|
Constant Wauters (painter)
Constant Wauters (born 25 April 1889) was a Belgian colonial official. He was commissioner of Lusambo Province in the Belgian Congo from 1 October 1933 to 17 August 1940. Life Constant Joseph Antoine Wauters was born on 25 April 1889. He entered the colonial service on 29 September 1910. In 1927 Wauters was urban commissioner of Léopoldville. He was concerned that the slum-like ''Cité Indigène'' was too close to the European town, and potentially a source of disease. He proposed four related policies for African townships: they should be separated from the European quarters by a "neutral zone"; sanitation should be provided for; they should be compact rather than fragmented; and they should adhere to standard construction approaches. Wauters favored having all the houses built by one firm rather than leaving it up to the residents, but did not want the government directly involved in construction of housing. Wauters was named Commissaire général assistant to the governor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Governors Of Kasaï (former Province)
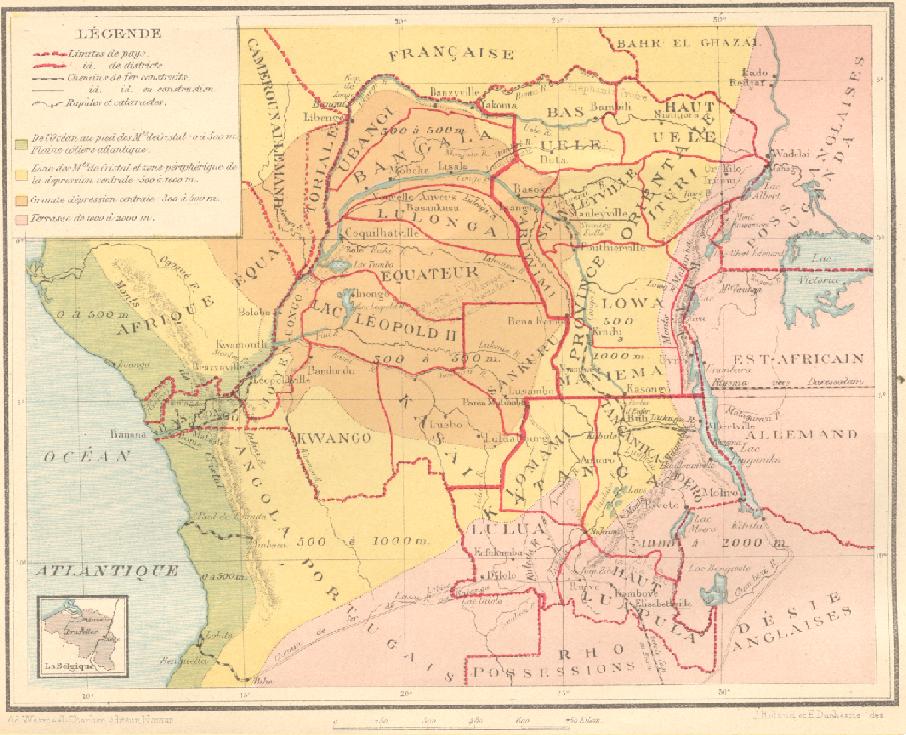
This list of governors of Kasaï includes governors or equivalent officeholders of the Congo-Kasaï/Kongo-Kasaï province established in the Belgian Congo in 1918. On 1 October 1933 it was split into the Lusambo and Léopoldville provinces. Lusambo included the Kasaï and Sankuru districts of Congo-Kasaï and parts of the Léopold II District (Équateur) and Lomami District (Katanga). On 27 May 1947 Lusambo was renamed Kasaï, which became an autonomous province of the Congo republic on 30 June 1960. On 14 August 1962 Kasaï was divided into five new provinces: Lomami, Luluabourg, Sankuru, Sud-Kasaï and Unité Kasaïenne. On 25 April 1966 Luluabourg and Unité Kasaïenne were united to form Kasaï-Occidental, while Lomami, Sankuru, and Sud-Kasaï were united in the new province of Kasaï-Oriental. Kasaï-Occidental was split in 2015 into the Kasaï-Central and Kasaï provinces. Congo-Kasaï (1922–1932) The governors (or equivalent) of Congo-Kasaï Province were: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congo-Kasaï
Congo-Kasaï was one of the four large provinces of the Belgian Congo defined in 1914. It was formally established in 1919, and in 1933 was divided into the new provinces of Léopoldville and Lusambo. Location Congo-Kasaï was named after the Kasai River, a major left tributary of the Congo River that provides access to the region. By 1910 a factory of the Kasai Company had been established near Misumba, which had about two thousand inhabitants. The company had made successful trial rubber plantations. The company also bought rubber and ivory from the local people, some of whom used it to buy liquor from the Portuguese territory (Angola). Congo-Kasaï had five districts: the urban district of Léopoldville, capital of the colony, and the districts (from west to east) of Bas-Congo, Kwango, Kasaï and Sankuru. The '' Huileries du Congo Belge'' company had two zones (or circles) of exploitation in the province based on Brabanta and Leverville, of which Leverville was the most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governors Of Kasaï (former Province)
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political region or polity, a ''governor'' may be either appointed or elected, and the governor's powers can vary significantly, depending on the public laws in place locally. The adjective pertaining to a governor is gubernatorial, from the Latin root ''gubernare''. Ancient empires Pre-Roman empires Though the legal and administrative framework of provinces, each administrated by a governor, was created by the Romans, the term ''governor'' has been a convenient term for historians to describe similar systems in antiquity. Indeed, many regions of the pre-Roman antiquity were ultimately replaced by Roman 'standardized' provincial governments after their conquest by Rome. Plato used the metaphor of turning the Ship of State with a rudder; the Latin wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1889 Births
Events January–March * January 1 ** The total solar eclipse of January 1, 1889 is seen over parts of California and Nevada. ** Paiute spiritual leader Wovoka experiences a vision, leading to the start of the Ghost Dance movement in the Dakotas. * January 4 – An Act to Regulate Appointments in the Marine Hospital Service of the United States is signed by President Grover Cleveland. It establishes a Commissioned Corps of officers, as a predecessor to the modern-day U.S. Public Health Service Commissioned Corps. * January 5 – Preston North End F.C. is declared the winner of the inaugural Football League in England. * January 8 – Herman Hollerith receives a patent for his electric tabulating machine in the United States. * January 15 – The Coca-Cola Company is originally incorporated as the Pemberton Medicine Company in Atlanta, Georgia. * January 22 – Columbia Phonograph is formed in Washington, D.C. * January 30 – Rudolf, Crown Prince of Austria and his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lomami River
The Lomami River is a major tributary of the Congo River in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The river is approximately long. It flows north, west of and parallel to the upper Congo. The Lomami rises in the south of the country, near Kamina and the Congo–Zambezi divide. It flows north through Lubao, , Kombe, Bolaiti, Opala, and Irema before joining the Congo at Isangi. Henry Morton Stanley reached the confluence of the two rivers on 6 Jan. 1877, "the affluent Lumami, which Livingstone calls 'Young's river,' entered the great stream, by a mouth 600 yards wide, between low banks densely covered with trees."Stanley, H.M., 1899, Through the Dark Continent, London: G. Newnes, Vol. One , Vol. Two In October 1889 M. Janssen, Governor-General of the Congo State, explored the Lomani river upstream from Isangi on the ''Ville de Bruxelles''. After steaming for 116 hours he was stopped by rapids at a latitude of 4°27'2" S. The river has lent its name to a number of biological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katanga Province
Katanga was one of the four large provinces created in the Belgian Congo in 1914. It was one of the eleven provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo between 1966 and 2015, when it was split into the Tanganyika Province, Tanganyika, Haut-Lomami, Lualaba Province, Lualaba, and Haut-Katanga provinces. Between 1971 and 1997 (during the rule of Mobutu Sese Seko when Congo was known as Zaire), its official name was Shaba Province. Katanga's area encompassed . Farming and ranching are carried out on the Katanga Plateau. The eastern part of the province is considered to be a rich mining region, which supplies cobalt, copper, tin, radium, uranium, and diamonds. The region's former capital, Lubumbashi, is the second-largest city in the Congo. History Copper mining in Katanga dates back over 1,000 years, and mines in the region were producing standard-sized ingots of copper for international transport by the end of the 10th century CE. In the 1890s, the province was beleaguered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lomami District
Lomami District (french: District du Lomami, nl, District Lomami) was a district of the Belgian Congo from 1912 to 1933, when it was dissolved. It covered very roughly the same area as the present Lomami Province and the northwest of Haut-Lomami Province. Location Parts of the Stanley Falls and Lualaba districts were combined to form Katanga in 1910, which was called a vice-government general. An ''arrêté royal'' of 28 March 1912 divided the Congo into 22 districts. A map of the colony after this division shows Lomami District bordering Maniema District to the northeast, Tanganika-Moero District to the east, Lulua District">Tanganika-Moero_District.html" ;"title="Maniema District to the northeast, Tanganika-Moero District">Maniema District to the northeast, Tanganika-Moero District to the east, Lulua District to the south, Kasai District to the west and Sankuru District to the northwest. The district was named after the Lomami River, whose upper reaches flowed northward throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Équateur (former Province)
Équateur ( French for "Equator") was a province in the northwest of the Belgian Congo and the successor Republic of the Congo, now known as Democratic Republic of the Congo. It had its origins in the Équateur District of the Congo Free State, the private property of King Leopold II of Belgium. It was upgraded to the status of a province in 1917. Between 1933 and 1947 it was named Coquilhatville. In 1962 it was divided into three smaller provinces, but there were recombined in 1966. Équateur was one of the eleven provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo until 2015, when it was split into the new, smaller Équateur province, as well as the Tshuapa, Mongala, Nord-Ubangi and Sud-Ubangi provinces. Located in the north of the country, the province bordered the Republic of the Congo to the west, the Central African Republic to the north, to the east the Orientale province, and to the south the Kasai-Oriental, Kasai-Occidental, and Bandundu provinces. The word "Équateu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pende People
The Pende people (singular: Mupende; plural: Bapende), also known as the Phende people, are an ethnic group in the south-western Democratic Republic of the Congo. The Pende are divided into two cultural groups: the Eastern Pende and the Western Pende who are distinct but consider themselves part of the same ethnic group. The number of people who consider themselves to be ethnically Pende is estimated at over 250,000. The Pende speak their own language ( Kipende) and are particularly known for their artistic works. They are considered to be culturally similar to the Yaka and Suku peoples who live in neighboring areas. History The Pende are divided into two distinct cultural groups: the Western Pende and the Eastern Pende. However, both groups see themselves as part of the same ethnic group. There is no centralised political authority and Pende society is organised around extended family groups rather than through chiefly authority. Much like the Yaka and Suku peoples, the P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Ermens
Paul-Charles Ermens (June 8, 1884 – November 1, 1957) was a senior Force Publique officer, Vice-governor general of the Belgian Congo and Commander of the Force Publique. His most famous post was when he served as the commander of the Force Publique in World War II. Career He graduated in 1903 from the Belgian Royal Military Academy and joined the Royal grenadiers regiment. In 1914 he was an officer in the Force Publique, on August 4, 1914, he was promoted to Captain-commandant. He commanded the 3rd battalion of the Force Publique in the East African Campaign (World War I), for his service he was awarded the title of knight in the Order of the African Star. In 1918 he became Commander of the Force Publique in East Africa. In 1925 he became General and was appointed as commander of the Force Publique. In 1930 he didn't agree with the plans to reform the Force Publique and returned to Belgium. In 1932 he was appointed as vice-governor general of the Belgian Congo and governor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auguste Tilkens
Lieutenant General Auguste Tilkens (1869–1949) was a Belgian career soldier and colonial civil servant who served as Governor-General of the Belgian Congo from 1927 until 1934. Biography Auguste Tilkens was born in 1869 into a large family in the Flemish coastal city of Ostend. He entered the Royal Military Academy in 1887 and became an artillery officer in the Belgian Army. Following the outbreak of World War I in August 1914, during German invasion of Belgium, Tilkens served in the Belgian forces and was decorated for valour at the Battle of the Yser. In 1916, with emergence of static trench warfare on the Western Front, he volunteered for service in Belgian Congo where fighting had broken out on the colony's border with German East Africa. He served under Charles Tombeur during the subsequent fighting in East Africa. In 1917, he returned to Europe where he became aide de camp to King Albert I. After the end of World War I in 1918, Tilkens remained in the army and rose thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Beernaert
Joseph-Edouard-Louis Beernaert (21 April 1883 – 1950) was a Belgian soldier who reached the rank of Lieutenant-General. He was governor of the province of Congo-Kasaï in the Belgian Congo from 1925 to 1929. Early career (1883–1929) Joseph Beernaert was born on 21 April 1883. He was attached to the Ministry of Colonies in 1909. He made many trips to the Belgian Congo during his term of office. He was commissioner general, assistant to the governor of the province of Congo-Kasaï from 1925 to 1929. From 1928 he was secretary general, assistant to the governor general of the colony. Governor of Congo-Kasaï (1929–1933) Beernaert replaced Alphonse Engels as governor and deputy governor-general of Congo-Kasaï on 19 June 1929. His headquarters were at Léopoldville. In 1931 there was an economic crisis in the Belgian Congo triggered by problems in Belgium, the primary market, and an overvalued currency, leading to reduced exports. The head tax (''impôt indigène'') increas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |