|
Conspiracy Of Suassuna
The Conspiracy of Suaçunas also known for its archaic spelling - The Conspiracy of Suassuna - was a conspiracy to overthrow Portuguese rule in Brazil at the dawn of the 19th century. The conspiracy was centered in Olinda. In 1796, influenced by the ideas of the Enlightenment and the French Revolution, several leaders, including Manuel Alvarez House - a member of the Literary Society of Rio de Janeiro, and Manuel Arruda da Câmara - founded the Areopagus Masonic Lodge. The Enlightenment and the French Revolution were also discussed by priests and students of the Seminary of Olinda, founded by Bishop José Joaquim da Cunha Azeredo Coutinho on February 16, 1800. This institution had, among its members, Father Miguel Joaquim de Almeida Castro, involved in a future revolution in Pernambuco, 1817. The philosophical and political discussions at the Areopagus Lodge evolved into a conspiracy against Portuguese rule in Brazil, with the goal of the emancipation of Pernambuco, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olinda
Olinda () is a historic city in Pernambuco, Brazil, in the Northeast Region, Brazil, Northeast Region. It is located on the country's northeastern Atlantic Ocean coast, in the Recife metropolitan area, Metropolitan Region of Recife, the state capital. It has a population of 393,115 people, covers , and has a population density of 9,437 inhabitants per square kilometer. It is noted as one of the best-preserved colonial cities in Brazil, and has been inhabited since 1535. As the former capital of the Captaincy of Pernambuco during the Colonial Brazil, colonial era, Olinda has many historical buildings--the center was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1982--and a rich culture. The Brazilian Carnival, ''Carnaval'' of Olinda, a popular street party, is very similar to traditional Portuguese carnivals, with the addition of African influenced dances, reflecting the history of the Northeast. All the festivities are celebrated on the streets with no bleachers or roping, and unlike in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career of Napoleon Bonaparte, successful campaigns during the French Revolutionary Wars, Revolutionary Wars. He was the ''de facto'' leader of the First French Republic, French Republic as First Consul from 1799 to 1804, then Emperor of the French from 1804 until 1814 and again in Hundred Days, 1815. Napoleon's political and cultural legacy endures to this day, as a highly celebrated and controversial leader. He initiated many liberal reforms that have persisted in society, and is considered one of the greatest military commanders in history. His wars and campaigns are studied by militaries all over the world. Between three and six million civilians and soldiers Napoleonic Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabanada
The Cabanada or War of Cabanos was a rebellion that occurred in the Empire of Brazil between 1832 and 1835. it started shortly after the abdication of Dom Pedro I, during the regency period. Background The new regime was facing financial difficulties, with foreign trade almost stagnant, cotton and cane sugar prices declining, and the privilege customs to England, in force since 1810, continuing. This financial instability led to riots that erupted throughout the Empire of Brazil in that period. The Cabanada movement was active in Pernambuco, Alagoas, and Pará, but insurrections arose in different places and different times. The first one deals with the revolt in Pernambuco and Alagoas and the second in the Pará region. Pernambuco and Alagoas In Pernambuco, where the rebellion was known as "The War of Cabanada," the conservative Cabanadas demanded the return of the Portuguese monarch to the throne of Brazil. Rioting occurred in Zona da Mata and Agreste. Its leader w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
April Revolt (Pernambuco)
The April Revolt, or Abrilada in Brazil's history was an episode in 1832 in the then province of Pernambuco, which fits into the Regency Period, in the context of Cabanagem. After the abdication of D. Pedro I of Brazil (Pedro IV of Portugal) and his return to Europe where he played a decisive role in the Portuguese Civil War (1828–1834), the movement in Pernambuco, a conservative and absolutist, aimed at the renewal of D. Pedro I to the throne. History The movement emerged among the major Portuguese merchants of Recife, who controlled the trade of the city and province, and since the country's independence, were much harassed by the population. Gathered around the Masonic Lodge "Column of the Throne and Altar." On April 14, 1832, promoted the rise of a military battalion in Recife, under the leadership of Lt. Col. José Francisco Martins and Major José Gabriel de Morais Meyer. On the 15th, clashes started in the streets that continued for nearly a week. After thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
November Rebellion
November is the eleventh and penultimate month of the year in the Julian and Gregorian Calendars, the fourth and last of four months to have a length of 30 days and the fifth and last of five months to have a length of fewer than 31 days. November was the ninth month of the calendar of Romulus . November retained its name (from the Latin ''novem'' meaning "nine") when January and February were added to the Roman calendar. November is a month of late spring in the Southern Hemisphere and late autumn in the Northern Hemisphere. Therefore, November in the Southern Hemisphere is the seasonal equivalent of May in the Northern Hemisphere and vice versa. In Ancient Rome, Ludi Plebeii was held from November 4–17, Epulum Jovis was held on November 13 and Brumalia celebrations began on November 24. These dates do not correspond to the modern Gregorian calendar. November was referred to as Blōtmōnaþ by the Anglo-Saxons. Brumaire and Frimaire were the months on which Novemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confederation Of The Equator
The Confederation of the Equator ( pt, Confederação do Equador) was a short-lived rebellion that occurred in the northeastern region of the Empire of Brazil in 1824, in the early years of the country's independence from Portugal. The secessionist movement was led by liberals who opposed the authoritarian and centralist policies of the nation's first leader, Emperor Pedro I. The fight occurred in the provinces of Pernambuco, Ceará and Paraíba. Background of the rebellion The dissolution of the Brazilian Constituent Assembly in 1823 was not well received in Pernambuco. The two greatest liberal leaders in the province, Manuel de Carvalho Pais de Andrade and Joaquim do Amor Divino Rabelo e Caneca, popularly known as "Frei Caneca" (''Friar Caneca''), supported it and blamed the Bonifacians for the act.Dohlnikoff, Miriam. Pacto imperial: origens do federalismo no Brasil do século XIX. São Paulo: Globo, 2005, p. 56 Both, as well as other coreligionists, were republicans who pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Brazil
The history of Brazil begins with indigenous people in Brazil. Europeans arrived in Brazil at the ending of the 15th century. The first European to claim sovereignty over Indigenous lands part of what is now the territory of the Federative Republic of Brazil on the continent of South America was Pedro Álvares Cabral (c. 1467/1468 – c. 1520) on 22 April 1500 under the sponsorship of the Kingdom of Portugal. From the 16th to the early 19th century, Brazil was a colony and a part of the Portuguese Empire. The country expanded south along the coast and west along the Amazon and other inland rivers from the original 15 donatary captaincy colonies established on the northeast Atlantic coast east of the Tordesillas Line of 1494 (approximately the 46th meridian west) that divided the Portuguese domain to the east from the Spanish domain to the west, although Brazil was at one time a colony of Spain. The country's borders were only finalized in the early 20th century. On 7 September 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
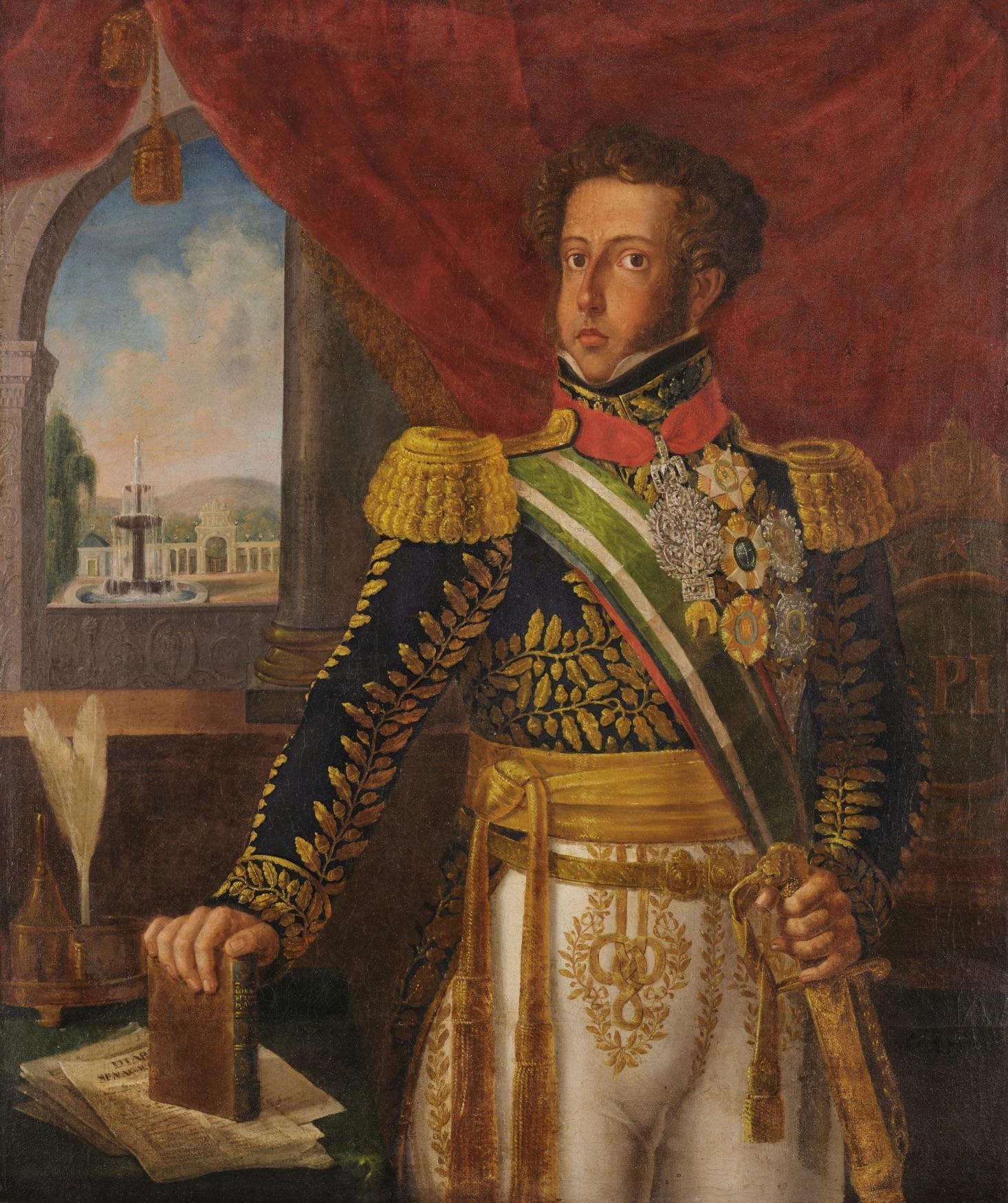
José Francisco De Paula Cavalcanti E Albuquerque
José is a predominantly Spanish and Portuguese form of the given name Joseph. While spelled alike, this name is pronounced differently in each language: Spanish ; Portuguese (or ). In French, the name ''José'', pronounced , is an old vernacular form of Joseph, which is also in current usage as a given name. José is also commonly used as part of masculine name composites, such as José Manuel, José Maria or Antonio José, and also in female name composites like Maria José or Marie-José. The feminine written form is ''Josée'' as in French. In Netherlandic Dutch, however, ''José'' is a feminine given name and is pronounced ; it may occur as part of name composites like Marie-José or as a feminine first name in its own right; it can also be short for the name ''Josina'' and even a Dutch hypocorism of the name ''Johanna''. In England, Jose is originally a Romano-Celtic surname, and people with this family name can usually be found in, or traced to, the English county ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luis Francisco De Paula
Luis is a given name. It is the Spanish form of the originally Germanic name or . Other Iberian Romance languages have comparable forms: (with an accent mark on the i) in Portuguese and Galician, in Aragonese and Catalan, while is archaic in Portugal, but common in Brazil. Origins The Germanic name (and its variants) is usually said to be composed of the words for "fame" () and "warrior" () and hence may be translated to ''famous warrior'' or "famous in battle". According to Dutch onomatologists however, it is more likely that the first stem was , meaning fame, which would give the meaning 'warrior for the gods' (or: 'warrior who captured stability') for the full name.J. van der Schaar, ''Woordenboek van voornamen'' (Prisma Voornamenboek), 4e druk 1990; see also thLodewijs in the Dutch given names database Modern forms of the name are the German name Ludwig and the Dutch form Lodewijk. and the other Iberian forms more closely resemble the French name Louis, a deriva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
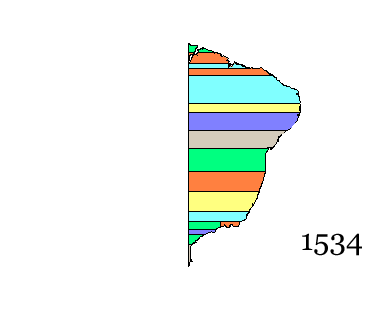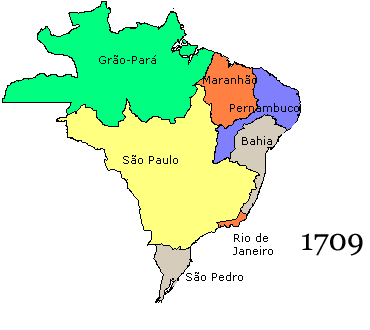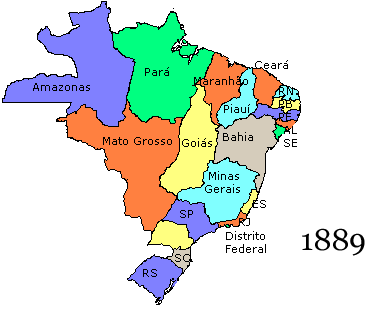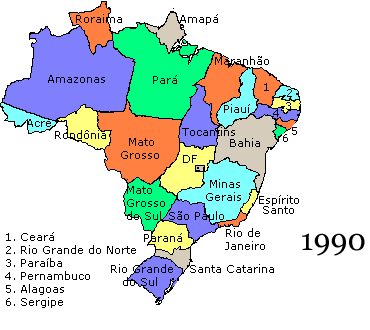
Colonial Brazil
Colonial Brazil ( pt, Brasil Colonial) comprises the period from 1500, with the arrival of the Portuguese, until 1815, when Brazil was elevated to a kingdom in union with Portugal as the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves. During the early 300 years of Brazilian colonial history, the economic exploitation of the territory was based first on brazilwood (''pau brazil'') extraction (16th century), which gave the territory its name; sugar production (16th–18th centuries); and finally on gold and diamond mining (18th century). Slaves, especially those brought from Africa, provided most of the work force of the Brazilian export economy after a brief period of Indian slavery to cut brazilwood. In contrast to the neighboring Spanish possessions, which had several viceroyalties with jurisdiction initially over New Spain (Mexico) and Peru, and in the eighteenth century expanded to viceroyalties of the Río de la Plata and New Granada, the Portuguese colony of Brazil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |