-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alagoas
Alagoas (, ) is one of the 27 federative units of Brazil and is situated in the eastern part of the Northeast Region. It borders: Pernambuco (N and NW); Sergipe (S); Bahia (SW); and the Atlantic Ocean (E). Its capital is the city of Maceió. It has 1.6% of the Brazilian population and produces 0.8% of the Brazilian GDP. It is made up of 102 municipalities and its most populous cities are Maceió, Arapiraca, Palmeira dos Índios, Rio Largo, Penedo, União dos Palmares, São Miguel dos Campos, Santana do Ipanema, Delmiro Gouveia, Coruripe, Marechal Deodoro, and Campo Alegre. It is the second smallest Brazilian state in area (larger only than Sergipe) and it is 16th in population. It is also one of the largest producers of sugarcane and coconuts in the country, and has an economy based on cattle raising. Land of the '' sururu'' (or Charru Mussel), lagoon shellfish which serves as food for the coastal population, and of coconut water, Alagoas also possesses some of the country ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
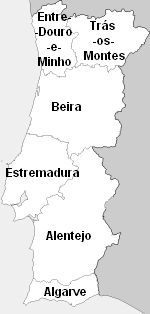
Estremadura Province (historical)
Estremadura Province (Portuguese pronunciation: ɨ)ʃtɾɨmɐˈðuɾɐ is one of the six historical provinces of Portugal. It is located along the Atlantic Ocean coast in the center of the country and includes Lisbon, the capital. The name of this province (and also the Spanish Extremadura) originates from the Spanish and Portuguese struggle with the Moors, and the Christian military victories over the Moors (moros) during the 12th century. These provinces were called Extrema Durii, which means "farthest from the Douro River." During the 19th century, Estremadura was the only province in the kingdom that did not border Spain. The provinces Beira and Alentejo bordered on the north, east, and south. Its western border was with the Atlantic Ocean, and it was wide at its widest point. In 1835, Portugal divided into districts, which were subdivided into counties and parishes. Estremadura Province included Districts of Lisbon, Santarém, Leiria and part of Setúbal with Lisboa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alentejo Region
Alentejo Region () is one of the seven NUTS 2 regions of Portugal. It covers all of the historical Alentejo Province and part of the historical Ribatejo and Estremadura provinces. The greater region is defined within Portugal by the land bordering the left bank of the river Tagus to the North and extending to the South where it borders the Algarve region. The origin of its name, "além" + "Tejo" combined as Alentejo, literally translates to "Beyond-the-Tagus". However, a large part of the subregion Lezíria do Tejo is located on the right bank of the Tagus. The Alentejo is completely located beyond the left margin of the Tagus River. Its main cities are Évora, Elvas, Portalegre, Beja, Moura, Serpa, Sines and Santarém. Subdivisions The region is subdivided into five intermunicipal communities ( NUTS 3 regions): * Alentejo Litoral * Alentejo Central * Alto Alentejo * Baixo Alentejo * Lezíria do Tejo Demographics The resident population of the Alentej ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beira (Portugal)
Beira () was one of the six traditional provinces or ''comarcas'' of Portugal. The territorial extension is different from that of the area called ''the Beiras'', which refers to three provinces of 1936, Beira Alta, Beira Baixa and Beira Litoral. Geography The most important cities within the borders of the traditional province are: Coimbra, Aveiro, Leiria, Viseu, Castelo Branco, Guarda, Figueira da Foz, Covilhã and Pinhel. The main river is the Mondego; other rivers include the Vouga, Dão, Côa, Zêzere and Paiva. The largest mountain range is Serra da Estrela – Continental Portugal's highest – other ranges being the Caramulo, Marofa, Gardunha, and Bussaco. Administrative history After the 15th Century, the new Kingdom of Portugal was divided into six great administrative units, referred to as comarcas. Since the Middle Ages there existed the Beira Province. 1832 In 1832 this province was divided into * Beira Alta * Beira Baixa 1936 In 1936 these were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trás-os-Montes E Alto Douro Province
Trás-os-Montes e Alto Douro () is a historical province of Portugal located in the northeastern corner of the country. Vast plateaus, river valleys, mountains, and castles abound in Trás os Montes e Alto Douro. History A first attempt to register its constitution was made under the reign of King Sancho II (1223–1248). A second was made in the reign of his son and successor, Afonso III (1248–1279), under the Inquirições or royal commissions in 1258, intending to base the territory of Trás-os-Montes on so-called "new towns" under direct control of the Crown. Afonso III gave it its charter in 1253, referring to the town, "a hill opposite the Crespos", which already had a core of settlements organized around the Church of St. Facundo. Since 1833 the region has been divided into two districts on the right (northern) bank of the Douro river — Vila Real and Bragança, with 5 other municipalities on the south bank of the Douro river included in the districts of Viseu an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minho Province
Minho () was a former province in Portugal, established in 1936 and dissolved in 1976. It consisted of 23 municipalities, with its capital in the city of Braga. Today, the area would include the districts of Braga and Viana do Castelo. Minho has substantial Celtic influences and shares many cultural traits with neighbouring Galicia in Northwestern Spain. The region was part of the Roman Province and early Germanic medieval Kingdom of Gallaecia. Historical remains of Celtic Minho include Briteiros Iron Age Hillfort, the largest Gallaecian native stronghold in the Entre Douro e Minho region, in North Portugal. The University of Minho, founded in 1973, takes its name from the former province. Minho is famous as being the origin of the soup caldo verde and Vinho Verde, a wine particular to the region. Historic cities * Braga (Bracara Augusta) * Guimarães (old Vimaranes). * Viana do Castelo, formerly Viana do Lima. * Barcelos * Fafe See also * Minho River * Gallaecia * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algarve
The Algarve (, , ; from ) is the southernmost NUTS II region of continental Portugal. It has an area of with 467,495 permanent inhabitants and incorporates 16 municipalities ( ''concelhos'' or ''municípios'' in Portuguese). The region has its administrative centre in the city of Faro, where both the region's international airport (IATA: FAO) and public university, the University of Algarve, are located. The region coincides with Faro District and is subdivided into two zones, one to the West ( Barlavento) and another to the East ( Sotavento). Tourism and related activities are extensive and make up the bulk of the Algarve's summer economy. Production of food, which includes fish and other seafood, as well as different types of fruit and vegetables, such as oranges, figs, plums, carob pods, almonds, avocados, tomatoes, cauliflowers, strawberries, and raspberries, are also economically important in the region. Although Lisbon surpasses the Algarve in terms of tourism reve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)