|
Constellation Cetus
Cetus () is a constellation, sometimes called 'the whale' in English. The Cetus was a sea monster in Greek mythology which both Perseus and Heracles needed to slay. Cetus is in the region of the sky that contains other water-related constellations: Aquarius, Pisces and Eridanus. Features Ecliptic Cetus is not among the 12 true zodiac constellations in the J2000 epoch, nor classical 12-part zodiac. The ecliptic passes less than 0.25° from one of its corners. Thus the moon and planets will enter Cetus (occulting any stars as a foreground object) in 50% of their successive orbits briefly and the southern part of the sun appears in Cetus for about one day each year. Many asteroids in belts have longer phases occulting the north-western part of Cetus, those with a slightly greater inclination to the ecliptic than the moon and planets. As seen from Mars, the ecliptic (apparent plane of the sun and also the average plane of the planets which is almost the same) passes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully aquatic placental marine mammals. As an informal and colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea, i.e. all cetaceans apart from dolphins and porpoises. Dolphins and porpoises may be considered whales from a formal, cladistic perspective. Whales, dolphins and porpoises belong to the order Cetartiodactyla, which consists of even-toed ungulates. Their closest non-cetacean living relatives are the hippopotamuses, from which they and other cetaceans diverged about 54 million years ago. The two parvorders of whales, baleen whales (Mysticeti) and toothed whales (Odontoceti), are thought to have had their last common ancestor around 34 million years ago. Mysticetes include four extant (living) families: Balaenopteridae (the rorquals), Balaenidae (right whales), Cetotheriidae (the pygmy right whale), and Eschrichtiidae (the grey whale). Odontocetes include the Monodontidae (beluga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mira
Mira (), designation Omicron Ceti (ο Ceti, abbreviated Omicron Cet, ο Cet), is a red-giant star estimated to be 200–400 light-years from the Sun in the constellation Cetus. ο Ceti is a binary stellar system, consisting of a variable red giant (Mira A) along with a white dwarf companion (Mira B). Mira A is a pulsating variable star and was the first non-supernova variable star discovered, with the possible exception of Algol. It is the prototype of the Mira variables. Nomenclature ο Ceti ( Latinised to ''Omicron Ceti'') is the star's Bayer designation. It was named Mira (Latin for 'wonderful' or 'astonishing') by Johannes Hevelius in his ''Historiola Mirae Stellae'' (1662). In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin of July 2016 included a table of the first two batches of names approved by the WGSN, which included Mira for this star. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy On Mars
In many cases astronomical phenomena viewed from the planet Mars are the same or similar to those seen from Earth but sometimes (as with the view of Earth as an evening/morning star) they can be quite different. For example, because the atmosphere of Mars does not contain an ozone layer, it is also possible to make UV observations from the surface of Mars. Seasons Mars has an axial tilt of 25.19°, quite close to the value of 23.44° for Earth, and thus Mars has seasons of spring, summer, autumn, winter as Earth does. As on Earth, the southern and northern hemispheres have summer and winter at opposing times. However, the orbit of Mars has significantly greater eccentricity than that of Earth. Therefore, the seasons are of unequal length, much more so than on Earth: In practical terms, this means that summers and winters have different lengths and intensities in the northern and southern hemispheres. Winters in the north are warm and short (because Mars is moving fast n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
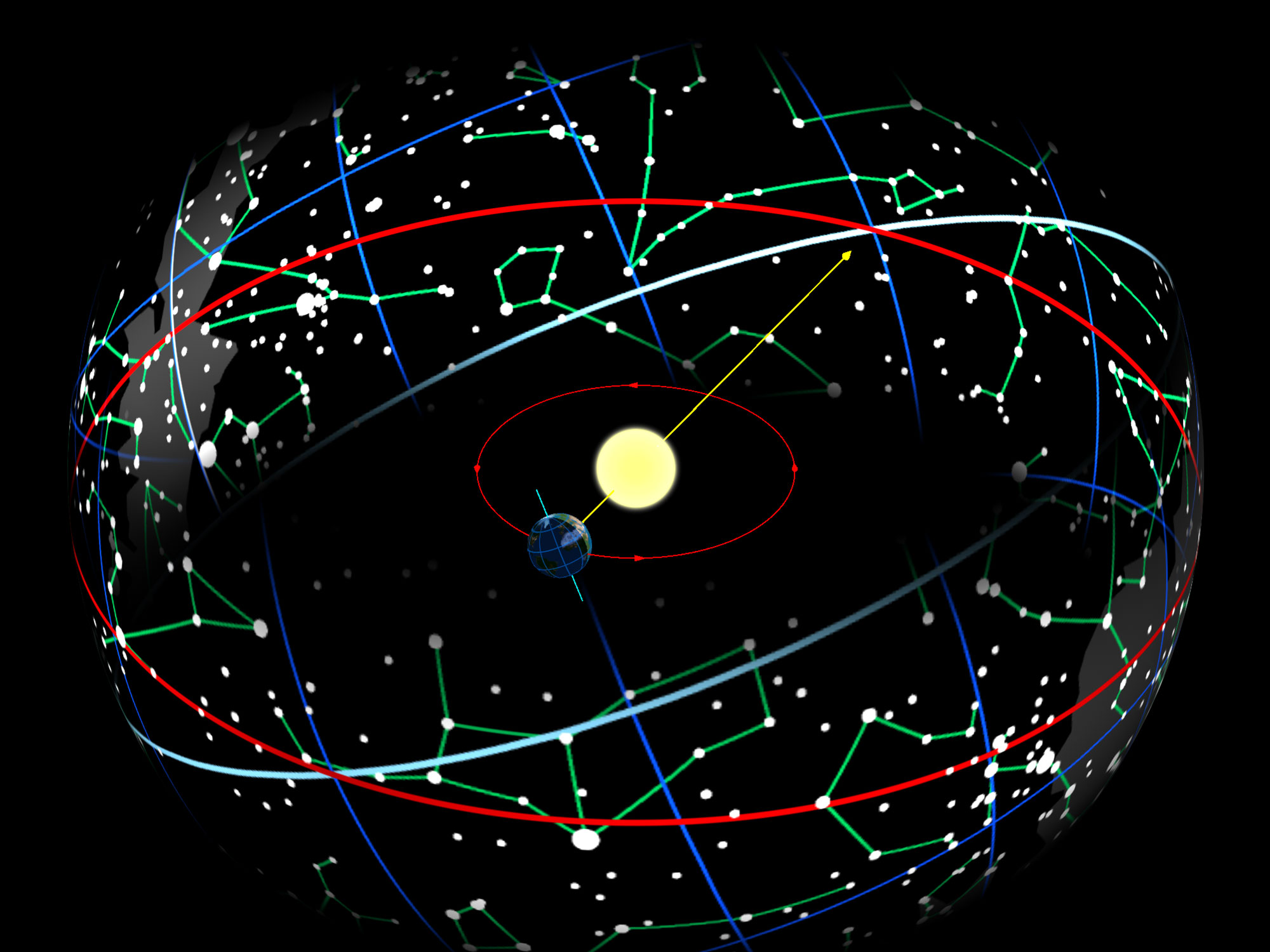
Inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a Plane of reference, reference plane and the orbital plane or Axis of rotation, axis of direction of the orbiting object. For a satellite orbiting the Earth directly above the Equator, the plane of the satellite's orbit is the same as the Earth's equatorial plane, and the satellite's orbital inclination is 0°. The general case for a circular orbit is that it is tilted, spending half an orbit over the northern hemisphere and half over the southern. If the orbit swung between 20° north latitude and 20° south latitude, then its orbital inclination would be 20°. Orbits The inclination is one of the six orbital elements describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit. It is the angle between the orbital plane and the plane of reference, normally stated in degree (angle), degrees. For a satellite orbiting a planet, the plane of reference is usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic against the background of stars. The ecliptic is an important reference plane and is the basis of the ecliptic coordinate system. Sun's apparent motion The ecliptic is the apparent path of the Sun throughout the course of a year. Because Earth takes one year to orbit the Sun, the apparent position of the Sun takes one year to make a complete circuit of the ecliptic. With slightly more than 365 days in one year, the Sun moves a little less than 1° eastward every day. This small difference in the Sun's position against the stars causes any particular spot on Earth's surface to catch up with (and stand directly north or south of) the Sun about four minutes later each day than it would if Earth did not orbit; a day on Earth is therefore 24 hours ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoch (astronomy)
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a celestial body, as they are subject to perturbations and vary with time. These time-varying astronomical quantities might include, for example, the mean longitude or mean anomaly of a body, the node of its orbit relative to a reference plane, the direction of the apogee or aphelion of its orbit, or the size of the major axis of its orbit. The main use of astronomical quantities specified in this way is to calculate other relevant parameters of motion, in order to predict future positions and velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for bodies in motion under the gravitational effects of other bodies) can be used to generate an ephemeris, a table of values giving the posit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zodiac
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north or south (as measured in celestial latitude) of the ecliptic, the Sun path, apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. The paths of the Moon and visible planets are within the belt of the zodiac. In Western astrology, and formerly astronomy, the zodiac is divided into astrological sign, twelve signs, each occupying 30° of celestial longitude and roughly corresponding to the following star constellations: Aries (astrology), Aries, Taurus (astrology), Taurus, Gemini (astrology), Gemini, Cancer (astrology), Cancer, Leo (astrology), Leo, Virgo (astrology), Virgo, Libra (astrology), Libra, Scorpio (astrology), Scorpio, Sagittarius (astrology), Sagittarius, Capricorn (astrology), Capricorn, Aquarius (astrology), Aquarius, and Pisces (astrology), Pisces. These astrological signs form a celestial coordinate system, or more specifically an ecliptic coordinate sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heracles
Heracles ( ; grc-gre, Ἡρακλῆς, , glory/fame of Hera), born Alcaeus (, ''Alkaios'') or Alcides (, ''Alkeidēs''), was a divine hero in Greek mythology, the son of Zeus and Alcmene, and the foster son of Amphitryon.By his adoptive descent through Amphitryon, Heracles receives the epithet Alcides, as "of the line of Alcaeus", father of Amphitryon. Amphitryon's own, mortal son was Iphicles. He was a great-grandson and half-brother (as they are both sired by the god Zeus) of Perseus, and similarly a half-brother of Dionysus. He was the greatest of the Greek heroes, the ancestor of royal clans who claimed to be Heracleidae (), and a champion of the Olympian order against chthonic monsters. In Rome and the modern West, he is known as Hercules, with whom the later Roman emperors, in particular Commodus and Maximian, often identified themselves. The Romans adopted the Greek version of his life and works essentially unchanged, but added anecdotal detail of their own, so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perseus
In Greek mythology, Perseus (Help:IPA/English, /ˈpɜːrsiəs, -sjuːs/; Greek language, Greek: Περσεύς, Romanization of Greek, translit. Perseús) is the legendary founder of Mycenae and of the Perseid dynasty. He was, alongside Cadmus and Bellerophon, the greatest Greek hero and slayer of monsters before the days of Heracles. He beheaded the Gorgon Medusa for Polydectes and saved Andromeda (mythology), Andromeda from the sea monster Cetus (mythology), Cetus. He was the son of Zeus and the mortal Danaë, as well as the half-brother and great-grandfather of Heracles (as they were both children of Zeus, and Heracles' mother was descended from Perseus). Etymology Because of the obscurity of the name "Perseus" and the legendary character of its bearer, most etymologists presume that it might be pre-Greek; however, the name of Perseus's native city was Greek and so were the names of his wife and relatives. There is some idea that it descended into Greek from the Proto-Indo-Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical cosmology, nature of the world, the lives and activities of List of Greek mythological figures, deities, Greek hero cult, heroes, and List of Greek mythological creatures, mythological creatures, and the origins and significance of the ancient Greeks' own cult (religious practice), cult and ritual practices. Modern scholars study the myths to shed light on the religious and political institutions of ancient Greece, and to better understand the nature of myth-making itself. The Greek myths were initially propagated in an oral tradition, oral-poetic tradition most likely by Minoan civilization, Minoan and Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaean singers starting in the 18th century BC; eventually the myths of the heroes of the Trojan War and its after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Monster
Sea monsters are beings from folklore believed to dwell in the sea and often imagined to be of immense size. Marine monsters can take many forms, including sea dragons, sea serpents, or tentacled beasts. They can be slimy and scaly and are often pictured threatening ships or spouting jets of water. The definition of a "monster" is subjective; further, some sea monsters may have been based on scientifically accepted creatures, such as whales and types of giant and colossal squid. Sightings and legends Sea monster accounts are found in virtually all cultures that have contact with the sea. For example, Avienius relates of Carthaginian explorer Himilco's voyage "...there monsters of the deep, and beasts swim amid the slow and sluggishly crawling ships." (lines 117–29 of ''Ora Maritima''). Sir Humphrey Gilbert claimed to have encountered a lion-like monster with "glaring eyes" on his return voyage after formally claiming St. John's, Newfoundland (1583) for England. Another ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)